G Inventory Transactions
This appendix contains these topics:
G.1 Generally Accepted Accounting Practices in the U.S. and France
Based on generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) in the United States, the expense due to the purchase of an inventory item is recognized only at the time of sale (the balance of the cost of sales account). The U.S. GAAP and the J.D. Edwards standard solution imply an accounting principle of permanent inventory. That is, each inventory transaction generates an accounting entry.
In France, the purchase must be recognized in a purchase account. It is customary to periodically identify the difference between the initial inventory and the final inventory and post an offset entry to a stock variation account.
G.2 Accounting Schemes
G.2.1 Final Stock Mode
Figure G-1 Final Stock Mode Journal Entry
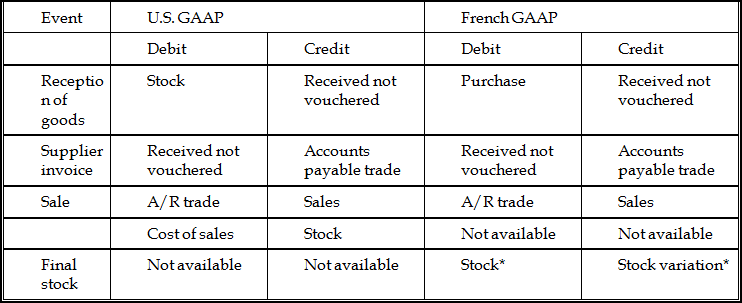
Description of "Figure G-1 Final Stock Mode Journal Entry"
*The entry can be inverted if the final stock is lower than the initial stock.
G.2.2 Permanent Inventory
Figure G-2 Permanent Inventory Journal Entry
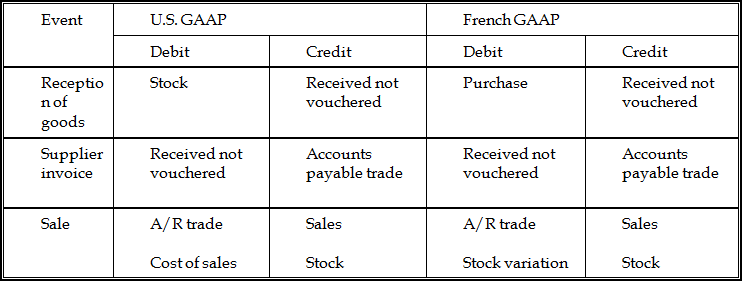
Description of "Figure G-2 Permanent Inventory Journal Entry"
Note the following about the final stock mode and permanent inventory schemes:
-
The entry for final stock in the Final Stock Mode scheme does not exist in the Permanent Inventory scheme.
-
The offsetting entry for the stock account is always the stock variation account.
-
The cost of sales (U.S. GAAP) is equal to purchase plus or minus the stock variation (French GAAP).
G.3 J.D. Edwards Solution
When goods are received, the system uses automatic accounting instructions (AAIs) to generate a single entry in the appropriate account. The French GAAP requires an additional entry.
You can use two tools within J.D. Edwards standard solution to generate the second entry:
The purchase of stock for a given period corresponds to the inventory entries of the same period. For clients working with a standard price, J.D. Edwards recommends using the Chart of Accounts to distinguish between the purchase at standard price and the variation. You can use the business unit or the object to achieve this distinction.
G.3.1 Example: Chart of Accounts
G.3.2 Automatic Accounting Instructions (AAIs)
G.3.2.1 Stock Entries
These entries are reserved for stock transactions that are not related to a purchase or a sale, such as inventory issues, transfers, and adjustments.
| AAI | Description | Object | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRI/4122 | Adjustments | 1410 | Stock |
| TRO/4124 | Adjustments | 6031 | Stock variation |
| PINV/4152 | Inventory | 1410 | Stock |
| PEXP/4154 | Inventory | 6031 | Stock variation |
G.3.2.2 Purchase Entries
| AAI | Description | Object | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| OPI/4310 | Reception of stocked raw materials | 6010 | Purchase |
| OPN/4315 | Reception of non-stocked items | xxxx | Purchase of non-stocked Items |
| OPR/4320 | Reception | 4115 | Received not vouchered* |
| OPV/4330 | Variation of standard price | 6011 | Variation of standard price |
| OPP/4335 | Variation of standard price | 6011 | Variation of standard price |
| OPX/4340 | Variation of currency | xxxx | Variation of currency |
*The offsetting entry for this account is generated through the AAI PCxxxx.
G.3.2.3 Sales Entries
| AAI | Description | Object | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOC/4220 | Sales | 6013 | Stock variation finished goods |
| SOS/4230 | Sales | 5010 | Sales* |
| SOI/4240 | Sales | 1420 | Stock |
| SOT/4250 | Sales | xxxx | Taxes* |
*The offsetting entry for the A/R Trade account is generated by the AAI RCxxxx.
G.3.2.4 Indexed Allocations (G0923)
Use allocations to generate accounting entries for the entry of stock based on the purchase account at standard price.
Set up your allocations as follows:
| Allocation | Code |
|---|---|
| Recurring Frequency | MO |
| Method | U |
| Using MTD/YTD | M |
| Offsetting Entries | 6031 Stock valuation |
| FROM | 6010 Purchase |
| Ledger Type | AA |
| Index or Rate | 1 |
| TO | 1410 Stock |
| Ledger Type | AA |
You can minimize the setup required for allocations by using a transit account. For example, if you have several accounting branches, you can use the following alternative:
| Allocation | Code |
|---|---|
| Offsetting Entries | Transit Account |
| FROM | 6010 Purchase |
| Ledger Type | AA |
| Index or Rate | 1 |
| TO | 1410 Stock |
| Ledger Type | AA |
| FROM | 6010 Purchase |
| Ledger Type | AA |
| Index or Rate | -1 |
| TO | 6031 Stock variation |
| Ledger Type | AA |