Oracle Inventory Optimization and Asset Intensive Planning
Introduction to Asset Intensive Planning
The purpose of this functionality is to plan asset intensive maintenance to enable Oracle Inventory Optimization (IO) to compute safety stock for consumables and rebuildables that will be required for maintenance in an asset intensive industry.
Oracle Inventory Optimization (IO) sets safety stock levels that understand the holistic supply chain, including planning for maintenance of assets. The planning of maintenance of assets includes rebuilding defective items into a usable state to fulfill maintenance component demands. A complex asset, such as an aircraft, a vehicle, or manufacturing equipment contains components that are considered repairable or rebuildable.
IO provides an inventory postponement optimization solution that leads to a much more efficient supply chain, characterized by lower levels of inventory and better delivery performance to customers.
In order to support postponement and to accomplish the rebuild of defective items into a usable state, IO will rebuild activity bill of material and routing.
Understanding the Asset Intensive Planning Process
Rebuild activity, as defined in Oracle eAM, is recognized in IO. IO uses the bill of material and routing that is associated with this rebuild activity to understand which materials and resources are used in the repair process. This helps IO to compute safety stock for components used in the repair process, in addition to the repair item itself.
IO supports the definition of a “rebuild” activity, which is used to calculate the points of postponement. This activity is collected to support ASCP planning of maintenance requirements.
Rebuildable items (rebuildables) are assets that you install, remove, overhaul, and reinstall, for example, engines, control boxes, and computer boards. Other components that you remove, discard, or replace are consumables.
Maintenance activities, such as, inspections, overhauls, lubrications, repairs, servicing, and cleanings, are the templates of work orders. The activities have an activity structure—the material requirements (maintenance bill of material) and operations and resource requirements (activity routing) that you need to perform the maintenance. You associate the activities with assets.
The rebuild activity tells IO which maintenance of asset and routing will be used for the maintenance of the asset. IO gets the repair lead times from the Item Attribute and respects it. In case no rebuild activity is specified for a component that has a repair sourcing rule specified, the repair lead time that is specified on the item attribute must be respected. This being the case where no Rebuild Activity has been specified, IO assumes that there are no additional components required to rebuild the defective part. The treatment here is identical to that of ASCP. For more details, refer to Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning Implementation and User's Guide Supplement.
The fact that items are being repaired or rebuilt implies that there are defective items in the supply chain. Inventory optimization will plan safety stocks only for usable items.
Computing Total Demand
Both eAM and cMRO maintenance applications produce a set of forecasted Maintenance Work Orders. These are collected into ASCP as a statement of forecasted maintenance activities and the associated material and resources requirements. These forecasted work orders are created based on the known condition and expected preventative maintenance schedule of each asset, such as aircraft, truck, metal press.
ASCP then produces a supply chain plan for these work orders that will be used by the Demantra Sales & Operations Planning (S&OP) process and combined with Demantra's traditional demand forecast for independent demand, based on historical sales orders. Demantra combines its sales order based forecast and with the forecasted work orders to create a single statement of total demand each item. This one number demand forecast is compared to actual historical demands to calculate the forecast accuracy, as shown in the diagram below:
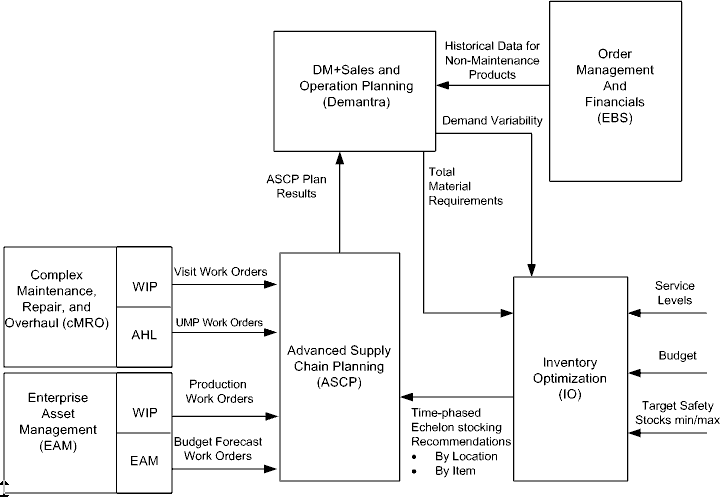
Calculating Total Demand
Contained in the supply plan that is calculated by ASCP, there are two distinct maintenance supply order types:
-
Maintenance Work Orders
-
Planned Repair Work Orders
Maintenance Work Orders
Maintenance Work Orders contain the collected work orders from eAM and cMRO maintenance applications. The collected Maintenance Work Orders represent both near term scheduled work as well as future forecasted maintenance work. They include CMRO Visit Work Orders, CMRO Unit Maintenance Plan Repair Work Orders, eAM Work Orders and eAM Budget Forecast Work Orders. In addition Maintenance Work orders represent both maintenance (will have Produce to Stock of No) as well as repair (will have Product to Stock of Yes) These Maintenance Work Orders contain material requirements for both consumable and repairable components.
Planned Repair Work Orders
ASCP may recommend Planned Repair Orders to satisfy component demands, depending on the available or expected defective supply and other constraints.
Demantra will exclude the demands associated with Planned Repair Work Order since these will be accounted for by IO, which determines its postponement strategy:
-
Demantra will calculate “Total Demand” as the sum of:
-
Consensus Forecasted This is the forecast for non-maintenance products.
-
Maintenance Work Order Demand
-
-
Demantra will calculate Demand Variability by comparing the total demand” to actual demands
Demantra will send a statement of Total Demand and Demand Variability to IO, which will then use this information to calculate optimized safety stocks, based on user input of service level targets and budget.
Modeling Repair Operations
As part of the enhancements, ASCP can now model repair operations. Each maintenance application (eAM and cMRO) supports a repair or rebuild process to transform a defective item into a usable item to satisfy maintenance demands. Contained in each set of Work Orders are component requirements for Rebuildable items ASCP will recommend “supplies to satisfy”
To support its postponement functionality, IO must be cognizant of the “Rebuildable” BOM and Route utilized in these rebuild activities. Inventory Optimization recognizes the Repair-at sourcing rule.
For more information on Asset Intensive Planning and the role of ASCP, refer to Oracle Advanced Supply Chain Planning Implementation and User's Guide Supplement.
eAM Activity Definition
The activity shown below, Rebuild T56-Engine, is the process of transforming a defective T56-Engine in to a usable T56-Engine. The BOM and Routing associated with the item define the process. This example uses the T56 Engine to illustrate the modeling setups.
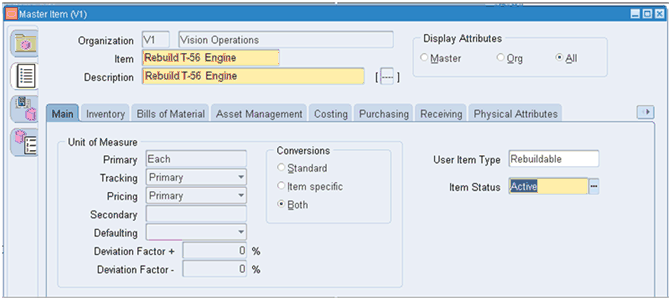
Rebuilding the T56 Engine Activity
The activity “Rebuild T56-Engine” Maintenance BOM and Maintenance Routing are defined with the following values as part of standard eAM setup:
Bill of Materials
| Item | Item Sequence | UOM | Quantity |
| Fuel Enrichment Valve | 10 | EA | 1 |
| Anti-Ice Valves | 10 | EA | 0.5 |
| Fuel Pump | 20 | EA | 1 |
| Compressor Bleed Valves | 10 | EA | 1 |
Routing
| Sequence | Description | Resource | UOM | Quantity |
| 10 | Rebuild Engine | Advanced A&P | Hour | 32 |
| 20 | Test Engine | Inspector | Hour | 4 |
Item and Activity Identification
The Asset type of Rebuildable Inventory identifies the asset as a rebuildable asset. For rebuildable assets the Asset Group is synonymous with the Rebuildable Item.
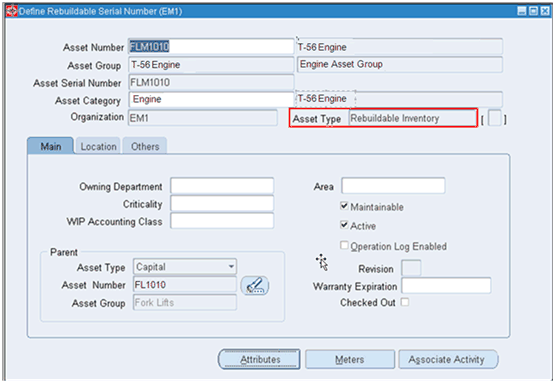
The Asset Group is setup as an inventory transactable item of the item type of Asset Group. The Asset Group is synonymous to an inventory item and is the item that is planned by ASCP.
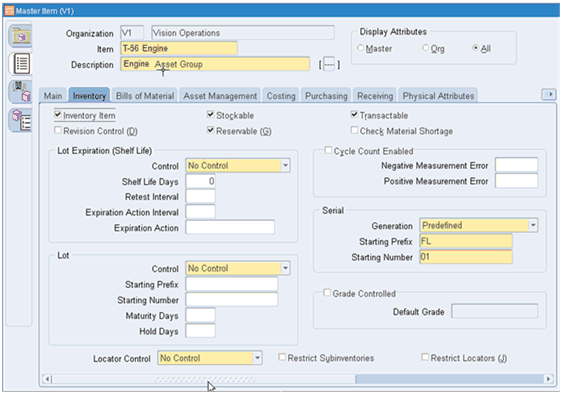
Activity Types describe the type of maintenance work that is performed on an asset, such as, inspections, lubrications, overhauls, calibration, and repetitive work. The “Rebuild – Rebuild Spare” activity determines which activity that is associated with a rebuildable item should be used by ASCP to plan for the rebuild or repair of the rebuildable item. Activity types of Rebuild are those collected over into ASCP for use in generating planned repair work orders.
Note: eAM does not enforce the assignment of one and only one Rebuild Activity type for each rebuildable asset group. Since ASCP needs to identify a specific rebuild activity to use in planning purposes, there is an attribute set on the destination that specifies which of these multiple rebuild activities is used for planning. It is an implementation task and business rule to enforce to assignment of Rebuild activities to rebuildable asset groups. For example:
| Activity Type | Description |
| Calibration | Calibration |
| Construction | Construction |
| Contracted | Contracted Services |
| Inspection | Inspection |
| Installation | Installation |
| Janitorial | Janitorial |
| Lubrication | Lubrication |
| Maintenance | Maintenance |
| Rebuild | Rebuild Spare |
| Reformat | Department Reformat |
| Reformat | Reformat |
| Repetitive | Repetitive |
| Replacement | Replacement |
| Service | Service |
Repair Lead Time
The Repair lead time for the rebuild of each item must be specified as an item attribute or in the simulation set. Inventory Optimization reads in the repair lead time and considers the time that is required to rebuild the item.
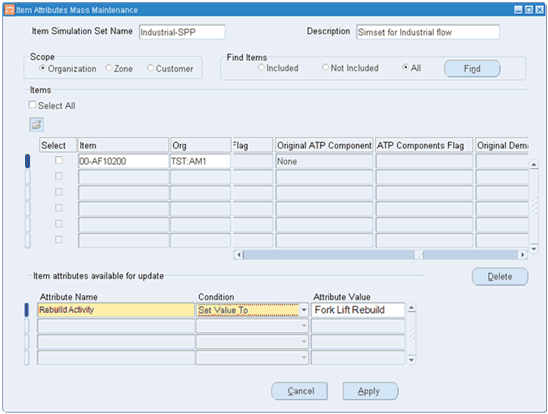
IMM Rebuild Activity
The 'Rebuild Activity” is a new item attribute, but it is not available in ERP. It is a destination-only attribute and will be added to the Item Attribute Mass Maintenance (IMM) form. This attribute is populated with the Rebuild Activity setup in eAM as the Maintenance BOM and Routes that will be used to plan for the items rebuild process. This new IMM attribute needs to be set for each organization that is used in creating Planned Repair Work Orders as well as during the release process of these work Orders. IO looks at the rebuild activity to determine a rebuild BOM and routing.
Note: Oracle Inventory Optimization assumes that there are no additional components required to rebuild the defective part. The treatment here is identical to ASCP.
Note: Oracle Inventory Optimization will not use the existing Maintenance Work Orders and External Repair Orders as sources of supply computing safety stock
Note: Oracle Inventory Optimization will not have the dummy work order construct used in ASCP to model shut-down of eAM resources while they are being maintained since the impact on the safety stock calculation will be fairly limited.