| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Trusted Extensions Administrator's Procedures Oracle Solaris 10 1/13 Information Library |
| Skip Navigation Links | |
| Exit Print View | |
|
Trusted Extensions Administrator's Procedures Oracle Solaris 10 1/13 Information Library |
1. Trusted Extensions Administration Concepts
2. Trusted Extensions Administration Tools
3. Getting Started as a Trusted Extensions Administrator (Tasks)
What's New in Trusted Extensions
Security Requirements When Administering Trusted Extensions
Role Creation in Trusted Extensions
Role Assumption in Trusted Extensions
Getting Started as a Trusted Extensions Administrator (Task Map)
How to Enter the Global Zone in Trusted Extensions
How to Exit the Global Zone in Trusted Extensions
How to Administer the Local System With the Solaris Management Console
How to Start CDE Administrative Actions in Trusted Extensions
4. Security Requirements on a Trusted Extensions System (Overview)
5. Administering Security Requirements in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
6. Users, Rights, and Roles in Trusted Extensions (Overview)
7. Managing Users, Rights, and Roles in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
8. Remote Administration in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
9. Trusted Extensions and LDAP (Overview)
10. Managing Zones in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
11. Managing and Mounting Files in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
12. Trusted Networking (Overview)
13. Managing Networks in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
14. Multilevel Mail in Trusted Extensions (Overview)
15. Managing Labeled Printing (Tasks)
16. Devices in Trusted Extensions (Overview)
17. Managing Devices for Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
18. Trusted Extensions Auditing (Overview)
19. Software Management in Trusted Extensions (Tasks)
A. Quick Reference to Trusted Extensions Administration
Familiarize yourself with the following procedures before administering Trusted Extensions.
|
By assuming a role, you enter the global zone in Trusted Extensions. Administration of the entire system is possible only from the global zone. Only superuser or a role can enter the global zone.
After assuming a role, the role can create a workspace at a user label to edit administration files in a labeled zone.
For troubleshooting purposes, you can also enter the global zone by starting a Failsafe session. For details, see How to Log In to a Failsafe Session in Trusted Extensions.
Before You Begin
You have created one or more roles, or you plan to enter the global zone as superuser. For pointers, see Role Creation in Trusted Extensions.
If you have been assigned a role, the role names are displayed in a list.
For the location and significance of Trusted Extensions desktop features, see Chapter 4, Elements of Trusted Extensions (Reference), in Trusted Extensions User’s Guide.
In Trusted CDE, a new role workspace is created, the workspace switch button changes to the color of the role desktop, and the title bar above each window shows Trusted Path. In Trusted JDS, the current workspace changes to the role workspace.
In Trusted CDE, you leave a role workspace by using the mouse to choose a regular user workspace. You can also delete the last role workspace to exit a role. In Trusted JDS, you click the role name on the trusted stripe, and from the menu, select a different role or user. This action changes the current workspace to the process of the new role or user.
The menu locations for exiting a role are different in Trusted JDS and Trusted CDE.
Before You Begin
You are in the global zone.
You can also exit the role workspace, and therefore the global zone, by doing one of the following:
When you click the role name, your user name and a list of roles that you can assume is displayed. When you select your user name, all subsequent windows that you create in that workspace are created by the selected name. The windows that you previously created on the current desktop continue to display at the name and label of the role.
If you choose a different role name, you remain in the global zone in a different role.
Click mouse button 3 over the workspace button and select Delete. You are returned to the last workspace you occupied.
The first time that you launch the Solaris Management Console on a system, a delay occurs while the tools are registered and various directories are created. This delay typically occurs during system configuration. For the procedure, see Initialize the Solaris Management Console Server in Trusted Extensions in Trusted Extensions Configuration Guide.
To administer a remote system, see Administering Trusted Extensions Remotely (Task Map).
Before You Begin
You must have assumed a role. For details, see How to Enter the Global Zone in Trusted Extensions.
In Solaris Trusted Extensions (JDS), use the command line.
$ /usr/sbin/smc &
In Trusted CDE, you have three choices.
A Trusted Extensions toolbox has Policy=TSOL as part of its name. The Files scope updates local files on the current system. The LDAP scope updates LDAP directories on the Oracle Directory Server Enterprise Edition. The toolbox names appear similar to the following:
This Computer (this-host: Scope=Files, Policy=TSOL) This Computer (ldap-server: Scope=LDAP, Policy=TSOL)
The password prompt is displayed.
For tools that Trusted Extensions has modified, click System Configuration.
Refer to the online help for additional information about Solaris Management Console tools. For an introduction to the tools that Trusted Extensions modifies, see Solaris Management Console Tools.
For details, see How to Enter the Global Zone in Trusted Extensions.
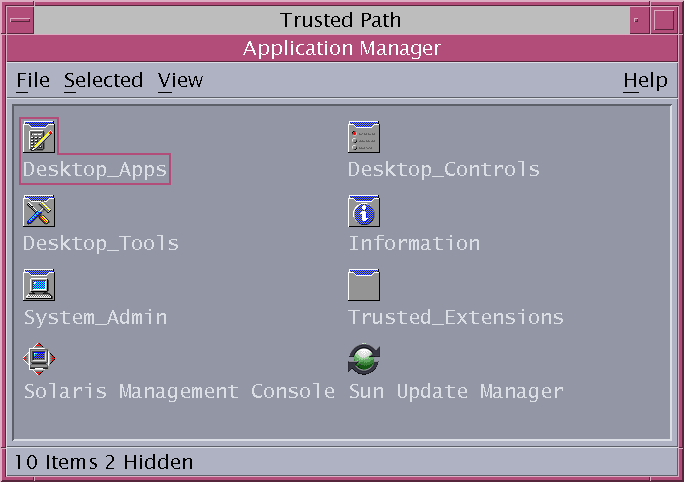
The Trusted_Extensions folder is in the Application Manager.
For a list of administrative actions, see Trusted CDE Actions.
Administrative files are edited with a trusted editor that incorporates auditing. This editor also prevents the user from executing shell commands and from saving to any file name other than the name of the original file.
For details, see How to Enter the Global Zone in Trusted Extensions.
The Trusted_Extensions folder is in the Application Manager.
You are prompted to provide a file name. For the format, see Step 3 and Step 4.
For details, see How to Assign the Editor of Your Choice as the Trusted Editor.
# /usr/dt/bin/trusted_edit filename
You must provide a filename argument.
When you save the file, the editor creates a temporary file.
Note - If your editor provides a Save As option, do not use it. Use the editor's Save option to save the file.