 Understanding Deductions for Hong Kong
Understanding Deductions for Hong Kong
This chapter provides overviews on deductions for Hong Kong and delivered deduction elements, and discusses how to:
Calculate leave without pay and daily rate reduction.
Schedule deductions using generation control.
 Understanding Deductions for Hong Kong
Understanding Deductions for Hong Kong
PeopleSoft has created several deductions to demonstrate the flexibility of the Global Payroll rules to meet common processing requirements such as the preservation of minimum net pay. The following sections discuss:
How you can use deductions and supporting elements to produce desired results.
How PeopleSoft has met specific deduction processing requirements.
Note. User keys enable you to track an accumulator at levels lower than the employee record. This directs the system to maintain different accumulated numbers for each of the employee's locations. User Key 1 for deductions on the Deduction Accumulators page is PAY ENTITY (required by Inland Revenue reporting). User Key 2 for all year to date accumulators is CM VR BAL GRP ID (balance group ID).
See Also
 Understanding Delivered Deduction Elements
Understanding Delivered Deduction Elements
This section discusses:
Delivered deduction elements.
Process lists and sections.
Viewing delivered elements.
Calculating cash advance recovery.
Calculating community chest.
Calculating MPF deductions.

 Delivered Deduction Elements
Delivered Deduction ElementsYou use these delivered deduction elements as delivered, modify them, or create new elements.
|
Name and Description |
Unit |
Rate |
Base |
Percent |
Amount |
|
CASHADVR Cash Advance Recovery (GC) |
NA |
NA |
OE FM CASHADVR BSE |
20 (N) |
NA |
|
COMCHST Community Chest (GC) |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
Payee Level |
|
ERMPFMN1 MPF Employer Mandatory 1 (Regular) |
NA |
NA |
MPF FM ERMN1 BASE |
5 (N) |
NA |
|
ERMPFMN2 MPF Employer Mandatory 2 (Permitted Period) |
NA |
NA |
MPF FM ERMN2 BASE |
5 (N) |
NA |
|
ERMPFVOL1 MPF Employer Voluntary 1 (Regular) |
NA |
NA |
MPF FM ERVOL1 BASE |
5 (N) |
NA |
|
ERMPFVOL2 MPF Employer Voluntary 2 (Permitted Period) |
NA |
NA |
MPF FM ERVOL2 BASE |
5 (N) |
NA |
|
EEMPFMN1 MPF Employee Mandatory 1 (Regular) |
NA |
NA |
MPF FM EEMN1 BASE |
5 (N) |
NA |
|
EEMPFMN2 MPF Employee Mandatory 2 (Permitted Period) |
NA |
NA |
MPF FM EEMN2 BASE |
5 (N) |
NA |
|
EEMPFVOL1 MPF Employer Voluntary 1 (Regular) |
NA |
NA |
Payee Level |
100 (N) |
NA |
|
EEMPFVOL2 MPF Employee Voluntary 2 (Permitted Period) |
NA |
NA |
Payee Level |
100 (N) |
NA |
In the following table, the first column combines the deduction name and description. The letters GC in a row indicate that the deduction has generation control. The other five columns indicate the deduction's calculation rule: Unit × Rate, Unit × Rate × Percent, or Base × Percent. The formulas used for some of the deduction codes are discussed in further detail. The letter N in a row indicates numeric.

 Process Lists and Sections
Process Lists and SectionsThe CASHADVR and COMCHST deductions are members of the DED SE COMMON process section.
The ERMPFMN1, ERMPFMN2, ERMPFVOL1, ERMPFVOL2, EEMPFMN1, EEMPFMN2, EEMPFVOL1, and EEMPFVOL2 deductions are members of the MPF SE DEDUCTION process section.
The DED SE COMMON and MPF SE DEDUCTION sections are included in the CM PR PAYROLL process list.

 Viewing Delivered Elements
Viewing Delivered ElementsPeopleSoft delivers a query that you can run to view the names of all delivered elements designed for Hong Kong. Instructions for running the query are provided in the PeopleSoft Global Payroll 9.1 PeopleBook.
See Also
Understanding How to View Delivered Elements

 Calculating Cash Advance Recovery
Calculating Cash Advance Recovery
Employees can be paid 50 percent of their basic salary cash advances (CASHADV), which they must pay back using CASHADVR in installments over five months. Use the cash advance recovery deduction exclusively to offset the cash advance. For cash advance payments, employees do not pay interest.
As the total cash advance recovery amount is deducted from the annual taxable income, the cash advance recovery is a taxable deduction.
The generation control CM GC RSLV CSHADVR determines when the deduction starts and stops, if period segmentation occurs.
The formula DED FM RSLV CSHADR is attached to the generation control and determines if the cash advance accumulator is greater than zero. If so, the deduction is resolved. The accumulator is timed after calculation because the deduction is resolved after the CASHADV earning is paid (the accumulator is updated after the deduction—not when the earning is resolved). The first time that the earning is paid, the deduction is not resolved because the accumulator is updated at the end of the pay run.
In the next period, the deduction is resolved because the accumulator would have been updated with the earning amount. The generation control determines if the goal amount balance has been reached.
Example
A salaried employee's current basic salary is 20000 HKD per month. The organization decided that 50 percent of that basic salary cash advance is paid on January 15, 2001. The cash advance amount that the employee will receive on January 15, 2001 is calculated as:
(50 percent) × 20000 = 10000 (Cash Advance) = 10000 HKD
After the cash advance is finalized, the deduction cash advance recovery is created (20 percent of cash advance with goal amount for the payee on the Earnings and Deductions Assignment page).
See Also

 Calculating Community Chest
Calculating Community Chest
The community chest deduction enables employees to donate to charity from their salaries. The donated amount is a taxable deduction and is paid at the earning assignment level. Proration is not applicable to the donation.
The generation control CM GC RSLV ONCE prevents deducting the allowance more than once if period segmentation occurs.

 Calculating Mandatory Provident Fund Deductions
Calculating Mandatory Provident Fund Deductions
All members of the workforce, between age 18 and 65, except those who are exempt, are required to make regular contributions to registered Mandatory Provident Fund (MPF) schemes. Contributions are calculated at 10 percent of the employee's income, with the employee and employer each paying 5 percent. Both the employee and employer can elect to make additional voluntary contributions.
The employer and employees' contributions are deducted and paid to the selected MPF scheme each pay period. After the MPF scheme receives the deductions, they are immediately deposited into the employees' retirement savings plans.
Eight MPF deductions are provided:
Employer MPF Regular Mandatory 1 - ERMPFMN1.
The ERMPFMN1 deduction is used for employer regular MPF mandatory contributions.
Employer MPF Permitted Period Mandatory 2 - ERMPFMN2.
The ERMPFMN2 deduction is used for employer MPF mandatory contributions during the 60-day permitted period.
Employer MPF Regular Voluntary 1- ERMPFVOL1.
The ERMPFVOL1 deduction is an additional 5 percent of relevant earnings and should be given to all employees. The rest of the rules are the same as for the MPF Employer Voluntary deduction. The deduction is used for employer MPF voluntary contributions.
Employer MPF Permitted Period Voluntary 2 - ERMPFVOL2.
The ERMPFVOL2 deduction is used for employer MPF voluntary contributions during the 60-day permitted period.
Employee MPF Regular Mandatory 1 - EEMPFMN1.
The EEMPFMN1 deduction is used for employee MPF mandatory contributions.
Employee MPF Permitted Period Mandatory 2 - EEMPFMN2.
The EEMPFMN2 deduction is used for employee MPF mandatory contributions during the 60-day permitted period.
Employee MPF Regular Voluntary 1 - EEMPFVOL1.
The EEMPFVOL1 deduction is used for employer MPF voluntary contributions.
Employee MPF Permitted Period Voluntary 2 - EEMPFVOL2.
The EEMPFVOL2 deduction is used for employee MPF voluntary contributions during the 60-day permitted period.
See Also
Administering Mandatory Provident Fund Contributions
 Calculating Leave Without Pay and Daily Rate Deduction
Calculating Leave Without Pay and Daily Rate Deduction
Employees might take leave without pay during their working periods. One calendar daily rate is taken from salary for one day of unpaid leave. Unpaid leave is a taxable deduction.
LWOP can be taken anytime during the servicing period. One DAILY RT is reduced from the employee's monthly income for every single day of LWOP taken. The value of one DAILY RT equals:
(Annual Salary) / 365
365 is used even in the leap year.
Example
Three days of unpaid leave has been taken in April and the basic salary in April is 10000 HKD. The April monthly salary is calculated as:
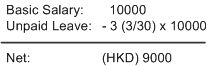
April Monthly Salary Calculation
A salary change can occur during unpaid leave. In this case, the unpaid leave is split into two segments: segment one is based on the old daily rate and segment two is based on the new daily rate.
See Also
Calculating Leave Without Pay (LWOP)
Calculating Leave Without Pay (LWOP2)
 Scheduling Deductions Using Generation Control
Scheduling Deductions Using Generation Control
Generation control elements enable you to specify whether to process a deduction element based on defined criteria. For Global Payroll for Hong Kong, the system controls deduction payments by assigning a generation control to the deductions.
For each generation control, there is a corresponding formula. When the formula returns TRUE, the deduction is resolved.
See Also
Defining Generation Control Elements