 Global Payroll for Japan
Global Payroll for JapanThis chapter discusses:
Global Payroll for Japan.
Global Payroll for Japan business processes.
Global Payroll for Japan integrations.
Delivered elements.
Element naming conventions.
Archiving Data for Global Payroll for Japan.
Element query.
 Global Payroll for Japan
Global Payroll for JapanGlobal Payroll for Japan is a country extension of the core Global Payroll application. It provides the payroll rules and elements needed to run a Japanese payroll.
 Global Payroll for Japan Business Processes
Global Payroll for Japan Business Processes
Global Payroll for Japan supports the following business processes:
Salary and Bonus.
Global Payroll for Japan provides the necessary elements to calculate earnings and deductions for salary and bonus for four pay types—monthly exempt, monthly non-exempt, daily, and hourly. Map your Global Payroll for Japan system to the base pay compensation rate codes in employees' compensation packages, and enter bonus amounts through positive input. Include commuting allowance in monthly payroll, adjust salaries for overtime and absence, and deduct social insurance and labor insurance premiums, income tax, and inhabitant tax as required by law.
Time Data.
Flexible rules enable tracking time data for the purpose of calculating salaries and tracking paid time off (PTO). Use variables for processing workdays, overtime, holidays, tardiness, absence, PTO, sick leave, and special leave. Use delivered formulas to track PTO entitlements, takes, and balances. Define processing of PTO that is carried over from the previous year according to your organization's practices.
Termination processing.
Global Payroll for Japan delivers rules and procedures that support the automatic calculation of year-end adjustment (YEA) for terminated employees.
Commuting Allowance.
Global Payroll for Japan provides the elements that are necessary to calculate and track payments of cash, non-cash, taxable, and nontaxable commuting allowances in frequencies of one day, one month, three months, and six months. The commuting allowance can be defined by total amount or by commuting route. The system provides a default value for the monthly maximum nontaxable commuting allowance. You can define the maximum nontaxable toll compensation for each employee and input the value of each employee's commuting allowance components. The system generates payment in the appropriate month and also tracks the value of the commuting allowance for calculating monthly remuneration.
Retirement Allowance.
With Global Payroll for Japan, you can enter an employee's retirement allowance and have the system automatically calculate and deduct the related income tax and inhabitant tax (prefecture tax and municipality tax ) on retirement earnings. The system can also generate a withholding tax report and payslips for retirement allowances.
Social Insurance.
Global Payroll for Japan provides variables, formulas, earnings and deductions, and other rules to calculate and track all aspects of social insurance premiums. The system calculates health insurance premiums, pension insurance premiums, and nursing care insurance premiums. It also calculates and tracks average monthly remuneration to support the regular decision process and to identify employees who are subject to occasional revision. A set of social insurance reports helps you complete your social insurance business process.
Labor Insurance.
Global Payroll for Japan calculates the employee contribution for employment insurance premiums by using the appropriate premium rate for the industry type based on the employee's total wages. The system also tracks short time labor insured workers, determines exemption from employment insurance, and supports labor insurance reporting.
Inhabitant Tax.
Global Payroll for Japan provides rules, pages, processes, and reports that you use to prepare wage payment reports and summaries for municipalities, load inhabitant tax amounts received from the municipalities, deduct inhabitant tax amounts from monthly salary, and prepare monthly inhabitant tax reports for municipalities.
Income Tax.
Global Payroll for Japan provides rules to calculate and deduct income tax from both salary and bonus and to adjust income tax on the final payment of the year. Use the Withholding Tax Register report to meet the statutory monthly reporting requirement.
Zaikei Deductions.
Global Payroll for Japan provides delivered elements to support funding Zaikei savings accounts.
Year-End Adjustment.
The delivered rules satisfy Japanese statutory and business requirements for year-end adjustment of the final salary or bonus payment and for independent year-end adjustment, as needed. After year-end adjustments are complete, and you prepare your data tables, you can generate the necessary reports to complete the year-end adjustment business process.
Banking.
Global Payroll for Japan supports electronic transfers from multiple company accounts to multiple employee accounts. For each employee, you can define the distribution amounts to multiple banks separately for salary, bonus, independent year-end adjustment, and retirement allowance. The system provides the direct deposit file in a common format that is used by all banks in Japan.
Payslips.
Global Payroll for Japan enables you to print payslips for monthly salaries, bonuses, independent year-end adjustment, and retirement allowance. Because the format of payslips varies greatly from one company to another, the system provides one format as an example. The system also provides a template that enables you to configure the format to accommodate the payslip style that your organization uses.
 Global Payroll for Japan Integrations
Global Payroll for Japan Integrations
This diagram shows the applications with which Global Payroll for Japan integrates, including HR, ePay, Core Global Payroll, Time and Labor, and General Ledger:
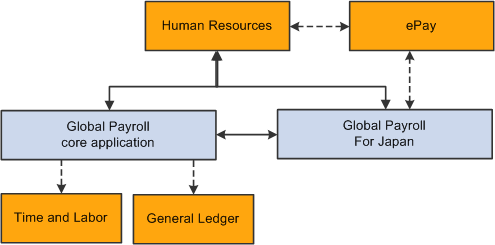
Global Payroll for Japan application integrations
 Delivered Elements
Delivered Elements
Global Payroll defines each business process for Japan in terms of delivered elements and rules. Some of these elements and rules are specifically designed to meet legal requirements, whereas others support common or customary payroll practices.
This section discusses:
Delivered element creation.
Element ownership and maintenance.

 Delivered Element Creation
Delivered Element Creation
All of the elements and rules delivered as part of your country extension were created using the core application—the same application that you will use to create additional elements or rules, and to configure some of the elements delivered as part of your Global Payroll system. Because the tools that you need to redefine or create new payroll elements are fully documented in the core application PeopleBook, this section does not repeat that information. Instead, this section briefly reviews the relationship between the core application (which contains the tools that you need to define your own elements and rules) and the country extensions (which contain country-specific rules and elements that are predefined in the system).
The core application has the following characteristics:
It consists of a payroll rules engine—a flexible tool that enables users to define the rules and elements of their payroll system and execute payroll and absence calculations.
Global Payroll does not embed payroll-specific logic or computations in application code. Instead, it specifies all business application logic, such as earnings, deductions, absences, and accumulators, in terms of payroll rules and elements. Global Payroll enables the user to enter and maintain payroll rules through a set of pages and offers a comprehensive set of features that enable users to work in their preferred language or currency.
It provides a payroll processing framework—a flexible way to define and execute payroll and absence processing flows, such as calendars, run types, pay periods, and process lists.
Country extensions have the following characteristics:
They are built using the core application.
They consist of statutory and customary objects (country-specific payroll rules, elements, payroll processes, reports, pages, and self-service applications).

 Element Ownership and Maintenance
Element Ownership and Maintenance
The delivered elements and rules of your Global Payroll country extension can be classified based on whether they are owned and maintained by the customer or by the PeopleSoft system. Some elements and rules are maintained exclusively by PeopleSoft and cannot be modified or reconfigured, whereas others can be configured to meet requirements that are unique to your organization.
Element Ownership in Global Payroll
Global Payroll has the following five categories of element ownership:
|
PS Delivered/Maintained |
Elements delivered and maintained on an ongoing basis by PeopleSoft. |
|
PS Delivered/Not Maintained |
Elements delivered by PeopleSoft that the customer must maintain. This category consists primarily of either customary (non-statutory) rules or statutory elements that customers may want to define according to a different interpretation of the rules. Although PeopleSoft may occasionally update elements that are defined as PS Delivered/Not Maintained, you are not required to apply these updates. |
|
Customer Maintained |
Elements created and maintained by your organization. PeopleSoft does not deliver rules that are defined as Customer Maintained. |
|
PS Delivered/Customer Modified |
Elements that were originally PS Delivered/Maintained elements, but which the customer has decided to control (this change is irreversible). |
|
PS Delivered /Maintained/Secure |
Delivered elements that the customer can never modify or control. |
Element Ownership in Global Payroll for Japan
The following table illustrates the approach to element ownership and maintenance in Global Payroll for Japan:
|
Functional Area |
Ownership |
Class |
|
Absence and Overtime. |
PS Delivered/Not Maintained. |
Customary. |
|
Commuting Allowance. |
PS Delivered/Maintained. |
Statutory. |
|
Earnings—base pay items. |
PS Delivered/Not Maintained. |
Customary. |
|
Earnings—other items. |
PS Delivered/Not Maintained. |
Statutory and Customary. |
|
Income Tax. |
PS Delivered/Maintained. |
Statutory. |
|
Inhabitant Tax. |
PS Delivered/Maintained. |
Statutory. |
|
Labor Insurance. |
PS Delivered/Maintained. |
Statutory. |
|
Social Insurance. |
PS Delivered/Maintained. |
Statutory. |
|
Year-End Adjustment. |
PS Delivered/Maintained. |
Statutory. |
|
Zaikei Deduction. |
PS Delivered/Not Maintained. |
Customary. |
See Also
 Element Naming Conventions
Element Naming Conventions
Understanding the naming convention developed for PeopleSoft-delivered elements can help you determine how an element is used, the element type, and even the functional area it serves. Depending on whether the element is a primary element, a component of a primary element, or a supporting element, one of the following naming conventions applies:
Supporting elements.
Primary elements.
Component names (suffixes).
This section also discusses:
Functional area codes for Japan.
Element type codes (PIN_TYPE).
Abbreviations in element names for Japan.
Suffixes for Japan.
Industry and regions feature.
Supporting Elements
Global Payroll for Japan uses the naming convention FF TT NAME for arrays, brackets, counts, dates, durations, formulas, rate codes, variables, historical rules, fictitious calculation rules, proration rules, rounding rules, accumulators, sections, element groups, and generation control conditions. This table explains the components of the naming convention:
|
FF |
Functional area code. |
|
TT |
Type of supporting element. |
|
NAME |
The description of the element. |
For example, in the social insurance variable SC VR MONTH REM, SC represents the functional area (Social Insurance), VR represents the element type (variable), and MONTH REM stands for monthly remuneration.
Primary Elements
Global Payroll does not use type codes in primary element names. Global Payroll for Japan uses the naming convention FF NAME for earning and deduction elements, which are primary elements. This table explains the components of the naming convention:
|
FF |
Functional area code. |
|
NAME |
The description of the element. |
For example, in the earning CM TX ALW, CM represents the functional area (commuting allowance) and TX ALW stands for taxable commuting allowance. In the earning ER BASE PAYM, ER represents the functional area (for elements related to earning contributions but not related to any other specific functional area), and BASE PAYM stands for monthly base pay.
Component Names (Suffixes)
When you create an earning or deduction element in Global Payroll, you must define the components that make up the element, such as base, rate, unit, and percentage. The system automatically generates the components and accumulators for the element based on the calculation rule or accumulator periods. The system also names the components and accumulators by appending a suffix to the element's name.
For example, you define the earning element named EARN1 with the calculation rule EARN1 = rate × unit. The system automatically creates two additional elements for the components in the calculation rule: a rate element called EARN1_RATE and a unit element called EARN1_UNIT.
In Global Payroll for Japan, all suffixes fall into one of the following types:
Separator.
Earnings and deductions component suffixes.
Earnings and deductions accumulator suffixes.
Deduction arrears component suffixes.
See Also
Defining General Element Information

 Functional Area Codes for Japan
Functional Area Codes for Japan
The following table contains the functional area codes used in the names of Japanese elements:
|
Functional Area Code |
Description |
|
AO |
Absence and Overtime. |
|
CM |
Commuting Allowance. |
|
ER |
Earning Contributions (Used for elements that are related to earning contributions but not specifically related to another functional area.) |
|
IH |
Inhabitant Tax. |
|
IN |
Income Tax. |
|
LA |
Labor Insurance. |
|
SC |
Social Insurance. |
|
YE |
Year-End Adjustment. |
|
ZK |
Zaikei Deduction. |

 Element Type Codes (PIN_TYPE)
Element Type Codes (PIN_TYPE)
The following table contains codes for all the element types. Because not all element types are delivered for Japan, not all of these codes appear in the names of Japanese elements:
|
Element Type Code |
Description |
|
AE |
Absence Entitlement |
|
AT |
Absence Take |
|
AC |
Accumulator |
|
AR |
Array |
|
AA |
Auto Assigned |
|
BR |
Bracket |
|
CT |
Count |
|
DT |
Date |
|
DD |
Deduction |
|
DR |
Duration |
|
ER |
Earning |
|
EG |
Element Group |
|
EM |
Error Message |
|
FC |
Fictitious Calculation |
|
FM |
Formula |
|
GC |
Generation Control |
|
HC |
Historical Rule |
|
PP |
Previous Period Rule |
|
PR |
Process |
|
PO |
Proration Rule |
|
RC |
Rate Code |
|
RR |
Rounding Rule |
|
SE |
Section |
|
SY |
System Element |
|
VR |
Variable |

 Abbreviations in Element Names for Japan
Abbreviations in Element Names for Japan
The following table lists some of the common abbreviations used in the names of Japanese elements:
|
Abbreviation |
Description |
|
ABS |
Absence |
|
AC |
Actual Result |
|
ADJ |
Adjusted |
|
ALW |
Allowance |
|
ANU |
Annual |
|
BAL |
Balance |
|
BON |
Bonus |
|
CD |
Code |
|
CHG |
Change |
|
CU |
Current |
|
D |
Daily |
|
DED |
Deduction |
|
DFT |
Default |
|
EST |
Establishment |
|
GR or GRD |
Grade |
|
HRS or H |
Hours, Hourly |
|
JDG |
Judge, evaluate, determine |
|
M |
Monthly |
|
MON |
Month |
|
MX |
Maximum |
|
NO |
Number |
|
NOM |
Normal |
|
NX |
Next |
|
O |
Occasional |
|
PR |
Previous |
|
PRM |
Premium |
|
PTO |
Paid Time Off |
|
RED |
Reduction |
|
REM |
Remuneration |
|
RET |
Retirement |
|
R |
Regular |
|
SAL |
Salary |
|
SK L or SCLE |
Sick Leave |
|
SP L or SPLE |
Special Leave |
|
STA |
Standard |
|
T |
Hourly |
|
TM |
Time |
|
TTL |
Total |
|
WRK |
Work |
|
YR |
Year |

 Suffixes for Japan
Suffixes for JapanGlobal Payroll for Japan uses the default core Global Payroll suffixes.

 Industry and Regions Feature
Industry and Regions FeatureThe PeopleSoft system does not use the industry and regions feature in defining elements for Japan.
 Archiving Data for Global Payroll for Japan
Archiving Data for Global Payroll for JapanPeopleSoft Global Payroll for Japan generates a large amount of result data. To keep the amount of saved data manageable, it can be helpful to archive it periodically. PeopleSoft PeopleTools delivers an archiving tool called the Data Archive Manager. To aid you in archiving your result data using the Data Archive Manager, PeopleSoft Global Payroll for Japan delivers a predefined archive object (GPJP_RSLT_ARCHIVE) and archive template (GPJPRSLT). The delivered archive template uses queries that select data by calendar group ID (CAL_RUN_ID field).
Note. Please use extreme caution when making changes to delivered archive objects, queries, or templates. Any modifications can result in the loss of important data.
See Archiving Data.
See Also
PeopleTools 8.52: Data Management PeopleBook, Using PeopleSoft Data Archive Manager
 Element Query
Element Query
PeopleSoft delivers a query that you can run to view the names of all delivered elements designed for Japan.
See Also