11g Release 5 (11.1.5)
Part Number E20384-05
Contents
Contact
Us
|
Oracle® Fusion
Applications Project Management Implementation Guide 11g Release 5 (11.1.5) Part Number E20384-05 |
Contents |
Contact Us |
|
Previous |
Next |
This chapter contains the following:
Define Common Project Configuration: Overview
Manage Inventory Organizations
In the Define Common Project Configuration activity, you configure components from other products that are used by Oracle Fusion Projects.
Setup tasks in the Define Common Project Configuration activity are grouped into the following task lists and tasks:
|
Task List |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Define Units of Measure for Project Management |
Define the prerequisite inventory setup for units of measure and the units of measure used in Oracle Fusion Projects. |
|
Define Subledger Accounting Rules |
Configure subledger accounting and set up subledger accounting rules. |
|
Define Project Notes |
Define project note types, mappings, and descriptive flexfields. |
|
Manage Employees and Contingent Workers |
Manage internal employees and contingent workers in Oracle Fusion Global Human Resources. |
|
Manage Trading Community Parties |
Enter customer, supplier, and partner organizations and contacts that will be associated with projects. |
|
Define Common Project Billing Configuration |
Configure common billing features and behavior such as tax calculations, intercompany rules, and general contract management. |
An inventory organization is a logical or physical entity in the enterprise that is used to store definitions of items or store and transact items.
You select the following usages in the inventory organization's properties:
Item management
Item and inventory management
Inventory organizations used for item management, which are the same as item organizations, store only definitions of items. Use inventory organizations for item management when the storage or movement of inventory does not need to be physically or financially tracked. For example, in a retail implementation you can create an inventory organization for item management to store the names of items that are listed by and sold through each retail outlet, while a different system tracks physical inventory and transactions. If it is necessary in the future, you can change an inventory organization's usage from item management to item and inventory management in the inventory organization's properties.
Inventory organizations used for item and inventory management store and transact items, in addition to item definitions. An inventory organization used for item and inventory management is associated with one business unit, one legal entity, and one primary ledger. Use inventory organizations for item and inventory management when the storage or movement of inventory needs to be physically and financially tracked. Inventory organizations used for item and inventory management can represent facilities such as manufacturing centers, warehouses, or distribution centers. You cannot change an inventory organization's use from item and inventory management to item management.
In Oracle Fusion, storage facilities, warehouses, and distribution centers are implemented as inventory organizations.
Inventory organizations are:
Managed by a business unit, with the materials management business function enabled.
Mapped to a legal entity and a primary ledger.
There are two types of inventory organizations:
Manufacturing facilities
Storage facilities
Storage and manufacturing facilities are related to other organizational entities through a business unit that stores, manufactures, and distributes goods through many factories, warehouses, and distribution centers. The material parameters are set for both the facilities, enabling movement of material in the organization. This business unit has the business function of Materials Management enabled. Oracle Fusion Applications allow many inventory organizations to be assigned to one business unit.
Note
Currently, Oracle Fusion Applications do not include manufacturing capabilities, so setup your manufacturing facilities outside of Oracle Fusion applications.
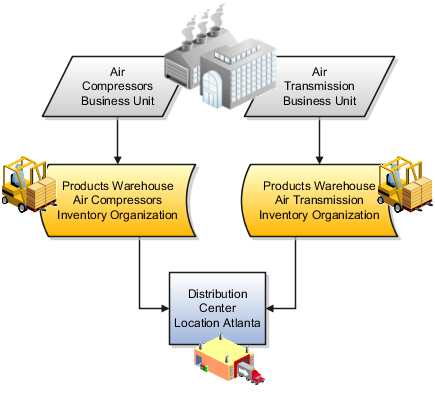
A distribution center can store inventory that is the responsibility of different business units. In this situation, assign an inventory organization to each business unit as a representation of the inventory in the distribution center. The multiple inventory organizations representing the inventory are defined with the same location to show that they are a part of the same distribution center.
In the following figure the two business units, Air Compressors and Air Transmission, share one distribution center in Atlanta. The two inventory organizations, Air Compressors and Air Transmission represent the inventory for each business unit in the Atlanta distribution center and are both assigned the Atlanta location.
A legal entity owns the inventory located in a storage or manufacturing facility. This ownership is assigned through the relationship of the inventory organization representing the inventory and the legal entity assigned to the inventory organization. The legal entity assigned to the inventory organization shares the same primary ledger as the inventory organization's business unit.
The inventory is tracked in the inventory organization owned by the legal entity of which the business unit is part. All transactions are accounted for in the primary ledger of the legal entity that owns the inventory.
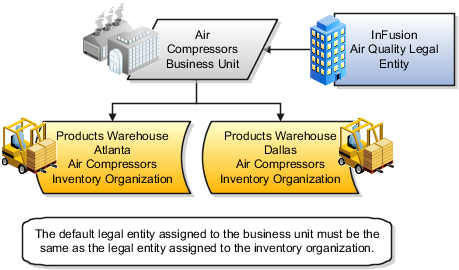
The figure below illustrates the inventory owned by InFusion Air Quality legal entity. The InFusion Air Quality legal entity is associated with the Air Compressors business unit, which is associated with the two Air Compressors inventory organizations. Therefore, InFusion Air Quality legal entity owns the entire inventory in both the Dallas and Atlanta locations.
A prerequisite to defining an inventory organization is to define a facility schedule. Oracle Fusion Applications allow you to associate an inventory organization with a schedule.
Facility schedules allow creating workday calendars for inventory organizations that are used in the Oracle Fusion Supply Chain Management product family. For example, use workday calendars in the scheduling of cycle counts and calculating transit time.
You can create a new inventory organization, or select an existing organization to define as an inventory organization.
Before creating inventory organizations:
Set up inventory organization dependencies
Plan inventory organization parameters
When you create an inventory organization, you must associate it to dependencies, such as business units and legal entities. For this reason, create these dependencies before creating an inventory organization.
Before creating an inventory organization, plan the inventory organization's parameters
Consider the following when planning to configure an inventory organization's parameters
Which schedule to use
Which inventory organization to serve as the item master organization
Whether to configure locator control and if so, the level at which to enforce the locator control
How you want to configure movement request settings such as pick slip batch size and replenishment movement request grouping
Consider the size of your operation, your usage of subinventories, and the type of labor or equipment required when considering whether you want to use organization- or subinventory-level replenishment movement request grouping.
How you want to configure lot, serial, and packing unit generation settings
To make appropriate choices for these settings, you should be familiar with:
Your company's guidelines for creating lot names, serial numbers, and packing unit numbers
Whether your company requires you to assign the same lot number to multiple items in the same organization, or a specific lot number to only one item in the same organization
Whether your company requires you to place purchase order or shipping order material under lot control
How you want to configure item sourcing details, such as the picking rule to use, and whether to specify the inventory organization as a logistics services organization
When you specify to round reorder quantities, min-max planning reorders for item subinventories are automatically rounded up or down.
Reorder quantities for an item subinventory are calculated based on:
The setting that you select for the Round Order Quantity parameter on the Manage Inventory Organization Parameters page, General tab, of the inventory organization containing the item subinventory
The value that you specify for the Fixed Lot Multiple text box on the Add Item to Subinventory window
If you enable rounding the reorder quantity for the inventory organization, and specify the fixed lot multiple for the item subinventory, the reorder quantity is rounded up. If you disable rounding the reorder quantity for the inventory organization, and specify the fixed lot multiple for the item subinventory, the reorder quantity is rounded down.
Note
To round reorder quantities, you must specify a fixed lot multiple.
Assume that the reorder quantity is 24. If you enable rounding the reorder quantity and specify 10 for the fixed lot multiple, the reorder quantity is rounded up to 30. If you disable rounding the reorder quantity and keep the fixed lot multiple at 10, the reorder quantity is rounded down to 20.
You can create or edit an inventory organization in the Oracle Fusion Global Human Resources application, on the Manage Inventory Organizations page.
An item master organization contains definitions of items that you can use across one or more item and inventory organizations. An item master organization does not contain subinventories, and is not used for inventory transactions.
When you create an inventory organization, you select an item or inventory organization to serve as the inventory organization's item master organization. Although you can select an item organization, you should follow best practices and select an inventory organization to separate item management from item storage and transaction functions.
Although it is typical for an implementation to contain one item master organization, an implementation can include multiple item master organizations if necessary. For example, your company performs an acquisition. During the integration period, you use your company's existing item master organization, and also use an additional item master organization to contain the definitions of the acquired company's items. Generally, however, you should use only a single item master organization to reduce the chances of confusion when defining and maintaining items.
If your company operates as a conglomerate, and there is no coordination between your company's subsidiaries, there might be reduced value in using a single item master organization between all subsidiaries.
Item organizations contain only definitions of items. Use item organizations in implementations when the storage or movement of inventory does not need to be physically or financially tracked. For example, in a retail implementation you can create an item organization to contain only the definitions of items that are listed by and sold through each retail outlet, while a different system tracks the physical inventory and transactions of those items. If Oracle Fusion Inventory Management is installed, you can change an item organization to an inventory organization.
Inventory organization-level min-max planning replenishes a particular item in an inventory organization. When you use inventory organization-level min-max planning, inventory balances, purchase requisitions, and internal sales orders are treated as supply; sales orders and account issue movement requests are treated as demand.
To set up organization-level min-max planning, navigate to the Create Item page, Specifications tab in Oracle Fusion Product Information Management. Select Min-Max Planning for the inventory planning method, then specify minimum and maximum levels.
Define units of measure, unit of measure classes, and base units of measure for tracking, moving, storing, and counting items.
The Quantity unit of measure class contains the units of measure Box of 8, Box of 4, and Each. The unit of measure Each is assigned as the base unit of measure.
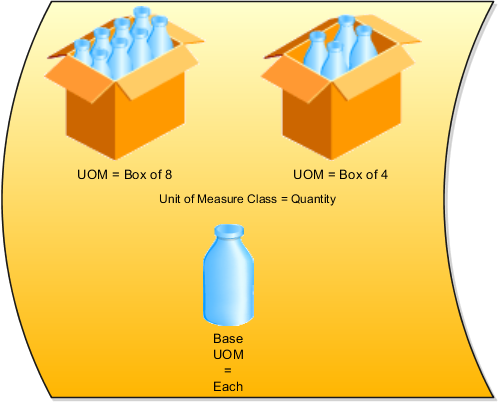
Unit of measure classes represent groups of units of measure with similar characteristics such as area, weight, or volume.
Units of measure are used by a variety of functions and transactions to express the quantity of items. Each unit of measure you define must belong to a unit of measure class.
Each unit of measure class has a base unit of measure. The base unit of measure is used to perform conversions between units of measure in the class. For this reason, the base unit of measure should be representative of the other units of measure in the class, and should generally be one of the smaller units. For example, you could use CU (cubic feet) as the base unit of measure for a unit of measure class called Volume.
Each unit of measure class must have a base unit of measure.
This table lists examples of unit of measure classes, the units of measure in each unit of measure class, and the unit of measure assigned as the base unit of measure for each unit of measure class. Note that each base unit of measure is the smallest unit of measure in its unit of measure class.
|
Unit of Measure Class |
Units of Measure |
Base Unit of Measure |
|---|---|---|
|
Quantity |
dozen box each |
each |
|
Weight |
pound kilogram gram |
gram |
|
Time |
hour minute second |
second |
|
Volume |
cubic feet cubic centimeters cubic inches |
cubic inches |
A unit of measure standard conversion specifies the conversion factor by which the unit of measure is equivalent to the base unit of measure.
This table lists examples of unit of measure classes, one unit of measure included in each class, the base unit of measure for the unit of measure class, and the conversion factor defined for the unit of measure.
|
Unit of Measure Class |
Unit of Measure |
Base Unit of Measure |
Conversion Factor |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Quantity |
dozen |
each |
12 (1 dozen = 12 each) |
|
Weight |
pound |
gram |
454 (1 pound = 454 grams) |
|
Time |
minute |
second |
60 (1 minute = 60 seconds) |
A unit of measure standard conversion defines the conversion factor by which the unit of measure is equivalent to the base unit of measure that you defined for the unit of measure class. Defining a unit of measure standard conversion allows you to perform transactions in units other than the primary unit of measure of the item being transacted. The standard unit of measure conversion is used for an item if an item-specific unit of measure conversion has not been defined.
A UOM interclass conversion defines the conversion between the source base unit of measure ("From Base UOM") in one unit of measure class ("From Class") and the destination base unit of measure ("To Base UOM") in a different unit of measure class ("To Class").
For example, the item is gasoline. The From Base UOM (of the From Class called "volume") is liters. The To Base UOM (of the To Class called "quantity") is Barrels. The conversion is 158.76 liters (volume) to 1 barrel of oil (quantity).
A UOM intraclass conversion specifies the conversion between a unit of measure (the "From UOM") and the base unit of measure of the same class.
For example, the item is soda pop. The unit of measure class is Quantity. The From UOM is Case (CS). The base unit of measure is Each (EA). The conversion is 24, to specify that 1 CS = 24 EA.