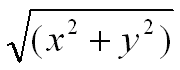12 java.lang.Math Functions
This chapter provides a reference to the java.lang.Math functions provided in Oracle Continuous Query Language (Oracle CQL).
For more information, see Section 1.1.11, "Functions".
This chapter includes the following section:
12.1 Introduction to Oracle CQL Built-In java.lang.Math Functions
Table 12-1 lists the built-in java.lang.Math functions that Oracle CQL provides.
Table 12-1 Oracle CQL Built-in java.lang.Math Functions
| Type | Function |
|---|---|
|
Trigonometric |
|
|
Logarithmic |
|
|
Euler's Number |
|
|
Roots |
|
|
Signum Function |
|
|
Unit of Least Precision |
|
|
Other |
Note:
Built-in function names are case sensitive and you must use them in the case shown (in lower case).
Note:
In stream input examples, lines beginning with h (such as h 3800) are heartbeat input tuples. These inform Oracle Event Processing that no further input will have a timestamp lesser than the heartbeat value.
For more information, see:
abs
abs returns the absolute value of the input integer argument as an integer.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#abs(int).
Consider the query q66 in Example 12-1. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-2, the query returns the stream in Example 12-3.
abs1
abs1 returns the absolute value of the input long argument as a long.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#abs(long).
Consider the query q67 in Example 12-4. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 float, c3 long) in Example 12-5, the query returns the stream in Example 12-6.
abs2
abs2 returns the absolute value of the input float argument as a float.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#abs(float).
Consider the query q68 in Example 12-7. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 float, c3 bigint) in Example 12-8, the query returns the stream in Example 12-9.
abs3
abs3 returns the absolute value of the input double argument as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#abs(double).
Consider the query q69 in Example 12-10. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 float, c3 bigint, c4 double) in Example 12-11, the query returns the stream in Example 12-12.
acos
acos returns the arc cosine of a double angle, in the range of 0.0 through pi, as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#acos(double).
Consider the query q73 in Example 12-13. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-14, the query returns the stream in Example 12-15.
asin
asin returns the arc sine of a double angle, in the range of -pi/2 through pi/2, as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#asin(double).
Consider the query q74 in Example 12-16. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-17, the query returns the stream in Example 12-18.
atan
atan returns the arc tangent of a double angle, in the range of -pi/2 through pi/2, as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#atan(double).
Consider the query q75 in Example 12-19. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-20, the query returns the stream in Example 12-21.
atan2
atan2 converts rectangular coordinates (x,y) to polar (r,theta) coordinates.
This function takes the following arguments:
-
double1: the ordinate coordinate. -
double2: the abscissa coordinate.
This function returns the theta component of the point (r,theta) in polar coordinates that corresponds to the point (x,y) in Cartesian coordinates as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#atan2(double,%20double).
Consider the query q63 in Example 12-22. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-23, the query returns the stream in Example 12-24.
Example 12-22 atan2 Function Query
<query id="q63"><![CDATA[
select atan2(c2,c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
cbrt
cbrt returns the cube root of the double argument as a double.
For positive finite a, cbrt(-a) == -cbrt(a); that is, the cube root of a negative value is the negative of the cube root of that value's magnitude.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#cbrt(double).
Consider the query q76 in Example 12-25. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 float, c3 bigint) in Example 12-26, the query returns the stream in Example 12-27.
ceil1
ceil1 returns the smallest (closest to negative infinity) double value that is greater than or equal to the double argument and equals a mathematical integer.
To avoid possible rounding error, consider using (long) cern.jet.math.Arithmetic.ceil(double).
For more information, see:
Consider the query q77 in Example 12-28. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-29, the query returns the stream in Example 12-30.
Example 12-28 ceil1 Function Query
<query id="q77"><![CDATA[
select ceil1(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
cos
cos returns the trigonometric cosine of a double angle as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#cos(double).
Consider the query q61 in Example 12-31. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-32, the query returns the stream in Example 12-33.
cosh
cosh returns the hyperbolic cosine of a double value as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#cosh(double).
Consider the query q78 in Example 12-34. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-35, the query returns the stream in Example 12-36.
exp
exp returns Euler's number e raised to the power of the double argument as a double.
Note that for values of x near 0, the exact sum of expm1(x) + 1 is much closer to the true result of Euler's number e raised to the power of x than EXP(x).
For more information, see:
Consider the query q79 in Example 12-37. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-38, the query returns the stream in Example 12-39.
expm1
expm1 returns the computation that Figure 12-1 shows as a double, where x is the double argument and e is Euler's number.
Note that for values of x near 0, the exact sum of expm1(x) + 1 is much closer to the true result of Euler's number e raised to the power of x than exp(x).
For more information, see:
Consider the query q80 in Example 12-40. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-41, the query returns the stream in Example 12-42.
Example 12-40 expm1 Function Query
<query id="q80"><![CDATA[
select expm1(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
floor1
floor1 returns the largest (closest to positive infinity) double value that is less than or equal to the double argument and equals a mathematical integer.
To avoid possible rounding error, consider using (long) cern.jet.math.Arithmetic.floor(double).
For more information, see:
Consider the query q81 in Example 12-43. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-44, the query returns the stream in Example 12-45.
Example 12-43 floor1 Function Query
<query id="q81"><![CDATA[
select floor1(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
hypot
hypot returns the hypotenuse (see Figure 12-2) of the double arguments as a double.
This function takes the following arguments:
-
double1: thexvalue. -
double2: theyvalue.
The hypotenuse is computed without intermediate overflow or underflow.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#hypot(double,%20double).
Consider the query q82 in Example 12-46. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-47, the query returns the stream in Example 12-48.
Example 12-46 hypot Function Query
<query id="q82"><![CDATA[
select hypot(c2,c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
IEEEremainder
IEEEremainder computes the remainder operation on two double arguments as prescribed by the IEEE 754 standard and returns the result as a double.
This function takes the following arguments:
-
double1: the dividend. -
double2: the divisor.
The remainder value is mathematically equal to f1 - f2 × n, where n is the mathematical integer closest to the exact mathematical value of the quotient f1/f2, and if two mathematical integers are equally close to f1/f2, then n is the integer that is even. If the remainder is zero, its sign is the same as the sign of the first argument.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#IEEEremainder(double,%20double).
Consider the query q72 in Example 12-49. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-50, the query returns the stream in Example 12-51.
Example 12-49 IEEEremainder Function Query
<query id="q72"><![CDATA[
select IEEEremainder(c2,c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
log1
log1 returns the natural logarithm (base e) of a double value as a double.
Note that for small values x, the result of log1p(x) is much closer to the true result of ln(1 + x) than the floating-point evaluation of log(1.0+x).
For more information, see:
Consider the query q83 in Example 12-52. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-53, the query returns the stream in Example 12-54.
log101
log101 returns the base 10 logarithm of a double value as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#log10(double).
Consider the query q84 in Example 12-55. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-56, the query returns the stream in Example 12-57.
Example 12-55 log101 Function Query
<query id="q84"><![CDATA[
select log101(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
log1p
log1p returns the natural logarithm of the sum of the double argument and 1 as a double.
Note that for small values x, the result of log1p(x) is much closer to the true result of ln(1 + x) than the floating-point evaluation of log(1.0+x).
For more information, see:
Consider the query q85 in Example 12-58. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-59, the query returns the stream in Example 12-60.
Example 12-58 log1p Function Query
<query id="q85"><![CDATA[
select log1p(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
pow
pow returns the value of the first double argument (the base) raised to the power of the second double argument (the exponent) as a double.
This function takes the following arguments:
-
double1: the base. -
double2: the exponent.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#pow(double,%20double).
Consider the query q65 in Example 12-61. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-62, the query returns the stream in Example 12-63.
rint
rint returns the double value that is closest in value to the double argument and equals a mathematical integer. If two double values that are mathematical integers are equally close, the result is the integer value that is even.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#rint(double).
Consider the query q86 in Example 12-64. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-65, the query returns the stream in Example 12-66.
round
round returns the closest integer to the float argument.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#round(float).
Consider the query q87 in Example 12-67. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-68, the query returns the stream in Example 12-69.
Example 12-67 round Function Query
<query id="q87"><![CDATA[
select round(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
round1
round1 returns the closest integer to the float argument.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#round(float).
Consider the query q88 in Example 12-70. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-71, the query returns the stream in Example 12-72.
Example 12-70 round1 Function Query
<query id="q88"><![CDATA[
select round1(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
signum
signum returns the signum function of the double argument as a double:
-
zero if the argument is zero
-
1.0 if the argument is greater than zero
-
-1.0 if the argument is less than zero
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#signum(double).
Consider the query q70 in Example 12-73. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-74, the query returns the stream in Example 12-75.
Example 12-73 signum Function Query
<query id="q70"><![CDATA[
select signum(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
signum1
signum1 returns the signum function of the float argument as a float:
-
zero if the argument is zero
-
1.0 if the argument is greater than zero
-
-1.0 if the argument is less than zero
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#signum(float).
Consider the query q71 in Example 12-76. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-77, the query returns the relation in Example 12-78.
Example 12-76 signum1 Function Query
<query id="q71"><![CDATA[
select signum1(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
sin
sin returns the trigonometric sine of a double angle as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#sin(double).
Consider the query q60 in Example 12-79. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 float, c3 bigint) in Example 12-80, the query returns the stream in Example 12-81.
sinh
sinh returns the hyperbolic sine of a double value as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#sinh(double).
Consider the query q89 in Example 12-82. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-83, the query returns the stream in Example 12-84.
sqrt
sqrt returns the correctly rounded positive square root of a double value as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#sqrt(double).
Consider the query q64 in Example 12-85. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 float, c3 bigint) in Example 12-86, the query returns the stream in Example 12-87.
tan
tan returns the trigonometric tangent of a double angle as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#tan(double).
Consider the query q62 in Example 12-88. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-89, the query returns the stream in Example 12-90.
tanh
tanh returns the hyperbolic tangent of a double value as a double.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#tanh(double).
Consider the query q90 in Example 12-91. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-92, the query returns the stream in Example 12-93.
todegrees
todegrees converts a double angle measured in radians to an approximately equivalent angle measured in degrees as a double.
The conversion from radians to degrees is generally inexact; do not expect COS(TORADIANS(90.0)) to exactly equal 0.0.
For more information, see:
Consider the query q91 in Example 12-94. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-95, the query returns the stream in Example 12-96.
Example 12-94 todegrees Function Query
<query id="q91"><![CDATA[
select todegrees(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
toradians
toradians converts a double angle measured in degrees to an approximately equivalent angle measured in radians as a double.
For more information, see:
Consider the query q92 in Example 12-97. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-98, the query returns the stream in Example 12-99.
Example 12-97 toradians Function Query
<query id="q92"><![CDATA[
select toradians(c2) from SFunc
]]></query>
ulp
ulp returns the size of an ulp of the double argument as a double. In this case, an ulp of the argument value is the positive distance between this floating-point value and the double value next larger in magnitude.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#ulp(double).
Consider the query q93 in Example 12-100. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-101, the query returns the stream in Example 12-102.
ulp1
ulp1 returns the size of an ulp of the float argument as a float. An ulp of a float value is the positive distance between this floating-point value and the float value next larger in magnitude.
For more information, see http://java.sun.com/javase/6/docs/api/java/lang/Math.html#ulp(float).
Consider the query q94 in Example 12-103. Given the data stream SFunc with schema (c1 integer, c2 double, c3 bigint) in Example 12-104, the query returns the relation in Example 12-105.