10 Using Web Services Atomic Transactions
This chapter describes how to use Web services atomic transactions for WebLogic Web services using Java API for XML Web Services (JAX-WS) to enable interoperability with other external transaction processing systems.
This chapter includes the following sections:
-
Configuring the Domain Resources Required for Web Service Advanced Features
-
Enabling Web Services Atomic Transactions on Web Service Clients
-
Configuring Web Services Atomic Transactions Using the Administration Console
-
Using Web Services Atomic Transactions in a Clustered Environment
Overview of Web Services Atomic Transactions
WebLogic Web services enable interoperability with other external transaction processing systems, such as Websphere, Microsoft .NET, and so on, through the support of the following specifications:
-
Web Services Atomic Transaction (WS-AtomicTransaction) Versions 1.0, 1.1, and 1.2:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wstx-wsat-1.2-spec-cs-01/wstx-wsat-1.2-spec-cs-01.html -
Web Services Coordination (WS-Coordination) Versions 1.0, 1.1, and 1.2:
http://docs.oasis-open.org/ws-tx/wstx-wscoor-1.2-spec-cs-01/wstx-wscoor-1.2-spec-cs-01.html
These specifications define an extensible framework for coordinating distributed activities among a set of participants. The coordinator, shown in the following figure, is the central component, managing the transactional state (coordination context) and enabling Web services and clients to register as participants.
Figure 10-1 Web Services Atomic Transactions Framework
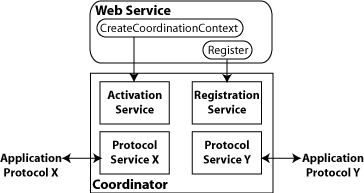
Description of "Figure 10-1 Web Services Atomic Transactions Framework"
The following table describes the components of Web services atomic transactions, shown in the previous figure.
Table 10-1 Components of Web Services Atomic Transactions
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
|
Coordinator |
Manages the transactional state (coordination context) and enables Web services and clients to register as participants. |
|
Activation Service |
Enables the application to activate a transaction and create a coordination context for an activity. Once created, the coordination context is passed with the transaction flow. |
|
Registration Service |
Enables an application to register as a participant. |
|
Application Protocol X, Y |
Supported coordination protocols, such as WS-AtomicTransaction. |
The following figure shows two instances of WebLogic Server interacting within the context of a Web services atomic transaction. For simplicity, two WebLogic Web service applications are shown.
Figure 10-2 Web Services Atomic Transactions in WebLogic Server Environment
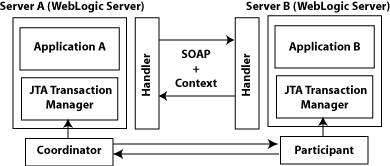
Description of "Figure 10-2 Web Services Atomic Transactions in WebLogic Server Environment"
Please note the following:
-
Using the local JTA transaction manager, a transaction can be imported to or exported from the local JTA environment as a subordinate transaction, all within the context of a Web service request.
-
Creation and management of the coordination context is handled by the local JTA transaction manager.
-
All transaction integrity management and recovery processing is done by the local JTA transaction manager.
For more information about JTA, see Programming JTA for Oracle WebLogic Server.
The following describes a sample end-to-end Web services atomic transaction interaction, illustrated in Figure 10-2:
-
Application A begins a transaction on the current thread of control using the JTA transaction manager on Server A.
-
Application A calls a Web service method in Application B on Server B.
-
Server A updates its transaction information and creates a SOAP header that contains the coordination context, and identifies the transaction and local coordinator.
-
Server B receives the request for Application B, detects that the header contains a transaction coordination context and determines whether it has already registered as a participant in this transaction. If it has, that transaction is resumed and if not, a new transaction is started.
Application B executes within the context of the imported transaction. All transactional resources with which the application interacts are enlisted with this imported transaction.
-
Server B enlists itself as a participant in the WS-AtomicTransaction transaction by registering with the registration service indicated in the transaction coordination context.
-
Server A resumes the transaction.
-
Application A resumes processing and commits the transaction.
Configuring the Domain Resources Required for Web Service Advanced Features
When creating or extending a domain, if you expect that you will be using other Web service advanced features in addition to Web service atomic transactions (either now or in the future), you can apply the WebLogic Advanced Web Services for JAX-WS Extension template (wls_webservice_jaxws.jar) to configure automatically the resources required to support the advanced Web service features. Although use of this extension template is not required, it makes the configuration of the required resources much easier. Alternatively, you can configure the resources required for these advanced features using the Oracle WebLogic Administration Console or WLST. For more information, see "Configuring Your Domain for Advanced Web Service Features" in Getting Started With JAX-WS Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Note:
If you do not expect to use other Web service advanced features with Web service atomic transactions, application of this extension template is not required, minimizing start-up times and memory footprint.
Enabling Web Services Atomic Transactions on Web Services
To enable Web services atomic transactions on a Web service:
-
When starting from Java (bottom-up), add the
@weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactionalannotation to the Web service endpoint implementation class or method. For more information, see Using the @Transactional Annotation in Your JWS File. -
When starting from WSDL (top-down), use
wsdlcto generate a Web service from an existing WSDL file. In this case, The WS-AtomicTransaction policy assertions that are advertised in the WSDL are carried forward and are included in the WSDL file for the new Web service generated bywsdlc. See Enabling Web Services Atomic Transactions Starting From WSDL. -
At deployment time, enable and configure Web services atomic transactions at the Web service endpoint or method level using the WebLogic Server Administration Console. For more information, see Configuring Web Services Atomic Transactions Using the Administration Console.
The following tables summarizes the configuration options that you can set when enabling Web services atomic transactions.
Table 10-2 Web Services Atomic Transactions Configuration Options
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
|
|
Version of the Web services atomic transaction coordination context that is used for Web services and clients. For clients, it specifies the version used for outbound messages only. The value specified must be consistent across the entire transaction. Valid values include |
|
|
Whether the Web services atomic transaction coordination context is passed with the transaction flow. For valid values, see Table 10-3. |
The following table summarizes the valid values for flow type and their meaning on the Web service and client. The table also summarizes the valid value combinations when configuring web services atomic transactions for an EJB-style web service that uses the @TransactionAttribute annotation.
| Value | Web Service Client | Web Service | Valid EJB @TransactionAttribute Values |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
JTA transaction: Do not export transaction coordination context. No JTA transaction: Do not export transaction coordination context. |
Transaction flow exists: Do not import transaction coordination context. If the CoordinationContext header contains No transaction flow: Do not import transaction coordination context. |
|
|
|
JTA transaction: Export transaction coordination context. No JTA transaction: Do not export transaction coordination context. |
Transaction flow exists: Import transaction context. No transaction flow: Do not import transaction coordination context. |
|
|
|
JTA transaction: Export transaction coordination context. No JTA transaction: An exception is thrown. |
Transaction flow exists: Import transaction context. No transaction flow: Service-side exception is thrown. |
|
Using the @Transactional Annotation in Your JWS File
To enable Web services atomic transactions, specify the @weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional annotation on the Web service endpoint implementation class or method.
Note:
This annotation is not to be mistaken with weblogic.jws.Transactional, which ensures that the annotated class or operation runs inside of a transaction, but not an atomic transaction.
Please note the following:
-
If you specify the
@Transactionalannotation at the Web service class level, the settings apply to all two-way methods defined by the service endpoint interface. You can override the flow type value at the method level; however, the version must be consistent across the entire transaction. -
You cannot explicitly specify the
@Transactionalannotation on a Web method that is also annotated with@Oneway. -
Web services atomic transactions cannot be used with the client-side asynchronous programming model.
The format for specifying the @Transactional annotation is as follows:
@Transactional(
version=Transactional.Version.[WSAT10|WSAT11|WSAT12|DEFAULT],
value=Transactional.TransactionFowType.[MANDATORY|SUPPORTS|NEVER]
)
For more information about the version and flow type configuration options, see Table 10-2.
The following sections provide examples of using the @Transactional annotation at the Web service implementation class and method levels, and with the EJB @TransactionAttribute annotation.
-
Example: Using @Transactional Annotation on a Web Service Class
-
Example: Using @Transactional Annotation on a Web Service Method
-
Example: Using the @Transactional and the EJB @TransactionAttribute Annotations Together
Example: Using @Transactional Annotation on a Web Service Class
The following example shows how to add @Transactional annotation on a Web service class. Relevant code is shown in bold. As shown in the example, there is an active JTA transaction.
Note:
The following excerpt is borrowed from the Web services atomic transaction example that is delivered with the WebLogic Server Samples Server. For more information, see More Examples of Using Web Services Atomic Transactions.
package examples.webservices.jaxws.wsat.simple.service; . . . import weblogic.jws.Policy; import javax.transaction.UserTransaction; . . . import javax.jws.WebService; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.Version; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.TransactionFlowType; /** * This JWS file forms the basis of a WebLogic WS-Atomic Transaction Web Service with the * operations: createAccount, deleteAccount, transferMonet, listAccount * */ @WebService(serviceName = "WsatBankTransferService", targetNamespace = "http://tempuri.org/", portName = "WSHttpBindingIService") @Transactional(value=Transactional.TransactionFlowType.MANDATORY, version=weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.Version.WSAT10) public class WsatBankTransferService { public String createAccount(String acctNo, String amount) throws java.lang.Exception{ Context ctx = null; UserTransaction tx = null; try { ctx = new InitialContext(); tx = (UserTransaction)ctx.lookup("javax.transaction.UserTransaction"); try { DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)ctx.lookup("examples-demoXA-2"); String sql = "insert into wsat_acct_remote (acctno, amount) values (" + acctNo + ", " + amount + ")"; int insCount = dataSource.getConnection().prepareStatement(sql).executeUpdate(); if (insCount != 1) throw new java.lang.Exception("insert fail at remote."); return ":acctno=" + acctNo + " amount=" + amount + " creating. "; } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("**** Exception caught *****"); e.printStackTrace(); throw new SQLException("SQL Exception during createAccount() at remote."); } } catch (java.lang.Exception e) { System.out.println("**** Exception caught *****"); e.printStackTrace(); throw new java.lang.Exception(e); } } public String deleteAccount(String acctNo) throws java.lang.Exception{ ... } public String transferMoney(String acctNo, String amount, String direction) throws java.lang.Exception{ ... } public String listAccount() throws java.lang.Exception{ ... } }
Example: Using @Transactional Annotation on a Web Service Method
The following example shows how to add @Transactional annotation on a Web service implementation method. Relevant code is shown in bold.
package examples.webservices.jaxws.wsat.simple.service; . . . import weblogic.jws.Policy; import javax.transaction.UserTransaction; . . . import javax.jws.WebService; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.Version; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.TransactionFlowType; /** * This JWS file forms the basis of a WebLogic WS-Atomic Transaction Web Service with the * operations: createAccount, deleteAccount, transferMonet, listAccount * */ @WebService(serviceName = "WsatBankTransferService", targetNamespace = "http://tempuri.org/", portName = "WSHttpBindingIService") public class WsatBankTransferService { @Transactional(value=Transactional.TransactionFlowType.MANDATORY, version=weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.Version.WSAT10) public String createAccount(String acctNo, String amount) throws java.lang.Exception{ Context ctx = null; UserTransaction tx = null; try { ctx = new InitialContext(); tx = (UserTransaction)ctx.lookup("javax.transaction.UserTransaction"); try { DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)ctx.lookup("examples-demoXA-2"); String sql = "insert into wsat_acct_remote (acctno, amount) values (" + acctNo + ", " + amount + ")"; int insCount = dataSource.getConnection().prepareStatement(sql).executeUpdate(); if (insCount != 1) throw new java.lang.Exception("insert fail at remote."); return ":acctno=" + acctNo + " amount=" + amount + " creating. "; } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("**** Exception caught *****"); e.printStackTrace(); throw new SQLException("SQL Exception during createAccount() at remote."); } } catch (java.lang.Exception e) { System.out.println("**** Exception caught *****"); e.printStackTrace(); throw new java.lang.Exception(e); } } public String deleteAccount(String acctNo) throws java.lang.Exception{ ... } public String transferMoney(String acctNo, String amount, String direction) throws java.lang.Exception{ ... } public String listAccount() throws java.lang.Exception{ ... } }
Example: Using the @Transactional and the EJB @TransactionAttribute Annotations Together
The following example illustrates how to use the @Transactional and EJB @TransactionAttribute annotations together. In this case, the flow type values must be compatible, as outlined in Table 10-3. Relevant code is shown in bold.
package examples.webservices.jaxws.wsat.simple.service; . . . import weblogic.jws.Policy; import javax.transaction.UserTransaction; . . . import javax.jws.WebService; import javax.ejb.TransactionAttribute; import javax.ejb.TransactionAttributeType; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.Version; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.TransactionFlowType; /** * This JWS file forms the basis of a WebLogic WS-Atomic Transaction Web Service with the * operations: createAccount, deleteAccount, transferMonet, listAccount * */ @WebService(serviceName = "WsatBankTransferService", targetNamespace = "http://tempuri.org/", portName = "WSHttpBindingIService") @Transactional(value=Transactional.TransactionFlowType.MANDATORY, version=weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.Version.WSAT10) @TransactionAttribute(TransactionAttributeType.REQUIRED public class WsatBankTransferService { . . . }
Enabling Web Services Atomic Transactions Starting From WSDL
When enabled, Web services atomic transactions are advertised in the WSDL file using a policy assertion.
Table 10-4 summarizes the WS-AtomicTransaction 1.2 policy assertions that correspond to a set of common Web services atomic transaction flow type and EJB Transaction attribute combinations. All other combinations result in a build-time error.
Table 10-4 Web Services Atomic Transaction Policy Assertion Values (WS-AtomicTransaction 1.2)
| Atomic Transaction Flow Type | EJB @TransactionAttribute |
WS-AtomicTransaction 1.2 Policy Assertion |
|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
No policy advertisement |
You can use wsdlc Ant task to generate, from an existing WSDL file, a set of artifacts that together provide a partial Java implementation of the Web service described by the WSDL file. The WS-AtomicTransaction policy assertions that are advertised in the WSDL are carried forward and are included in the WSDL file for the new Web service generated by wsdlc.
The wsdlc Ant tasks creates a JWS file that contains a partial (stubbed-out) implementation of the generated JWS interface. You need to modify this file to include your business code. After you have coded the JWS file with your business logic, run the jwsc Ant task to generate a complete Java implementation of the Web service. Use the compiledWsdl attribute of jwsc to specify the JAR file generated by the wsdlc Ant task which contains the JWS interface file and data binding artifacts. By specifying this attribute, the jwsc Ant task does not generate a new WSDL file but instead uses the one in the JAR file. Consequently, when you deploy the Web service and view its WSDL, the deployed WSDL will look just like the one from which you initially started (with the WS-AtomicTransaction policy assertions).
For complete details about using wsdlc to generate a Web service from a WSDL file, see "Developing WebLogic Web Services Starting From a WSDL File: Main Steps" in Getting Started With JAX-WS Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Enabling Web Services Atomic Transactions on Web Service Clients
On a Web service client, enable Web services atomic transactions using one of the following methods:
-
Add the
@weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactionalannotation on the Web service reference injection point for a client. For more information, see Using @Transactional Annotation with the @WebServiceRef Annotation. -
Pass an instance of the
weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.TransactionalFeatureas a parameter when creating the Web service proxy or dispatch. For more information, see Passing the TransactionalFeature to the Client. -
At deployment time, enable and configure Web services atomic transactions at the Web service client endpoint or method level using the WebLogic Server Administration Console. For more information, see Configuring Web Services Atomic Transactions Using the Administration Console.
-
At run-time, if the non-atomic transactional Web service client calls an atomic transaction-enabled Web service, then based on the flow type advertised in the WSDL:
-
If the flow type is set to
SUPPORTSorNEVERon the service-side, then the call is included as part of the transaction. -
If the flow type is set to
MANDATORY, then an exception is thrown.
-
For information about the configuration options that you can set when enabling Web services atomic transactions, see Table 10-2.
Using @Transactional Annotation with the @WebServiceRef Annotation
To enable Web services atomic transactions, specify the @weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional annotation on the Web service client at the Web service reference (@WebServiceRef) injection point.
The format for specifying the @Transactional annotation is as follows:
@Transactional(
version=Transactional.Version.[WSAT10|WSAT11|WSAT12|DEFAULT],
value=Transactional.TransactionFlowType.[MANDATORY|SUPPORTS|NEVER]
)
For more information about the version and flow type configuration options, see Table 10-2.
The following example illustrates how to annotate the Web service reference injection point. Relevant code is shown in bold. As shown in the example, the active JTA transaction becomes a part of the atomic transaction.
Note:
The following excerpt is borrowed from the Web services atomic transaction example that is delivered with the WebLogic Server Samples Server. For more information, see More Examples of Using Web Services Atomic Transactions.
package examples.webservices.jaxws.wsat.simple.client; . . . import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; . . . import java.net.URL; import javax.xml.namespace.QName; import javax.transaction.UserTransaction; import javax.transaction.SystemException; import javax.xml.ws.WebServiceRef; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional; */ /** * This example demonstrates using a WS-Atomic Transaction to create or delete an account, * or transfer money via Web service as a single atomic transaction. */ public class WsatBankTransferServlet extends HttpServlet { . . . String url = "http://localhost:7001"; URL wsdlURL = new URL(url + "/WsatBankTransferService/WsatBankTransferService"); . . . DataSource ds = null; UserTransaction utx = null; try { ctx = new InitialContext(); utx = (UserTransaction) ctx.lookup("javax.transaction.UserTransaction"); utx.setTransactionTimeout(900); } catch (java.lang.Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } WsatBankTransferService port = getWebService(wsdlURL); try { utx.begin(); if (remoteAccountNo.length() > 0) { if (action.equals("create")) { result = port.createAccount(remoteAccountNo, amount); } else if (action.equals("delete")) { result = port.deleteAccount(remoteAccountNo); } else if (action.equals("transfer")) { result = port.transferMoney(remoteAccountNo, amount, direction); } } utx.commit(); result = "The transaction is committed " + result; } catch (java.lang.Exception e) { try { e.printStackTrace(); utx.rollback(); result = "The transaction is rolled back. " + e.getMessage(); } catch(java.lang.Exception ex) { e.printStackTrace(); result = "Exception is caught. Check stack trace."; } } request.setAttribute("result", result); . . . @Transactional(value = Transactional.TransactionFlowType.MANDATORY, version = Transactional.Version.WSAT10) @WebServiceRef(wsdlLocation = "http://localhost:7001/WsatBankTransferService/WsatBankTransferService?WSDL", value = examples.webservices.jaxws.wsat.simple.service.WsatBankTransferService.class) WsatBankTransferService_Service service; private WsatBankTransferService getWebService() { return service.getWSHttpBindingIService(); } public String createAccount(String acctNo, String amount) throws java.lang.Exception{ Context ctx = null; UserTransaction tx = null; try { ctx = new InitialContext(); tx = (UserTransaction)ctx.lookup("javax.transaction.UserTransaction"); try { DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)ctx.lookup("examples-dataSource-demoXAPool"); String sql = "insert into wsat_acct_local (acctno, amount) values ( " + acctNo + ", " + amount + ")"; int insCount = dataSource.getConnection().prepareStatement(sql).executeUpdate(); if (insCount != 1) throw new java.lang.Exception("insert fail at local."); return ":acctno=" + acctNo + " amount=" + amount + " creating.. "; } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("**** Exception caught *****"); e.printStackTrace(); throw new SQLException("SQL Exception during createAccount() at local."); } } catch (java.lang.Exception e) { System.out.println("**** Exception caught *****"); e.printStackTrace(); throw new java.lang.Exception(e); } } public String deleteAccount(String acctNo) throws java.lang.Exception{ . . . } public String transferMoney(String acctNo, String amount, String direction) throws java.lang.Exception{ . . . } public String listAccount() throws java.lang.Exception{ . . . } }
Passing the TransactionalFeature to the Client
To enable Web services atomic transactions on the client of the Web service, you can pass an instance of the weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.TransactionalFeature as a parameter when creating the Web service proxy or dispatch, as illustrated in the following example. Relevant code is shown in bold.
Note:
The following excerpt is borrowed from the Web services atomic transaction example that is delivered with the WebLogic Server Samples Server. For more information, see More Examples of Using Web Services Atomic Transactions.
package examples.webservices.jaxws.wsat.simple.client; . . . import javax.servlet.*; import javax.servlet.http.*; . . . import java.net.URL; import javax.xml.namespace.QName; import javax.transaction.UserTransaction; import javax.transaction.SystemException; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.TransactionalFeature; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.Version; import weblogic.wsee.wstx.wsat.Transactional.TransactionFlowType; */ /** * This example demonstrates using a WS-Atomic Transaction to create or delete an account, * or transfer money via Web service as a single atomic transaction. */ public class WsatBankTransferServlet extends HttpServlet { . . . String url = "http://localhost:7001"; URL wsdlURL = new URL(url + "/WsatBankTransferService/WsatBankTransferService"); . . . DataSource ds = null; UserTransaction utx = null; try { ctx = new InitialContext(); utx = (UserTransaction) ctx.lookup("javax.transaction.UserTransaction"); utx.setTransactionTimeout(900); } catch (java.lang.Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } WsatBankTransferService port = getWebService(wsdlURL); try { utx.begin(); if (remoteAccountNo.length() > 0) { if (action.equals("create")) { result = port.createAccount(remoteAccountNo, amount); } else if (action.equals("delete")) { result = port.deleteAccount(remoteAccountNo); } else if (action.equals("transfer")) { result = port.transferMoney(remoteAccountNo, amount, direction); } } utx.commit(); result = "The transaction is committed " + result; } catch (java.lang.Exception e) { try { e.printStackTrace(); utx.rollback(); result = "The transaction is rolled back. " + e.getMessage(); } catch(java.lang.Exception ex) { e.printStackTrace(); result = "Exception is caught. Check stack trace."; } } request.setAttribute("result", result); . . . // Passing the TransactionalFeature to the Client private WsatBankTransferService getWebService(URL wsdlURL) { TransactionalFeature feature = new TransactionalFeature(); feature.setFlowType(TransactionFlowType.MANDATORY); feature.setVersion(Version.WSAT10); WsatBankTransferService_Service service = new WsatBankTransferService_Service(wsdlURL, new QName("http://tempuri.org/", "WsatBankTransferService")); return service.getWSHttpBindingIService(new javax.xml.ws.soap.AddressingFeature(), feature); } public String createAccount(String acctNo, String amount) throws java.lang.Exception{ Context ctx = null; UserTransaction tx = null; try { ctx = new InitialContext(); tx = (UserTransaction)ctx.lookup("javax.transaction.UserTransaction"); try { DataSource dataSource = (DataSource)ctx.lookup("examples-dataSource-demoXAPool"); String sql = "insert into wsat_acct_local (acctno, amount) values ( " + acctNo + ", " + amount + ")"; int insCount = dataSource.getConnection().prepareStatement(sql).executeUpdate(); if (insCount != 1) throw new java.lang.Exception("insert fail at local."); return ":acctno=" + acctNo + " amount=" + amount + " creating.. "; } catch (SQLException e) { System.out.println("**** Exception caught *****"); e.printStackTrace(); throw new SQLException("SQL Exception during createAccount() at local."); } } catch (java.lang.Exception e) { System.out.println("**** Exception caught *****"); e.printStackTrace(); throw new java.lang.Exception(e); } } public String deleteAccount(String acctNo) throws java.lang.Exception{ . . . } public String transferMoney(String acctNo, String amount, String direction) throws java.lang.Exception{ . . . } public String listAccount() throws java.lang.Exception{ . . . } }
Configuring Web Services Atomic Transactions Using the Administration Console
The following sections describe how to configure Web services atomic transactions using the Administration Console.
Securing Messages Exchanged Between the Coordinator and Participant
Using transport-level security, you can secure messages exchanged between the Web services atomic transaction coordinator and participant by configuring the properties defined in the following table using the WebLogic Server Administration Console. These properties are configured at the domain level. For detailed steps, see "Configure Web services atomic transactions" in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Help.
Table 10-5 Securing Web Services Atomic Transactions
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
|
Web Services Transactions Transport Security Mode |
Specifies whether two-way SSL is used for the message exchange between the coordinator and participant. This property can be set to one of the following values:
For more information, see "Configure two-way SSL" in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Help. |
|
Web Service Transactions Issued Token Enabled |
Flag the specifies whether to use an issued token to enable authentication between the coordinator and participant. The |
Enabling and Configuring Web Services Atomic Transactions
To enable Web services atomic transactions and configure the version and flow type, you can customize the configuration at the endpoint or method level for the Web service or client. For detailed steps, see "Configure Web services atomic transactions" in the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console Help.
Using Web Services Atomic Transactions in a Clustered Environment
For considerations when using atomic transaction-enabled Web services in a clustered environment, see Chapter 9, "Managing Web Services in a Cluster".
More Examples of Using Web Services Atomic Transactions
Refer to the following sections for additional examples of using Web services atomic transactions:
-
For an example of how to sign and encrypt message headers exchanged during the Web services atomic transaction, see "Securing Web Services Atomic Transactions" in Securing WebLogic Web Services for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Note:
You can secure applications that enable Web service atomic transactions using only WebLogic Web service security policies. You cannot secure them using Oracle Web Services Manager (WSM) policies.
-
A detailed example of Web services atomic transactions is provided as part of the WebLogic Server sample application. For more information about running the sample application and accessing the example, see "Sample Application and Code Examples" in Information Roadmap for Oracle WebLogic Server .