Most implementations that use the Application Controller will follow the general setup outlined below.
The following illustration shows the architecture of a typical implementation that uses the Application Controller.
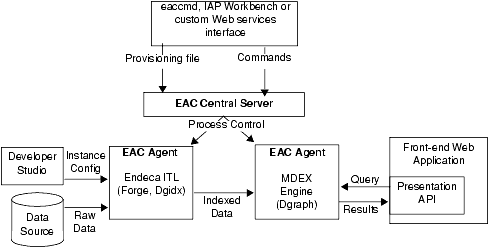
In this architecture diagram, the following happens:
- The developer creates an instance configuration, using Developer Studio, that determines what data and features will be incorporated into the index.
- The developer creates a provisioning document in XML format that defines all the hosts and components in the implementation.
- The developer sends the provisioning files to the EAC Central Server machine. The developer can use three methods for the provisioning tasks:
- Endeca Workbench
- The eaccmd utility
- A custom Web services interface.
- Once the Agent machines in the implementation are provisioned, the developer sends commands (again using either eaccmd, Endeca Workbench, or a custom interface) to the EAC Central Server. The EAC Central Server communicates these tasks to its Agents, which reside on each machine that is running Endeca components.
- The Application Controller manages the entire data update process, according to the instructions it receives. This includes running Forge and the Indexer (Dgidx) to create indexed data, and starting the MDEX Engine (Dgraph) based on that indexed data.
For detailed information on configuring and using the Endeca Application Controller, see the Oracle Endeca Application Controller Guide.
