| Oracle® Fusion Middleware High Availability Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E10106-20 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Fusion Middleware High Availability Guide 11g Release 1 (11.1.1) Part Number E10106-20 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter describes high availability concepts and configuration procedures for Oracle Application Development Framework (Oracle ADF) and Oracle WebCenter Portal.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Section 6.2, "Configuring an Oracle ADF High Availability Deployment"
Section 6.3, "WebCenter Portal and High Availability Concepts"
Section 6.4, "Configuring High Availability for WebCenter Portal"
Section 6.5, "Configuring High Availability for WebCenter Portal Applications"
Oracle ADF is an end-to-end application framework that builds on Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) standards and open-source technologies to simplify and accelerate implementing service-oriented applications. Oracle ADF is suitable for enterprise developers who want to create applications that search, display, create, modify, and validate data using web, wireless, desktop, or web services interfaces. Used in tandem, Oracle JDeveloper 11g and Oracle ADF provide an environment that covers the full development lifecycle from design to deployment, with drag-and-drop data binding, visual UI design, and team development features built in.
Section 6.1.2, "Oracle ADF High Availability Considerations"
Section 6.1.3, "Configuring Oracle ADF for High Availability"
Section 6.1.4, "Troubleshooting Oracle ADF High Availability"
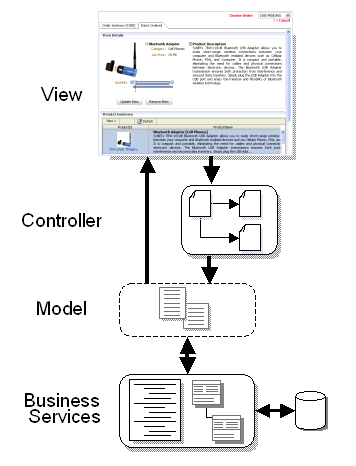
In line with community best practices, applications built using the Fusion web technology stack achieve a clean separation of business logic, page navigation, and user interface by adhering to a model-view-controller (MVC) architecture supported by the following layers.
As shown in Figure 6-1, in an MVC architecture:
The model layer represents the data values related to the current page
The view layer contains the UI pages used to view or modify that data
The controller layer processes user input and determines page navigation
The business service layer handles data access and encapsulates business logic
Figure 6-1 Overview of Oracle ADF Architecture
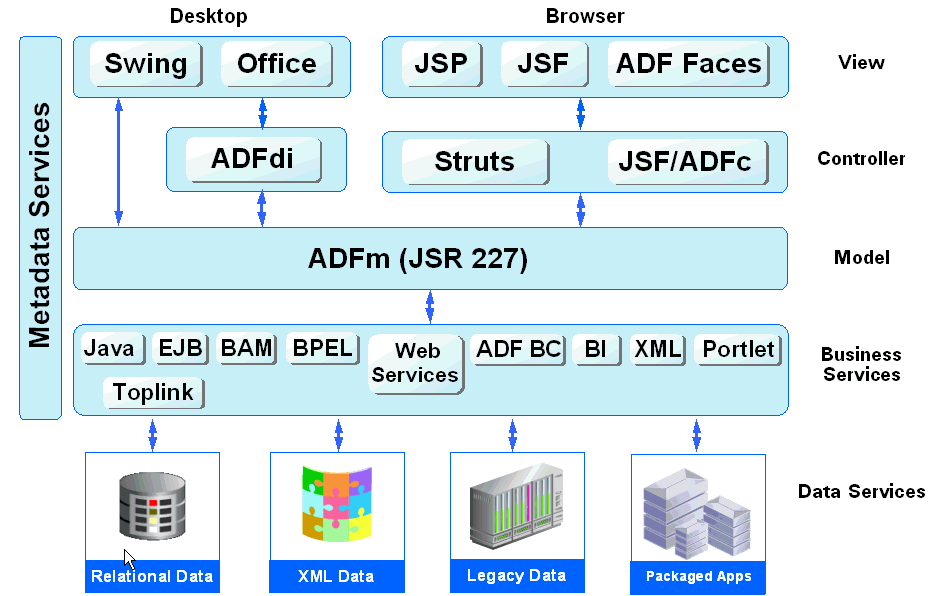
The core module in the framework is Oracle ADF Model. The Oracle ADF Model layer enables a unified approach to bind any user interface to any business service, without the need to write code.
The other modules that make up a Fusion web application technology stack are:
Oracle ADF Business Components, which simplifies building business services.
Oracle ADF Faces, which offers a rich library of AJAX-enabled UI components for Web applications built with JavaServer Faces (JSF).
Oracle ADF Controller, which integrates JSF with Oracle ADF Model. The ADF Controller extends the standard JSF controller by providing additional functionality, such as reusable task flows that pass control not only between JSF pages, but also between other activities, for instance method calls or other task flows.
Figure 6-2 shows where each Oracle ADF module fits in the Fusion web application architecture.
Figure 6-2 Simple Oracle ADF Architecture
ADF Business Components are prebuilt application objects that accelerate the job of delivering and maintaining high-performance, richly functional, database-centric services. When building service-oriented Java EE applications, developers implement the core business logic as one or more business services. These backend services provide clients with a way to query, insert, update, and delete business data as required while enforcing appropriate business rules. ADF Business Components provides a ready-to-use implementation of Java EE design patterns and best practices.
Oracle ADF Business Components provides the following key components to simplify building database-centric business services:
Entity object
An entity object represents a row in a database table and simplifies modifying its data by handling all data manipulation language (DML) operations. It can encapsulate business logic to ensure that business rules are consistently enforced. Developers can associate an entity object with others to reflect relationships in the underlying database schema to create a layer of business domain objects to reuse in multiple applications.
View object
A view object represents a SQL query and simplifies working with its results. Developers use the SQL language to join, project, filter, sort, and aggregate data into the shape required by the end-user task being represented in the user interface. This includes the ability to link a view object with other entity objects to create master-detail hierarchies of any complexity. When end users modify data in the user interface, view objects collaborate with entity objects to consistently validate and save the changes.
Application module
An application module is the transactional component that UI clients use to work with application data. It defines an updateable data model and top-level procedures and functions (called service methods) related to a logical unit of work related to an end-user task.
For more information about Oracle ADF Business Components, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
In the model layer, Oracle ADF Model implements data controls that abstract the implementation technology of a business service. Standard metadata interfaces describe the service's operations and data collections, including information about the properties, methods, and types involved. In Oracle JDeveloper, developers see that information as icons that they can drag and drop onto a page. When a developer drags the representation of a service onto a page, Oracle JDeveloper automatically creates the bindings from the page to the services. At runtime, the ADF Model layer reads the information describing the application's data controls and data bindings from appropriate XML files and implements the two-way connection between the user interface and the application's business service.
Oracle ADF provides out-of-the-box data control implementations for the most common business service technologies. Using Oracle JDeveloper and Oracle ADF together provides a declarative, drag-and-drop data binding experience for building user interfaces. Along with support for ADF Business Components application modules, ADF Model also supports the following service technologies:
Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) session beans and JPA entities
JavaBeans
Web services
XML
CSV files
For more information about Oracle ADF Model, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
In the controller layer, where handling page flow of the web applications is a key concern, ADF Controller provides an enhanced navigation and state management model on top of JSF. JDeveloper supports declarative creation of task flows that can manage application control between different types of activities, such as pages, methods on managed beans, declarative case statements, or calls to other task flows.
For more information about Oracle ADF Controller, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
ADF Faces rich client (ADF Faces) is a set of standard JSF components that include built-in AJAX functionality. AJAX is a combination of asynchronous JavaScript, dynamic HTML (DHTML), XML, and XmlHttpRequest communication channel. This combination enables requests to be made to the server without fully rerendering the page. While AJAX enables rich client-like applications to use standard internet technologies, JSF provides server-side control, which reduces the dependency on an abundance of JavaScript often found in typical AJAX applications.
ADF Faces provides over 100 rich components, including hierarchical data tables, tree menus, in-page dialogs, accordions, dividers, and sortable tables. ADF Faces also provides ADF Data Visualization components, which are Flash- and SVG-enabled components capable of rendering dynamic charts, graphs, gauges, and other graphics that provide a real-time view of underlying data. Each component also supports customization and skinning, along with internationalization and accessibility.
To achieve these front-end capabilities, ADF Faces components use a rendering kit that handles displaying the component and also provides the JavaScript objects needed for the rich functionality. This built-in support enables developers to build rich applications without needing extensive knowledge of the individual technologies on the front or back end.
For more information about ADF Faces, including the architecture and detailed information about each of the components, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Web User Interface Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
You can install the Oracle ADF runtime to the Oracle WebLogic Server using either the Oracle JDeveloper Installer or the Oracle Fusion Middleware Application Developer Installer. The Application Developer Installer also lets you optionally install Fusion Middleware Control to provide web-based administration support for all Managed Servers in the domain. The Oracle JDeveloper installer does not install Fusion Middleware Control. See the deployment chapter of the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
When you use the Application Developer Installer to install the Oracle ADF runtime, it creates an Oracle Application Developer home directory (by default, Oracle_APPDEV1) under the Middleware home. After you use the domain configuration wizard to create an Application Developer domain (base_domain) based on the JRF domain template, you can configure the server topology. In a typical set up, the domain has an Administration server containing the WLS Administration Console and Fusion Middleware Control. Typically, the Oracle ADF runtime libraries (part of the Java Required Files) get deployed to the Managed Servers, in addition to the user-facing custom Fusion web applications. To provide customization and personalization features, you can install an optional MDS repository and configure it separately. Figure 6-3 shows a basic single-node Oracle ADF architecture.
Figure 6-3 Basic Single-Node Oracle ADF Architecture
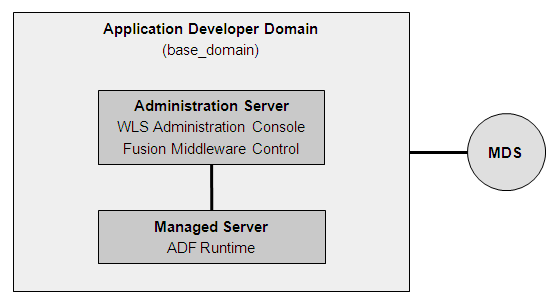
For more information about domains and servers, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
If the Fusion web application involves customization using Oracle Metadata Services (MDS), Oracle recommends that you register your MDS repository with the Oracle WebLogic Server domain before you deploy the application. For information about registering MDS, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
Then, when you deploy the application, JDeveloper prompts you to choose the target metadata repository or shared metadata repository. You will be able to choose from the list of metadata repositories registered with the Oracle WebLogic Administration Server.
To ensure that you receive the metadata repository prompt, the application's adf-config.xml file must define a cust-config element in the mds-config section. This element specifies an ordered and named list of customization classes. A customization class is the interface that MDS uses to define which customization applies to the base definition metadata. In JDeveloper, you can use the overview editor for the adf-config.xml file to define a cust-config element.
For information about configuring the adf-config.xml file for MDS, see the chapter on customizing with MDS in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
For more information about the MDS architecture and metadata repositories and archives (EAR, MAR), see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
The operations performed by the Fusion web application are logged directly to the WebLogic Managed Server where the application is running:
DOMAIN_HOME/servers/server_name/logs/server_name-diagnostic.log
The log files for the different WebLogic Managed Servers are also available from the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console. To verify the logs, access the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console http://<admin_server_host>:<port>/console and click on Diagnostics-Log Files.
This log's granularity and logging properties can be changed using Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control (Fusion Middleware Control). Fusion Middleware Control is a Web browser-based, graphical user interface that you can use to monitor and administer a farm. To receive high availability warning diagnostic messages for Oracle ADF, set the level to FINE, as Section 6.1.4.3, "Troubleshooting Oracle ADF Replication and Failover Issues" describes.
For more information about the level of diagnostics you can specify for Fusion web applications, see the chapter on testing and debugging in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
For details about using Fusion Middleware Control to change the log settings of WebLogic Managed Servers and Oracle ADF, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide.
Fusion web applications built on the Oracle ADF technology stack are Java EE applications (and J2EE applications). This section includes the following topics:
Section 6.1.2.2, "Oracle ADF Failover and Expected Behavior"
Section 6.1.2.4, "Configuring the ADF Application Module for Oracle RAC"
At runtime, ADF objects such as the binding container and managed beans are instantiated. Each of these objects has a defined life span set by its scope attribute.
There are six types of scopes in a Fusion web application:
Application scope: The object is available for the duration of the application.
Session scope: The object is available for the duration of the session.
Page flow scope: The object is available for the duration of a bounded task flow.
Request scope: The object is available from the time an HTTP request is made until a response is sent back to the client.
Backing bean scope: Used for managed beans for page fragments and declarative components only, the object is available from the time an HTTP request is made until a response is sent back to the client.
View scope: The object is available until the view ID for the current view activity changes. This scope can be used to hold values for a given page. However, unlike request scope, which can be used to store a value needed from one page to the next, anything stored in view scope will be lost once the view ID changes.
When the Fusion web application runs in a clustered environment, a portion of the application's state is serialized and copied to another server or a data store at the end of each request so that the state is available to other servers in the cluster.
When you design an application to run in a clustered environment, you must:
Ensure that all managed beans with a life span longer than one request are serializable (that is, they implement the java.io.Serializable interface). Specifically, beans stored in session scope, page flow scope, and view scope must be serializable.
Verify that Oracle ADF is aware of changes to managed beans stored in ADF scopes (view scope and page flow scope) and enable tracking changes to ADF memory scopes.
When you modify a value within a managed bean in either view scope or page flow scope, the application must notify Oracle ADF so that it can ensure the bean's new value is replicated.
In Example 6-1, an attribute of an object in view scope is modified.
Example 6-1 Code that Modifies an Object in viewScope
Map<String, Object> viewScope =
AdfFacesContext.getCurrentInstance().getViewScope();
MyObject obj = (MyObject)viewScope.get("myObjectName");
Obj.setFoo("newValue");
Without additional code, Oracle ADF will be unaware of this change and will not know that a new value must replicate within the cluster. To inform Oracle ADF of the change and need for replication, use the markScopeDirty() method shown in Example 6-2. The markScopeDirty() method accepts only viewScope and pageFlowScope as parameters.
Example 6-2 Additional Code to Notify Oracle ADF of Changes to an Object
controllerContext ctx = ControllerContext.getInstance(); ctx.markScopeDirty(viewScope);
This code is needed for any request that modifies an existing object in one of the ADF scopes. If the scope itself is modified by the scope's put(), remove(), or clear() methods, it is not necessary to notify Oracle ADF.
To enable ADF Controller to track changes to ADF memory scopes and replicate the page flow scope and view scope within the server cluster, you can enable the<adf-scope-ha-support> parameter in the adf-config.xml file, as described in Section 6.1.3.3, "Configuring adf-config.xml."
For more information about ADF object scopes, see the chapter on Fusion page lifecycle in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
An Oracle WebLogic cluster provides application high availability. If one member of the cluster is unavailable, any other available member of the cluster is able to handle the request.
Session Failover Requirements
For seamless failover of a Fusion web application, the application must meet the following conditions:
The application is in a cluster and at least one member of the application cluster is available to serve the request.
For stateful applications, state replication is configured correctly as described in Section 6.1.3, "Configuring Oracle ADF for High Availability."
If you are using Oracle HTTP Server, the server is configured with the WebLogicCluster directive to balance among all available application instances.
If you are using a hardware load balancer, the load balancer is:
Routing traffic to all available instances
Configured correctly with a health monitor to mark unavailable instances
Configured to support persistence of session state
Expected Behavior for Application Failover
If the environment has been configured correctly, application users do not notice when an application instance in a cluster becomes unavailable. The sequence of events in an application failover is, for example, as follows:
A user makes a request and is routed by a hardware load balancer to instance A of the application.
Instance A of the application becomes unavailable because of node failure, process failure, or network failure.
The hardware load balancer marks instance A as unavailable.
The user makes a subsequent request. The request is routed to instance B.
Instance B is configured as a replication partner of Instance A and has the user's session state.
The application resumes using the session state on Instance B and the user continues working without interruption.
The Fusion technology stack includes the Active Data Service (ADS), which enables you to bind ADF Faces components to an active data source using the ADF Model layer. In JDeveloper, you configure individual components in your JSF pages to show active data. When you configure components to use active data, data is pushed to the client whenever a change event is raised by the data source. The data is pushed from the server to the client and shown by the browser.
To support failover for pages configured to show active data, it is necessary to enable failover for the ADF Business Components application module and to enable ADF Controller to track changes to the ADF memory scopes. With these ADF settings configured, when failover occurs, the ADF server will detect the failover and request all pages configured to show active data to refresh themselves, after that ADS restarts and data is pushed to the client.
For details about how to enable failover for the Fusion web application, see Section 6.1.3, "Configuring Oracle ADF for High Availability."
For more information about using Oracle ADF Faces components with an active data service, see the chapter on ADS in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
When configuring the ADF application module to access a highly available database system, such as redundant databases or Oracle Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) as the backend, the data source must be container-defined. In this scenario, it is required to use a GridLink data source or multi data source. However, from the standpoint of the application module configuration, the naming convention for the multi data source or GridLink data source is the same as it is for a non-multi data source or GridLink data source. This naming convention ensures that the correct data source is used at runtime. For details about configuring GridLink data sources for high availability applications, see Section 4.1.4, "Configuring GridLink Data Sources with Oracle RAC." For multi data sources, see Section 4.1.5, "Configuring Multi Data Sources with Oracle RAC.".
To support automatic replication and failover for web applications within a clustered environment, Oracle WebLogic Server supports mechanisms for replicating HTTP session state across clusters. You can configure Oracle ADF to ensure the Fusion web application's state can be restored from any server in the cluster.
An application module is the transactional component that UI clients use to work with application data. It defines an updateable data model and top-level procedures and functions (called service methods) related to a logical unit of work related to an end-user task. An application module supports passivating, or storing, its transaction state as a snapshot in the database. It also supports the reverse operation of activating the transaction state from one of these saved snapshots.
For more information on the management of application module state, see "Introduction to Fusion Web Application State Management" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
To enable support for ADF Business Components failover, set the jbo.dofailover parameter to true so that the application module state is saved on release. This enables Oracle ADF to restore the application module state from a snapshot saved from a previous checkin. By contrast, when the failover feature is disabled, which it is by default, then application module state is saved only when the application is reused by a subsequent user session and only when the application module pool cannot find an unused application module.
You can set this parameter in your application module configuration on the Pooling and Scalability tab of the Edit Business Components Configuration dialog.
To configure application modules for high availability:
Launch JDeveloper and open the application.
In the Application Navigator, expand the project that contains the data model and locate the application module.
Right-click the application module and select Configurations.
Click Edit.
Click the Pooling and Scalability tab.
Select the Failover Transaction State Upon Managed Release checkbox.
Click OK to close the Edit Business Components Configuration dialog.
Click OK to close the Manage Configurations dialog.
For more information about Oracle ADF state management facilities and how to use them, see the chapter on application state management in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
To enable support for replicating HTTP session state, you must assign a value to the persistent-store-type element in the Oracle WebLogic Server weblogic.xml file. The value replicated_if_clustered ensures that the in-effect persistent store type will be replicated so that sessions on the clustered environment are stored in accordance with the value set for the cluster of servers to which this server belongs.
To configure the weblogic.xml file for high availability:
Launch JDeveloper and open the application.
In the Application Navigator, expand the project that contains the web application and expand the WEB-INF folder.
Double-click the weblogic.xml file, and click the Source tab to edit the file.
In the file, add the persistent-store-type definition to the session-descriptor element:
<weblogic-web-app>
<session-descriptor>
<persistent-store-type>
replicated_if_clustered
</persistent-store-type>
</session-descriptor>
</weblogic-web-app>
When you design an application to run in a clustered environment, you must ensure that Oracle ADF is aware of changes to managed beans stored in ADF scopes (view scope and page flow scope).
When a value within a managed bean in either view scope or page flow scope is modified, the application must notify Oracle ADF so that it can ensure the bean's new value is replicated.
To enable ADF Controller to track changes to ADF memory scopes and replicate the page flow scope and view scope within the server cluster, you must set the ADF Controller parameter <adf-scope-ha-support> in the application's adf-config.xml file to true. For example, when set to true for an application and that application adds or removes a bean from a page flow scope during a request, the change will automatically replicated within a cluster.
The adf-config.xml file is the central configuration file for all ADF components. The file contains sections to configure the runtime behavior for ADF components, including, ADF Controller.
Note:
If your application uses MDS and will use an Oracle database that supports failover, Oracle recommends enabling MDS retry on failover. To do this, add the following retry-connection entry to the MDS configuration section of adf-config.xml.
<persistence-config>
<metadata-namespaces>...
<metadata-store-usages>...
<external-change-detection enabled="false" polling-interval-secs="30"/>
<read-only-mode enabled="true"/>
<retry-connection enabled="true"/>
</persistence-config>
To configure the adf-config.xml file for high availability:
Launch JDeveloper and open the application.
In the Application Navigator, expand the Application Resources.
Select Descriptors, and then select the ADF META-INF node.
Double-click the adf-config.xml file, and click the Source tab to edit the file.
Add the following to the file:
<adf-controller-config xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/controller/config"> <adf-scope-ha-support>true</adf-scope-ha-support> </adf-controller-config>
For more information about using the adf-config.xml file to configure ADF, see the chapter on creating complex task flows in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Fusion Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Development Framework.
This section describes procedures for troubleshooting possible issues with Oracle ADF.
When you develop the Fusion web application in Oracle JDeveloper, the integrated development environment provides support for detecting potential High Availability issues. The warnings that JDeveloper provides are generated by the audit framework and are triggered to appear in the JDeveloper source editors. The warnings the editors show are based on the audit rules for High Availability applications.
The High Availability audit rules that JDeveloper enables by default are:
ADF Controller Configuration - High Availability for ADF Scopes is not Enabled warns the developer that the adf-scope-ha-support flag in the adf-config.xml file is set is not set to true. This audit rule fires only when the <adf-controller-config> element is in the ADF application-level configuration file (adf-config.xml).
ADF Page Flows - Bean in Scope Map is Modified warns the developer when the some code calls a setter method on a bean to indicate that the code did not subsequently call the ControllerContext.markScopeDirty() method. This audit rule fire only when the adf-scope-ha-support flag in the adf-config.xml file is set to true.
ADF Page Flows - EL Bean is Modified warns the developer when some code evaluates an EL expression that mutates a bean to indicate that the code did not subsequently call the ControllerContext.markScopeDirty() method. This audit rule fire only when the adf-scope-ha-support flag in the adf-config.xml file is set to true.
ADF Page Flows - Managed Bean Class Not Serializable warns the developer that a managed bean has a non-serializable class defined in viewScope, pageFlowScope, or sessionScope. This audit rule fire only when the adf-scope-ha-support flag in the adf-config.xml file is set to true.
You can modify the High Availability audit rule settings using the Preference dialog in JDeveloper. From the JDeveloper toolbar, choose Tools - Preferences, under Audit - Profiles expand ADF Controller Configuration or ADF Pages Flows and make the desired audit rule selections.
You can also trigger the audit by choosing Build - Audit project.jpr from the JDeveloper toolbar.
Fusion web applications are deployed when the managed server is first started. Use the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console first to check that all application deployments were successful:
Click Deployments in the left hand pane. The right hand pane shows the application deployments and their status. The state of all applications, assuming all the servers are running, should be ACTIVE.
If an application deployment has failed, the server logs may provide some indication of why the application was not deployed successfully. The server logs are located in the DOMAIN_HOME/servers/server_name/logs directory. Common issues include:
Unavailability of external resources, such as database resources. Examine the error, fix it, and attempt to redeploy the application.
The appropriate applications or libraries are not targeted correctly to the right managed server or Cluster.
State Replication is most prominent in failover scenarios. A user working on one server may discover that, upon failover:
Windows may close or the state might reset.
Screens may require a reset.
The application may redirect to the logon screen.
To diagnose and troubleshoot state replication issues.
Confirm that this is not a known replication issue.
See Section 6.1.2.2, "Oracle ADF Failover and Expected Behavior" for possible expected behaviors. Before proceeding to further diagnose the issue, first confirm that the failover behavior is not an expected behavior.
Check load balancer settings.
For replication and failover to function correctly, the load balancer must be configured with the appropriate persistence settings. For more details on configuring Hardware Load Balancers for Oracle WebLogic Server, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Using Clusters for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Check the cluster status.
Replication occurs within the context of a cluster. For failover to be successful, there must be at least one other healthy member of the cluster available. You can check cluster status in one of two ways:
Check the cluster status using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - In the Left-hand pane, click on Servers. Verify the state of all servers in the cluster.
Check the cluster status using weblogic.Admin utility The weblogic.Admin command can be used to query the state of all servers in a specific cluster. For example:
$ java weblogic.Admin -url Adminhost:7001 -username <username> -password <password> CLUSTERSTATE -clustername Spaces_Cluster
This example returns:
There are 2 server(s) in cluster: Spaces_Cluster The alive servers and their respective states are listed below: Application Server---RUNNING Managed Server---RUNNING
Check cluster communications.
Although Cluster members may all be running, there may be communication issues which prevent them from communicating replication information to each other. There are two types of cluster communication configurations. Troubleshooting depends on the cluster type:
Checking Unicast cluster communications - For Unicast clusters, managed servers must be able to access each other's hosts and each other's default listening port.
Ensure that all individual managed servers have their Listen Address set correctly. You can find this setting by selecting Configuration, General for each managed server.
Checking Multicast cluster communications - For multicast clusters, servers must be able to intercept the same multicast traffic. Ensure that multicast is configured correctly by running the WebLogic utility utils.MulticastTest on each machine. For example:
$ java utils.MulticastTest -H
Confirm Oracle WebLogic Server application configuration.
Oracle WebLogic Server is not configured by default for failover. In-memory replication takes place only with the proper setting in the weblogic.xml file:
<session-descriptor> <persistent-store-type>replicated_if_clustered</persistent-store-type> </session-descriptor>
A persistent-store-type of replicated is also acceptable. This setting can be made in JDeveloper, as described in Section 6.1.3.2, "Configuring weblogic.xml."
Confirm Oracle ADF Business Components configuration.
Oracle ADF is not configured by default for failover. Failover is supported only with the proper setting in the ADF Business Components configuration file (bc4j.xcfg):
<AppModuleConfig ... <AM-Pooling jbo.dofailover="true"/> </AppModuleConfig>
This setting is made in JDeveloper through the Edit Business Components Configuration dialog, as described in Section 6.1.3.1, "Configuring Application Modules."
Confirm Oracle WebLogic Server connection pool parameter.
Set an appropriate value for the weblogic-application.xml deployment descriptor parameter inactive-connection-timeout-seconds on the element <connection-check-params> pool-params.
When enabling application module state passivation, a failure can occur when Oracle WebLogic Server is configured to forcibly release connections back into the pool. The failure creates an exception "Connection has already been closed" that gets saved to the server log. The user interface does not show this exception.
Set inactive-connection-timeout-seconds to several minutes. In most cases, this setting avoids forcing the inactive connection timeout and passivation failure. Adjust the setting as needed for your environment.
Confirm Oracle ADF Controller configuration.
Oracle ADF is not configured by default to replicate changes to ADF objects in ADF memory scopes. ADF object replication is supported only with the proper setting in the ADF application-level configuration file (adf-config.xml):
<adfc:adf-controller-config> <adfc:adf-scope-ha-support>true</adfc:adf-scope-ha-support> </adfc:adf-controller-config>
This setting is made in JDeveloper through the source editor. See Section 6.1.3.1, "Configuring Application Modules."
Check default logger messages.
By default the ADF log shows high-level messages (INFO level). The default logging often reports problems with serialization and replication without the need to enable more detailed log messages. For more information about the log, see Section 6.1.1.4, "Oracle ADF Log File."
Enable log messages for ADF high availability applications.
Configure the ADF logger to output runtime messages for high availability. By default the ADF log shows high-level messages (INFO level). You enable high availability diagnostics for ADF Controller by setting the logging level in Fusion Middleware Control to FINE.
When enabled, the logger outputs a warning if the adfc:adf-scope-ha-support setting in the adf-config.xml file is not set. For more information about the ADF logger, see Section 6.1.1.4, "Oracle ADF Log File."
Enable debug.
Check the server logs for any unusual messages on managed server startup. In particular, if the managed server is unable to locate other members of the cluster. The server logs are located in the DOMAIN_HOME/servers/SERVER_NAME/logs directory.
For further debugging, enable the flags DebugCluster, DebugClusterAnnouncements, DebugFailOver, DebugReplication, and DebugReplicationDetails. Each flag can be enabled with the weblogic.Admin utility:
$ java weblogic.Admin -url Adminhost:7001 -username <username> -password <password> SET -type ServerDebug -property DebugCluster true
Enable component state serialization checking.
Enable server checking to ensure no unserializable state content on session attributes is detected. This check is disabled by default to reduce runtime overhead. Serialization checking is supported by the Java server system property org.apache.myfaces.trinidad.CHECK_STATE_SERIALIZATION.
Table 6-1 shows the options you can use with the property. Use commas to delimit the options.
Table 6-1 CHECK_STATE_SERIALIZATION Options
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
|
tree |
Checks whether the entire component tree is serializable. This is the fastest component check. Most testing should be performed with this flag enabled. |
|
component |
Checks each component individually for serializability. This option is much slower than "tree." It is typically turned on only after testing with "tree" reports an error. This option narrows down the problematic component. |
|
property |
Checks each component attribute individually for serializability. This is slower than "component" and narrows down the specific problematic component attribute after a failure has been detected in the "tree" or "component" modes. |
|
session |
Checks that all attributes in the JSF Session Map that are marked as Serializable are serializable. |
|
application |
Checks that all attributes in the JSF Application Map that are marked as Serializable are serializable. |
|
beans |
Checks that any serializable object in the appropriate map has been marked as dirty if the serializable content of the object changes during the request. |
|
all |
Checks everything. |
For high availability testing, start off by validating that the Session and JSF state is serializable by launching the application server with the system property:
-Dorg.apache.myfaces.trinidad.CHECK_STATE_SERIALIZATION=session,tree
Add the beans option to check that any serializable object in the appropriate map has been marked as dirty if the serialized content of the object has changed during the request:
-Dorg.apache.myfaces.trinidad.CHECK_STATE_SERIALIZATION=session,tree,beans
If a JSF state serialization failure is detected, relaunch the application server with the system property to enable component and property flags and rerun the test:
-Dorg.apache.myfaces.trinidad.CHECK_STATE_SERIALIZATION=all
These are Java system properties and you must specify them when you start the application server.
This section describes how to configure an example Oracle ADF high availability deployment.
Note:
Oracle strongly recommends reading the release notes for any additional installation and deployment considerations prior to starting the setup process.
This list describes the directories and variables used in this section:
ORACLE_BASE: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the base directory under which Oracle products are installed.
MW_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the location where Oracle Fusion Middleware resides.
WL_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path contains installed files necessary to host a WebLogic Server.
ORACLE_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the location where Oracle SOA Suite is installed.
ORACLE_COMMON_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the Oracle home that contains the binary and library files required for the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control and Java Required Files (JRF).
DOMAIN directory: This directory path refers to the location where the Oracle WebLogic domain information (configuration artifacts) is stored.
ORACLE_INSTANCE: An Oracle instance contains one or more system components, such as Oracle Web Cache, Oracle HTTP Server, or Oracle Internet Directory. An Oracle instance directory contains updateable files, such as configuration files, log files, and temporary files.
For consistency, the values used and recommended for directories are:
ORACLE_BASE: /u01/app/oracle
MW_HOME (application tier): ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw
WL_HOME: MW_HOME/wlserver_10.3
ORACLE_HOME: MW_HOME/adf
This step is required only if your ADF application needs to use any of schemas that are part of Oracle Fusion Middleware. Typically, this is done if the ADF application uses MDS repository, in which case you must install the 11g (11.1.1) Oracle Fusion Middleware Metadata Store into a Real Application Clusters (Oracle RAC) database before you install Oracle Fusion Middleware. Oracle Fusion Middleware provides a tool, the Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility (RCU), to create the component schemas in an existing database.
Use the latest version of RCU to install the 11g (11.1.1) Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository into a Real Application Clusters database.
See Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility User's Guide for more information about obtaining and running the latest version of RCU.
To check if your database is certified or to see all certified databases, refer to the "Certified Databases" section in the Certification Document:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/software/products/ias/files/fusion_certification.html
To install the required metadata for Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g:
Start RCU using the following command:
RCU_HOME/bin/rcu &
In the Welcome screen, click Next.
In the Create Repository screen, select Create to load component schemas into a database, and click Next.
In the Database Connection Details screen, enter connection information for your database:
Database Type: Select Oracle Database
Host Name: Enter the name of the node that is running the database. For an Oracle RAC database, specify the VIP name or one of the node names as the hostname: ADFDBHOST1VIRTUAL.
Port: The port number for the database: 1521
Service Name: Enter the service name of the database: adfha.mycompany.com
Username: SYS
Password: Enter the password of the SYS user.
Role: SYSDBA
Click Next.
If you see the following message, click Ignore or Stop:
The database you are connecting is with non-UTF8 charset, if you are going to use this database for multilingual support, you may have data loss. If you are not using for multilingual support you can continue, otherwise, Oracle strongly recommends using a UTF-8 database.
In the Select Components screen, select Create a New Prefix and enter a prefix to use for the database schemas, for example, ADFHA.
Write down the schema names so they are available in later procedures.
Select the following schemas:
AS Common Schemas
Metadata Services
Click Next.
In the Schema Passwords screen, enter passwords for the main and additional (auxiliary) schema users and click Next.
In the Map Tablespaces screen, choose tablespaces for the selected components and click Next.
In the Summary screen, click Create.
In the Completion Summary screen, click Close.
See the Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility User's Guide for more information about installing RCU.
To install Oracle HTTP Server on WEBHOST1:
Verify that the servers meet the following requirements:
The system, patch, kernel, and other requirements meet the requirements specified in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility User's Guide.
This example uses port 7777. If you choose port 7777, ensure that no services on the nodes use it by running the following command:
UNIX: netstat -an | grep LISTEN | grep ":7777" Windows: netstat -an | findstr "LISTEN" | findstr ":7777"
If port 7777 is in use, choose another port or make it available.
On UNIX platforms, if the /etc/oraInst.loc or /var/opt/oracle/oraInst.loc file exists, check that its contents are correct. Specifically, check that the inventory directory is correct and that you have write permissions for that directory.
If the /etc/oraInst.loc file does not exist, skip this step.
Start Oracle Universal Installer for Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Webtier Utilities CD installation as follows:
For UNIX, run this command: ./runInstaller
For Windows, double-click setup.exe.
In the Specify Inventory Directory screen, enter the location for the inventory and the user group, and click OK.
Run the root privileged actions that the dialog indicates and click OK.
In the Welcome screen, click Next.
In the Select Installation Type screen, select Install and Configure, and click Next.
In the Prerequisite Checks screen, ensure that all the prerequisites are met and click Next.
In the Specify Installation Location screen, set the location to:
/u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.1/ohs_1
Click Next.
In the Configure Components screen:
Select Oracle HTTP Server.
Do not select Associate Selected Components with WebLogic Domain.
Click Next.
In the Specify Component Details screen, enter the following values:
Instance Home Location:
/u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.1/ohs_1/instances/ohs_instance1
Instance Name: ohs_instance1
OHS Component Name: ohs1
Click Next.
In the Specify Webtier Port Details screen:
Select Specify Custom Ports. If you specify a custom port, select Specify Ports using Configuration File and then use the Browse function to select the file.
Enter Oracle HTTP Server port. For example, enter 7777.
Click Next.
Note:
For more information about setting ports, refer to the Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle SOA Suite and Oracle Business Process Management Suite.
In the Configuration Summary screen, ensure that the selections are correct. Click Install.
In the Installation Progress screen:
For UNIX systems, a dialog box appears prompting you to run the oracleRoot.sh script. Open a command window and run the script, following the prompts.
Click Next.
In the Configuration screen, several configuration assistants are started in succession. When the configuration assistants are finished, the Configuration Completed screen appears.
In the Configuration Completed screen, click Finish to exit.
Use the information in these sections to install Oracle Fusion Middleware components:
See "Understanding Your Installation Starting Point" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Planning Guide for the version of Oracle WebLogic Server to use with the latest version of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
To install Oracle WebLogic Server on all nodes in the application tier:
On UNIX platforms, if the /etc/oraInst.loc or /var/opt/oracle/oraInst.loc file exists, check that its contents are correct. Specifically, check that the inventory directory is correct and that you have write permissions for that directory.
If the /etc/oraInst.loc file does not exist, skip this step.
Start the Oracle WebLogic Server installer.
In the Welcome screen, click Next.
In the Choose Middleware Home Directory screen:
Select Create a New Middleware Home.
For the Middleware Home Directory field, enter:
ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw
Click Next.
In the Register for Security Updates screen, enter your contact information for security update notifications, and click Next.
In the Choose Install Type screen, select Custom, and click Next.
In the JDK Selection screen, select only Oracle JRockit 1.6.0_<version> SDK. Click Next.
In the Choose Product Installation Directories screen, accept the following directory:
ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/wlserver_10.3
Click Next.
In the Application Server screen, select WebLogic. Click Next.
In the Installation Summary screen, click Next.
In the Installation Complete screen, deselect Run QuickStart, and click Done.
To install Oracle Fusion Middleware for Oracle ADF, use the Application Developer Install and perform the following on all the nodes in the application tier:
Start the Oracle Fusion Middleware for Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Application Developer installer:
On UNIX (Linux used in this example): APPHOST1> runInstaller On Windows: APPHOST1> setup.exe
When Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Application Developer installer prompts you for a JRE/JDK location enter the Oracle SDK location created in the Oracle WebLogic Server installation in Section 6.2.4.1, "Installing Oracle WebLogic Server," for example:
ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/jrockit_160_<version>
In the Welcome screen, click Next.
In the Prerequisite Check screen, verify that the checks complete successfully, and click Next.
In the Specify Installation Location screen:
For Middleware Home, enter: ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw
For Oracle Home Directory, enter the directory you want to use, for example: adf
Click Next.
In the Application Server screen, select WebLogic.
In the Installation Summary screen, click Install.
In the Installation Complete screen, click Finish.
Note:
Before you run the Configuration Wizard by following the instructions in Section 6.2.6, "Running the Configuration Wizard on APPHOST1 to Create the WebLogic Server ADF Domain," ensure that you applied the latest Oracle Fusion Middleware patch set and other known patches to your Middleware Home, so that you have the latest version of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
See "Understanding Your Installation Starting Point" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Planning Guide for the steps you must perform to get the latest version of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
For information about configuring Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Server, see Chapter 12, "Active-Passive Topologies for Oracle Fusion Middleware High Availability."
Run the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard from the adf directory in the Middleware home to create a domain containing the Administration Server and Oracle components.
Start Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard from the MW_HOME/common/bin directory using the following command:
APPHOST1> ./config.sh
In the Welcome screen, select Create a New WebLogic Domain and click Next.
In the Select Domain Source screen, select Generate a domain configured automatically to support the following products, and select the following products:
Oracle Enterprise Manager - 11.1.1.0
Oracle JRF - 11.1.1.0
Click Next.
Enter the Domain Name, Domain Location, and Application Location and click Next.
In the Configure Administrator Username and Password screen, enter the username and password to be used for the domain's administrator, and click Next.
In the Configure Server Start Mode and JDK screen, make the following selections:
WebLogic Domain Startup Mode: select Production Mode
JDK Selection: select Oracle JRockit 1.6.0_<version>
Click Next.
In the Select Optional Configuration screen, select the following:
Deployments and Services
Managed Servers, Clusters and Machines
Administration Server
Click Next.
In the Customize Server and Cluster Configuration screen, select Yes, and click Next.
In the Configure the Administration Server screen, enter the following values:
Name: AdminServer
Listen Address: APPHOST1
Listen Port: 7001
SSL listen port: NA
SSL enabled: Leave unchecked
Click Next.
In the Configure Managed Servers screen, add the following managed servers:
| Managed Server Name | Listen Address | Listen Port | SSL Listen Port | SSL Enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WLS_ADF1 |
Hostname of APPHOST1 |
8889 |
NA |
unchecked |
|
WLS_ADF2 |
Hostname of APPHOST2 |
8889 |
NA |
unchecked |
Click Next.
In the Configure Clusters screen, add the following cluster:
Name: ADF_CLUSTER
Cluster Messaging Mode: unicast
Cluster Address Enabled: Leave blank
Click Next.
In the Assign Servers to Clusters screen, assign the following servers to the Cluster:
ADF_CLUSTER:
WLS_ADF1
WLS_ADF2
Click Next.
In the Configure Machines screen:
Delete the LocalMachine that appears by default.
Click the Unix Machine tab, and add the following machines:
| Name | Node Manager Listen Address |
|---|---|
|
APPHOST1 |
Hostname of APPHOST1 |
|
APPHOST2 |
Hostname of APPHOST2 |
Click Next.
In the Assign Servers to Machines screen, assign servers to machines as follows:
APPHOST1: AdminServer, WLS_ADF1
APPHOST2: WLS_ADF2
In the Target Deployment to Clusters or Servers screen, click Next. In the Target Services to Clusters or Servers screen, click Next.
In the Configuration Summary screen, click Create.
In the Creating Domain screen, click Done.
This is an optional step for enabling the Administration Server to start without prompting you for the administrator username and password. Create a boot.properties file for the Administration Server and for the managed servers on APPHOST1.
For the Administration Server, follow these steps:
Create the following directory:
APPHOST1> mkdir -p MW_HOME/wls/user_projects/domains/adfdomain/servers/AdminServer/security
Use a text editor to create a file named boot.properties in the directory created in the previous step, and enter the following lines in the file:
username=adminUser password=adminUserPassword
For example:
username=weblogic password=weblogic
Note:
When you start the Administration Server or Managed Server, username and password entries in the file are encrypted.
For security reasons, minimize the time the entries in the file are left unencrypted. After you edit the file, start the server as soon as possible in order for the entries to be encrypted.
For the WLS_ADF Managed Servers, complete the following:
Copy the file you created for the Administration Server to all servers.
This section describes procedures for starting the system in APPHOST1.
To start the Administration Server on APPHOST1 run the following commands:
APPHOST1> cd ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/user_projects/domains/adfdomain/bin
APPHOST1> ./startWebLogic.sh
To verify that the Administration Server is properly configured:
In a Web browser, go to http://VIP1:7001/console.
Log in as the administrator.
Verify that the WLS_ADF1 and WLS_ADF2 managed servers are listed.
Verify that the ADF_Cluster cluster is listed.
Verify that you can access Enterprise Manager at http://VIP1:7001/em.
You must perform this procedure if you have not set up SSL communication between the Administration Server and the Node Manager. If SSL is not set up, you receive an error message unless you disable hostname verification.
You can re-enable hostname verification when you have set up SSL communication between the Administration Server and the Node Manager.
To disable hostname verification on APPHOST1:
In Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, select Administration Server, SSL and then Advanced.
In the Change Center click Lock & Edit.
When prompted, save the changes and activate them.
Set Hostname Verification to None.
Select WLS_ADF1, SSL and then Advanced.
Set Hostname Verification to None.
Restart the Administration Server and the WLS_ADF1 Managed Server.
To disable hostname verification on APPHOST2:
In Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, select WLS_ADF2, SSL, and then Advanced.
Set Hostname Verification to None.
Restart the Administration Server and the WLS_ADF2 Managed Server.
To start Node Manager on APPHOST1:
Run the setNMProps.sh script located in the ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin directory to set the StartScriptEnabled property to true before starting Node Manager:
OAHOST1> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin APPHOST1> ./setNMProps.sh
Note:
You must use the StartScriptEnabled=true property to avoid class loading failures and other problems.
Start Node Manager:
APPHOST1> cd WL_HOME/server/bin
APPHOST1> ./startNodeManager.sh
Repeat the procedures for installing WebLogic Server and Oracle ADF for APPHOST2, start with Section 6.2.3, "Installing Oracle HTTP Server on WEBHOST1." The directory paths for binary files and domains used when installing new nodes must be exactly the same as those used for the first node. If these paths and domains are not exactly the same as those used for the first node, failover does not occur.
To propagate the domain configuration to APPHOST2 using pack/unpack utilities:
Run the following pack command on APPHOST1 to create a template pack:
APPHOST1> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin APPHOST1> ./pack.sh -managed=true -domain=ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/user_projects/domains/adfdomain/ -template=adfdomaintemplate.jar -template_name=adf_domain_template
Copy the template file created in the previous step from APPHOST1 to APPHOST2. For example, on a Unix platform:
APPHOST1> scp adfdomaintemplate.jar user@node2:ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin
Run the unpack command on APPHOST2 to unpack the propagated template:
APPHOST2> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin APPHOST2> ./unpack.sh -domain=ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/user_projects/domains/adfdomain/ -template=adfdomaintemplate.jar
To create a boot.properties file for the Administration Server and for the Managed Servers on APPHOST2:
Create the following directories:
APPHOST1> mkdir -p MW_HOME/wls/user_projects/domains/adfdomain/servers/WLS_ADF2 APPHOST2> mkdir -p MW_HOME/wls/user_projects/domains/adfdomain/servers/WLS_ADF2/security
Use a text editor to create a file named boot.properties in the directory created in the previous step, and enter the following lines in the file:
username=adminUser password=adminUserPassword
For example:
username=weblogic password=weblogic
Note:
When you start the Administration Server or Managed Server, the username and password entries in the file are encrypted.
For security reasons, minimize the time the entries in the file are left unencrypted. After you edit the file, start the server as soon as possible in order for the entries to be encrypted.
To start the Node Manager on APPHOST2, repeat the steps from Section 6.2.7.4, "Starting Node Manager on APPHOST1" on APPHOST2.
Use the procedures in this section to configure your application for replication.
Clustering Requirement
The application must be deployed to an Oracle WebLogic Cluster. This automatically establishes a replication channel for the multiple instances of the application.
Note:
In a Unicast cluster, the default replication channel is configured using the Listen address of each managed server. Therefore, the Listen address should be configured to be a specific IP address or hostname, instead of being configured to listen on Any.
Oracle ADF Replication
It is essential that Oracle ADF is configured properly. The following tag should be in the adf-config.xml file, one of the Application Resources, for a stateful application:
<adfc:adf-controller-config><adfc:adf-scope-ha-support>true</adfc:adf-scope-ha-support></adfc:adf-controller-config>
Applications must also have replication enabled. Oracle WebLogic Server enables several types of persistent stores for replication. For more information on persistent stores, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Using Clusters for Oracle WebLogic Server manual.
The ADF application can be enabled by for this by default with the following setting in the weblogic.xml file:
<session-descriptor> <persistent-store-type>replicated_if_clustered</persistent-store-type> </session-descriptor>
The replicated_if_clustered setting disables replication for standalone application environments, and uses in-memory replication within a cluster environment.
Ensure that any custom application is configured for in-memory replication.
After the cluster is set up, you can deploy the ADF application. Be aware of the following:
Deploy the ADF application to an EAR file using the Administration Server Console.
Ensure that the deployment is to a cluster.
If your application uses MDS, register the MDS with the domain using the instructions in the "Registering a Database-Based MDS Repository" section in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide manual.
Enable Oracle HTTP Server to route to the Administration Server that contains WebCenter Portal managed servers by setting the WebLogicCluster parameter to the list of nodes in the cluster. Follow these steps:
Add the following lines to the OHS_HOME/instances/ohs_instance1/config/OHS/ohs1/mod_wl_ohs.conf file:
# Spaces
<Location /applicationMountpoint>
WebLogicCluster apphost1.com:8888,apphost2.com:8889
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
Restart Oracle HTTP Server on WEBHOST1:
WEBHOST1> OHS_HOME/instances/ohs_instance1/bin/opmnctl restartproc ias-component=OHS_COMPONENT1
Verify the URLs to ensure that appropriate routing and failover is working from the HTTP Server to WebCenter Portal cluster. Follow these steps:
Start WC_Spaces1, WC_Spaces2, WC_Collaboration1, WC_Collaboration2, WC_Utilities1, WC_Utilities2, WC_Portlet1, and WC_Portlet2 from the WebLogic Server Administration Console as follows:
Access the Administration Console at the following URL:
http://APPHOST1/console
Click on one of the Managed Servers, for example, WC_Spaces1.
Select the Control tab.
Select Start to start the Managed Server.
Repeat the previous steps for each Managed Server.
Verify direct access to the Managed Servers using the following URLs:
apphost1:8888/applicationMountpoint apphost2:8888/applicationMountpoint apphost1:8889/applicationMountpoint apphost2:8889/applicationMountpoint
While WLS_ADF2 is running, stop WLS_ADF1 from Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Access the following URL and verify the appropriate functionality:
WebHost1:7777/applicationMountpoint
Start WLS_ADF1 from the WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Stop WLS_ADF2.
Access the following URL and verify the appropriate functionality:
WebHost2:7777/applicationMountpoint
You can scale out and scale up an Oracle ADF topology. When you scale up the topology, you add new managed servers to nodes that are already running one or more managed servers. When you scale out the topology, you add new managed servers to new nodes.
In this case, you already have a node that runs a managed server configured with Oracle ADF. The node contains a Middleware home in shared storage.
You can use the existing installations (Middleware home and domain directories) for creating new servers. There is no need to install Oracle Fusion Middleware binaries in a new location or to run pack and unpack.
To scale up the topology:
Using the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, clone WLS_ADF1 into a new managed server. The source managed server to clone should be one that already exists on the node where you want to run the new managed server.
To clone a managed server:
Select Environment > Servers from the Administration Console.
Select the managed server that you want to clone.
Select Clone.
Name the new managed server WLS_ADFn, where n is a number to identify the new managed server.
For the listen address, assign the hostname or IP to use for this new managed server.
Ensure that the port number for this managed server is available on this node.
Reconfigure the Oracle HTTP Server module with the new member in the cluster. See Section 6.2.9.5, "Configuring Oracle HTTP Server for the Administration Server and WebCenter Portal Managed Servers."
In scaling out your topology, you add new managed servers configured with Oracle ADF applications to new nodes.
Before performing the steps in this section, check that you meet these requirements:
In your topology, there are existing nodes running managed servers configured with ADF applications.
ADF managed servers are clustered and the new managed server will also be part of that cluster.
The new node can access the existing home directories for WebLogic Server. You use the existing installations in shared storage for creating a new managed server. There is no need to install WebLogic Server binaries in a new location, although you must run pack and unpack to create a managed server domain.
To scale out the topology:
On the new node, mount the existing Middleware home, and ensure that the new node has access to this directory, just like the rest of the nodes in the domain.
To update the Middleware home list, create (or edit, if another WebLogic installation exists in the node) the MW_HOME/bea/beahomelist file and add ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw to it.
Log into the Oracle WebLogic Administration Console.
Create a new machine for the new node that will be used, and add the machine to the domain.
Update the machine's Node Manager's address to map the IP of the node that is being used for scale out.
Use the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console to clone WLS_ADF1 into a new managed server. Name it WLS_ADFn, where n is a number and assign it to the new machine.
For the listen address, assign the hostname or IP to use for the new managed server.
To set the managed server listen address:
Log into the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
In the Change Center, click Lock & Edit.
Expand the Environment node in the Domain Structure window.
Click Servers.
Select the managed server whose listen address you want to update in the Names column of the table.
Set the Listen Address to APPHOSTn where APPHOSTn is the DNS name of your new machine.
Click Save.
Save and activate the changes.
The changes do not take effect until the managed server restarts.
Run the pack command on APPHOST1 to create a template pack as follows:
APPHOST1> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin APPHOST1> ./pack.sh -managed=true -domain=MW_HOME/user_projects/domains/ adfdomain/ -template=adfdomaintemplateScale.jar -template_name=adf_domain_templateScale
Run the following command on APPHOST1 to copy the template file created to APPHOSTn:
APPHOST1> scp adfdomaintemplateScale.jar oracle@APPHOSTN:/
ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin
Run the unpack command on APPHOSTn to unpack the template in the managed server domain directory as follows:
APPHOSTn> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin APPHOSTN> ./unpack.sh -domain=ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/user_projects/domains/adfdomain/ -template=adfdomaintemplateScale.jar
Start the Node Manager on the new node. To start the Node Manager, use the installation in shared storage from the existing nodes, and start Node Manager by passing the hostname of the new node as a parameter as follows:
APPHOSTn> WL_HOME/server/bin/startNodeManager <new_node_ip>
Start and test the new managed server from the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console:
Shut down all the existing managed servers in the cluster.
Ensure that the newly created managed server is running.
Access the application on the newly created managed server. The application should be functional.
The information in this section guides you through the issues and considerations necessary for designing a WebCenter Portal high availability cluster.
WebCenter Portal combines the standards-based, declarative development of Java Server Faces (JSF), the flexibility and power of portals, and a set of integrated Web 2.0 services.
WebCenter Portal includes the following components.
Oracle WebCenter Portal: Spaces offers a single, integrated, Web-based environment for social networking, communication, collaboration, and personal productivity through a robust set of services and applications.
The Spaces application is built using JSF, Oracle ADF, Oracle WebCenter Portal: Framework, Oracle WebCenter Portal Services, and Composer. The Spaces application provides:
A browser-based platform for creating enterprise portals, multiple sites and communities.
A Home space for each user, providing a private work area for storing personal content, keeping notes, viewing and responding to business process assignments, emailing, and so on.
Threaded discussions, blogs, wikis, worklists, announcements, RSS, recent activities, search, and more.
Oracle WebCenter Portlets Framework supports deployment and execution of both standards-based portlets (JSR 168, WSRP 1.0 and 2.0), and traditional Oracle PDK-Java based portlets. WebCenter Portal provides several out-of-the-box producers, such as OmniPortlet, Web Clipping, and WSRP Tools.
Oracle WebCenter Portal:Framework provides the following capabilities:
Run-time application customization (you can make in-place changes to WebCenter Portal applications using Composer without re-deploying the application)
Support for JSR-168 and JSR-286 standards-based WSRP portlets, and PDK-Java portlets
Content integration through JCR (JSR170), to content repositories such as Oracle WebCenter Content Server, Oracle Portal, and file systems
Oracle JSF Portlet Bridge, which lets you expose JSF pages and Oracle ADF task flows as standards-based portlets
Oracle WebCenter Portal's Discussions server provides the ability to integrate discussion forums and announcements into your applications.
Oracle WebCenter Portal's Analytics Collector provides users with the ability to view reports on the various user activities within WebCenter Portal applications, for example:
Logins
Page views
Portlet views
Document views
Search metrics
Response times
Oracle WebCenter Portal's Activity Graph service provides users with the ability to analyze the statistics collected by Oracle WebCenter Portal's Analytics. The output of an Activity Graph analysis is the collected scores for objects and users, which are used to give recommendations. The scores are stored in the Activities database.
Oracle WebCenter Portal's Personalization Server is a lightweight service that client applications access by means of RESTful web service. The Personalization server enables you to deliver application content to targeted users based on selected criteria.
WebCenter Portal applications can also integrate with WebCenter Portal: Services. See the table Services Data Repositories in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Portal. This guide also describes how to configure WebCenter Portal services.
WebCenter Portal installation creates a WebCenter directory under the Middleware home directory. The installation creates a WebCenter domain (wc_domain), which contains the Administration Server and four WebLogic Managed Servers: WC_Spaces1 (which hosts the Spaces application), WC_Portlet (which hosts several out-of-the-box portlet producers), WC_Collaboration1 (which host the Discussions server), WC_Utilities1 (which hosts Analytics, Activity Graph, and the Personalization server), and any other WebCenter Portal services that you choose to integrate.
WebCenter Portal applications that you build using WebCenter Portal: Framework are referred to as Framework applications. When you create additional custom managed servers, the appropriate libraries provision them so that they can draw on the same external resources as WebCenter Portal: Spaces. For more information about managed servers, see “Understanding Oracle Fusion Middleware Concepts” in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide. Figure 6-4 shows a basic single-node WebCenter Portal architecture.
Figure 6-4 Basic Single-Node WebCenter Portal Architecture
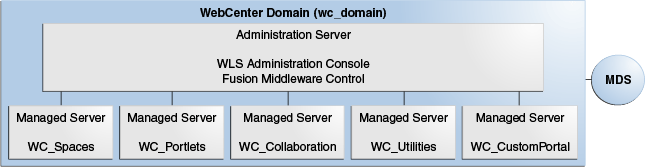
See WebCenter Portal State and Configuration Persistence in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Portal.
See WebCenter Portal Log File Locations in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Portal.
An Oracle WebLogic cluster provides high availability for applications. When one member of the cluster is unavailable, another member of the cluster handles the request.
You can deploy each of the managed servers in a WebCenter Portal deployment as a cluster, with different cluster members on the same node or on different nodes. In Figure 6-5, either cluster member can serve all requests sent to the cluster equally.
Figure 6-5 WebCenter Portal Two-Node High Availability Architecture
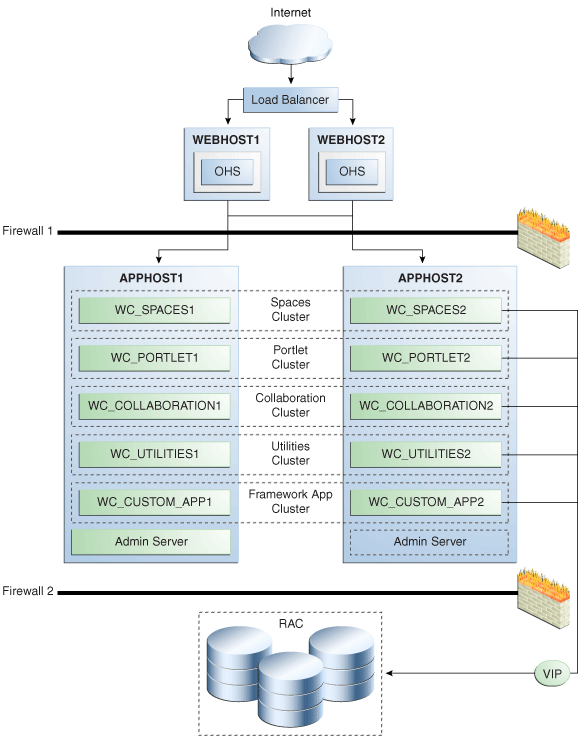
The following sections contain more information on the runtime and configuration of WebCenter Portal clusters.
During WebCenter Portal installation, the managed servers are provisioned with system libraries and ADF libraries. Table 6-2 lists the managed servers and the applications which run on them.
Table 6-2 WebCenter Portal's Managed Servers and Applications
| Managed Server | Installed Application(s) |
|---|---|
|
WC_Spaces |
Spaces Spaces Online Help |
|
WC_Portlet |
OmniPortlet and Web Clipping WSRP Tools Pagelet Producer WebCenter Services Producer |
|
WC_Collaboration |
Discussions Server |
|
WC_Utilities |
Analytics Collector Activity Graph Engines Personalization Services |
When you start a managed server, applications and libraries start in the following order:
Oracle System libraries, known as the JRF libraries.
Oracle ADF libraries.
Instrumentation applications such as Oracle DMS.
WebCenter Portal applications.
The startup order is also the order of dependency. If a dependent component does not deploy successfully, a later component may not function correctly. WebCenter Portal application startup does not depend on the availability of external services such as a discussions server, or other back-end servers.
For a WebCenter Portal cluster deployment such as the one shown in Figure 6-5, follow these rules for the targeting of applications, libraries, and system resources:
Target applications and libraries to the cluster target. For example, target the Spaces application to the Spaces cluster.
Target JDBC resources to the cluster target.
WebCenter Portal applications and the WebCenter Portal Discussions server deploy as Oracle WebLogic stage applications. During the initial deployment of each application, the deployment files are received from the Administration Server and deployed locally.
Cluster Communications
By default, each WebCenter Portal cluster is configured as unicast. To configure your WebCenter Portal cluster for multicast, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Using Clusters for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Analytics in WebCenter Portal consists of individual Analytics Collectors that receive requests from analytics clients such as the Spaces application.
This section describes how an Analytics Collector cluster works.
In a clustered environment, producers (clients of the collector) and collectors are configured with a cluster-specific channel name. Each collector periodically broadcasts a heartbeat with its location to the cluster-specific channel. The producer listens to the channel for these collector heartbeats and, when it hears one, adds the collector to its list of known collectors. When the producer needs to send an event, it uses a round robin algorithm to select a collector from its list and sends the event to that collector. If a collector stops (intentionally or due to failure), it stops broadcasting a heartbeat. When the producer stops hearing the heartbeat it removes the collector from its list and stops sending events to that collector. If the producer does not hear any collector heartbeats, it does not send any events.
WebCenter Portal Analytics uses UDP and multicast on a configured set of ports to communicate with its clients. For a single node setup, the client is configured with a WLST command that has the server host/port location and transmits all events to this location via UDP. For a multiple node setup, the server is configured to broadcast (via UDP multicast) the location(s) of the various servers running on the cluster; the client is configured with the same WLST command, so it receives the server locations and keeps the list of available servers (which persists in memory.) If a client does not receive a periodic heartbeat from a server, it removes that server from its list of known servers and stops sending events to it.
Oracle recommends that you configure Analytics Collectors as unicast, forming a 1-1 relationship with the WebCenter Portal application client.
WebCenter Portal relies on Oracle ADF, which has several stateful components. Oracle WebCenter itself is also a stateful application. Therefore, you must configure state replication in cluster scenarios.
For more information on how state replication works in Oracle WebLogic Server, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Using Clusters for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Oracle WebLogic Server supports two types of state replication:
In-memory replication - Using in-memory replication, Oracle WebLogic Server copies a session state from one server instance to another. The primary server creates a primary session state on the server to which the client first connects, and a secondary replica on another WebLogic Server instance in the cluster. The replica is kept up to date so that it may be used if the server that hosts the servlet fails.
JDBC-based persistence - In JDBC-based persistence, Oracle WebLogic Server maintains the HTTP session state of a servlet or JSP using file-based or database-based persistence.
To configure state replication successfully, you must configure both the environment and the application properly. For information on state replication behavior under failover conditions see Section 6.3.2.8, "Expected Behavior for Application Failover."
For more information on diagnosing state replication issues see Section 6.3.2.5, "WebCenter Portal State Replication."
WebCenter Portal applications use a distributed Java Object Cache for greater performance. Configure this cache across all WebCenter Portal clusters, with one distributed cache per cluster.
Table 6-3 lists examples of the object types that WebCenter Portal places in the Java Object Cache.
Table 6-3 WebCenter Portal Object Types for Java Object Cache
| WebCenter Portal Component | Object Cached |
|---|---|
|
Discussions service |
Topics and forums |
|
Announcements service |
Announcements |
|
Instant Messaging and Presence service |
Presence subscription lists User's presence/subscription status |
|
Worklist service |
Called Worklist items, such that cached data is used until refresh is called. |
|
Content Integration (Oracle Portal) |
JCR: type information and metadata obtained from the repository. |
|
Service Framework |
User profile. Queried usernames. |
|
Recent Activity service |
Recent activity results per user. |
|
Spaces application |
Global list of spaces and space templates in the application. List of spaces and space templates that a user can access. |
|
Page service |
List of pages in a scope. |
|
WSRP server |
Preference store values for WSRP producers. |
|
Documents service |
Provisioning and configuration checks for the Documents service configured for the Spaces application |
|
Profile management |
Lightweight user profile objects |
|
Navigation service |
List of active Navigation Model objects |
|
Portlet Consumer |
Portlet markup |
Collaboration
Collaboration services cache objects in the Java Object Cache on a per user session basis. These cached user sessions are destroyed when the HTTP session is destroyed.
Worklist
Worklist caches the called items so that unless you click refresh or trigger a fifteen-minute refresh poll, the same items appear as the user changes the sort and group by settings. Group and sort order settings also cache the display, updating when a change occurs. This is read-only data which, if not present, is fetched and stored on the cache.
Spaces Application
The list of all templates and public spaces are maintained in the Java Object Cache. All users share the list, in addition to the list of spaces and templates that a particular user can access. These are cached per user. A template created on one JVM does not show up if the template cache has been initialized in another JVM unless JOC distributes the data or an administrator in the second JVM does an explicit refresh where the cache is rebuilt.
Documents Service
The Documents service uses Java Object Cache to cache provisioning and configuration checks for document services, as applies to Spaces application configuration. For provisioning, cached objects are flagged as distributed. They are replicated by a correctly configured Java Object Cache in a high availability environment, the configuration cached state is kept locally. All cached objects are flagged to expire after one minute. Caching reduces the number of times Oracle WebCenter Content calls are made to check the state of the Oracle WebCenter Content Server, as the Spaces application repeatedly checks provisioning and configuration to control service rendering in the UI.
Portlet Consumer
The portlet consumer caches portlet mark-up in the Java Object Cache according to the cache headers in the portlet response. The cache can be expires based or validation based.
Profile Management caches the lightweight user profile objects in Java Object Cache. If particular profile data is not found, it will queried from the backend and the cache would be populated. The number of objects stored have an upper bound of 1000 and are in the Java Object Cache for one hour.
Navigation caches the Navigation Model objects in the Java Object Cache on a per user session basis. These cached objects are destroyed when the HTTP session is destroyed.
Recent Activity
The list of recent activity results are cached for each user to prevent a requery of results each time the recent activity task flow or RSS feed is viewed. The cache is automatically refreshed every fifteen minutes, or can be manually refreshed using the refresh icon in the recent activity task flow.
For Java Object Cache configuration procedures, see Section 6.4.13, "Configuring the Java Object Cache."
An Oracle WebLogic cluster provides application high availability. If one member of the cluster is unavailable, any other available member of the cluster is able to handle the request.
Session Failover Requirements
For seamless failover of a WebCenter Portal application, the application must meet the following conditions:
Must be in a cluster and at least one member of the application cluster is available to serve the request.
If stateful, state replication is configured correctly as described in Section 6.4.15, "Configuring WebCenter Portal for Replication."
If you using Oracle HTTP Server, the server configuration is configured with the WebLogicCluster directive to balance among all available application instances.
If you are using a hardware load balancer, the load balancer is:
Routing traffic to all available instances
Configured correctly with a health monitor to mark unavailable instances
Configured to support persistence of session state
If the environment is configured correctly, application users do not notice when an application instance in a cluster becomes unavailable. An example of the sequence of events during an application failover follows:
A user makes a request and is routed by a hardware load balancer to instance A of the application.
Instance A becomes unavailable because of node, process, or network failure.
The hardware load balancer marks Instance A as unavailable.
The user makes a subsequent request that is routed to instance B.
Instance B is configured as a replication partner of Instance A and has the user's session state.
The application resumes using the session state on Instance B and the user continues working without interruption.
Exceptions to Expected Behavior
For WebCenter Portal, known exceptions are as follows:
Oracle ADF Pop-ups - Open pop-ups close on failover, affecting the following components which otherwise have no exceptions:
Composer (Property Inspector, EL Builder, Task Flow parameter picker, Resource String Editor)
Save (confirmation dialog box)
Lists
Links (link deletion pop-up)
When failover occurs, you must repeat the action that leads to the pop-up to make it reappear. The specific ways in which this appears in Spaces and suggested remedies are listed in Table 6-4.
Table 6-4 WebCenter Portal Troubleshooting Scenarios
| Action Before Failover | After Failover | Suggested Remedy |
|---|---|---|
|
Go to any page and click Create Page. |
Type in a name, select a theme, and click OK. When you select the theme, the page creation pop-up closes. |
Repeat the operation. |
|
Launch Manage Pages. |
Perform any operation within the pop-up, except for closing the pop-up, for example, click Page Actions. When you perform any operation, the Manage Pages pop-up is closed. |
Repeat the operation. |
|
Launch Manage Pages, click Page Actions against a page, and then the Delete option in the menu. |
Click OK on the confirmation pop-up. Clicking OK closes the confirmation pop-up and the Manage Pages pop-up. The result of the deletion (which may have gone through) is not visible among the tabs. |
Relaunch the Manage Pages pop-up to see if the page is deleted. If not, try deleting once again. |
|
Launch Personalize Applications pop-up. Perform any operation that sends a request, other than clicking OK, for example, expand the Applications node. |
Perform any operation that sends a request, other than clicking OK, for example, expand the Applications node. When you perform any operation that sends a request to the server, the Personalize Applications pop-up is closed. |
Repeat the operation |
|
Launch Preferences. |
Switch between the Preferences tabs (General, Accounts, Messaging, Search). When you switch between the Preference tabs, the Preferences pop-up is closed. |
Repeat the operation |
|
Launch Manage Favorites. Stop the server, perform any operation other than closing the pop-up. For example, expand a folder, click Edit favorite information. |
Perform any operation other than closing the pop-up, for example, expand a folder, and click Edit favorite information. When you perform any operation, the Manage Favorites pop-up is closed. |
Relaunch the Manage Favorites pop-up to see if the operation was successful. If not, retry the operation. |
|
Choose to edit applications and create a new folder |
An MDS exception opens. |
Retry the operation |
|
Work in Composer Customization Manager. |
Oracle Composer loses the state associated with the Customization Manager |
Relaunch Customization Manager. |
|
Select a component while in Oracle Composer Source View |
Oracle Composer loses track of the component. |
Repeat the operation |
Component Specific Issues - Other issues which are specific to different components in WebCenter Portal are listed in Table 6-5.
Table 6-5 WebCenter Portal Exceptions to Expected Behavior
| WebCenter Portal Component | Exceptions to Expected Behavior |
|---|---|
|
Pagelet Producer |
Unsaved data or pending changes are not preserved on failover. If failover occurs, administrators must reestablish their administrative session and users may need to reestablish their session if the proxy is required to have a state. If SSO is configured, credentials are automatically provided, and the session is reestablished. |
|
Space Events |
When changing certain fields (start or end date/hour/minute), the event form closes when failover occurs. |
|
Portlets |
Failures are fully transparent. |
|
Lists |
Failures are fully transparent. |
|
Links |
Failures are fully transparent. |
|
Search |
In the midst of a long-running query. The results that come back are not guaranteed (note there is no "write" operation here), the user can just reissue the query. |
|
Tagging |
Failures are fully transparent. |
|
Recent Activities |
The open/close state of the tree nodes is not replicated. After after failover, the tree of results closes all of the nodes. The nodes need to be reopened. |
|
Worklist |
Failures are fully transparent. |
|
Document Manager |
When a user uploads a document and a document with the same name already exists, the user is taken to the Confirm new version screen. While on that screen, the file is stored in a temporary local location. If failover occurs at that moment, the uploaded file is lost and you must restart the upload process. |
Use Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console to check the status of the application deployments. You can also use Oracle WebLogic Server infrastructure and Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control for starting stopping, and monitoring WebCenter Portal processes.
For the Spaces application and portlet producers, all configuration data is stored in the MDS repository and portlet producers. Additional cluster deployments automatically read the latest configuration upon application startup.
For the discussions server, the configuration information should be moved over from an existing cluster server. The pack/unpack utility of Oracle WebLogic Server does this automatically. Oracle recommends this procedure.
For the Spaces application and portlet producers, all configuration data is stored in the MDS repository and portlet producers. Any changes made to the configuration of one server in the cluster are immediately visible to all other members.
Changes to discussions server are not frequent, however, when they do occur, the changes must be reapplied to other members of the cluster. You can do this by connecting directly to each discussions server, instead of using the load balancer, and making the necessary administration changes.
Figure 6-5 shows a two-node WebCenter Portal cluster running on two Oracle WebLogic Servers in one WebLogic Server domain. Oracle WebLogic Servers are front-ended by Oracle HTTP Server which load balances incoming requests to them. An Oracle RAC database stores metadata and schemas. VIPs are used for the Administration Server (for manual failover).
Note:
Oracle strongly recommends reading the release notes for any additional installation and deployment considerations prior to starting the setup process.
Note:
All command examples are for k or bash shell. No C shell examples are provided.
Steps to configure WebCenter Portal for a high availability configuration are:
Section 6.4.8, "Install WebLogic Server and WebCenter Portal on APPHOST2"
Section 6.4.9, "Propagating the Domain Configuration to APPHOST2 with pack/unpack Utilities"
Section 6.4.12, "Configuring Manual Failover of the Administration Server to APPHOST2"
Section 6.4.14, "Configuring the Distributed Notifications for the MDS Repository"
Section 6.4.15, "Configuring WebCenter Portal for Replication"
Section 6.4.18, "Configuring Clustering for Discussions Server"
Section 6.4.20, "Troubleshooting WebCenter Portal High Availability"
Section 6.4.21, "Converting Discussions from Multicast to Unicast"
The following sections provide prerequisite steps before setting up a WebCenter Portal high availability configuration.
For information about platform-specific commands, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle WebCenter.
WebCenter Portal requires the presence of a supported database and schemas.
To check if your database is certified or to see all certified databases, refer to the "Certified Databases" section in the Certification Document:
http://www.oracle.com/technology/software/products/ias/files/fusion_certification.html
To determine the database version, run the following query:
SQL>select version from sys.product_component_version where product like 'Oracle%';
To configure a virtual IP for the Administration Server, see Section 12.2.3.5, "Transforming the Administration Server for Cold Failover Cluster."
This section describes how to install and configure the database repository.
Oracle Clusterware
For 10g Release 2 (10.2), see Oracle Database Oracle Clusterware and Oracle Real Application Clusters Installation Guide.
For 11g Release 1 (11.1) and later, see Oracle Clusterware Installation Guide.
Automatic Storage Management
For 10g Release 2 (10.2), see Oracle Database Oracle Clusterware and Oracle Real Application Clusters Installation Guide.
For 11g Release 1 (11.1) and later, see Oracle Real Application Clusters Installation Guide.
When you run the installer, select the Configure Automatic Storage Management option in the Select Configuration page to create a separate Automatic Storage Management home.
Oracle Real Application Clusters
For 10g Release 2 (10.2), see Oracle Database Oracle Clusterware and Oracle Real Application Clusters Installation Guide.
For 11g Release 1 (11.1) and later, see Oracle Real Application Clusters Installation Guide.
You must install the 11g (11.1.1) Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository into a Real Application Clusters database before you install the Oracle Fusion Middleware components. Oracle Fusion Middleware provides a tool, Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility (RCU), to create the component schemas in an existing database. You install RCU in its own, separate Middleware home.
Use the latest version of RCU to install the 11g (11.1.1) Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository into a Real Application Clusters database.
See Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility User's Guide for more information about obtaining and running the latest version of RCU.
Database Initialization Parameters
Ensure that the following initialization parameter is set to the required value. It is checked by Repository Creation Assistant.
Table 6-6 Required Initialization Parameters
| Parameter | Required Value | Parameter Class |
|---|---|---|
|
|
300 or greater |
Static |
To check the value of the initialization parameter using SQL*Plus, you can use the SHOW PARAMETER command.
As the SYS user, issue the SHOW PARAMETER command as follows:
SQL> SHOW PARAMETER processes
Set the initialization parameter using the following command:
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM SET processes=300 SCOPE=SPFILE
Restart the database.
Note:
The method that you use to change a parameter's value depends on whether the parameter is static or dynamic and on whether your database uses a parameter file or a server parameter file. See the Oracle Database Administrator's Guide for details on parameter files, server parameter files, and how to change parameter values.
For production environments, it is a mandatory requirement for WebCenter Portal high availability topologies to have an external LDAP policy store. For more information on the supported policy stores and instructions to configure LDAP, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Portal.
The follow list describes the directories and variables used in this chapter:
ORACLE_BASE: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the base directory under which Oracle products are installed.
MW_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the location where Fusion Middleware (FMW) resides.
WL_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path contains installed files necessary to host a WebLogic Server.
ORACLE_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the location where WebCenter Portal is installed.
ORACLE_COMMON_HOME: This environment variable and related directory path refers to the Oracle home that contains the binary and library files required for the Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control and Java Required Files (JRF).
DOMAIN_HOME: This directory path refers to the location where the Oracle WebLogic Domain information (configuration artifacts) is stored.
Recommended values for consistency for these directories are:
ORACLE_BASE:
/u01/app/oracle
MW HOME (application tier):
ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw
WL_HOME:
MW_HOME/wlserver_10.3
ORACLE_HOME:
MW_HOME/WC1
ORACLE_COMMON_HOME:
MW_HOME/oracle_common
Install the 11g (11.1.1) Oracle Fusion Middleware Metadata Store and WebCenter Portal schemas into a Real Application Cluster database before you install WebCenter Portal components. Oracle Fusion Middleware provides a tool, Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility (RCU), to create the component schemas in an existing database.
Use the latest version of RCU to install the 11g (11.1.1) Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository into a Real Application Clusters database.
See Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility User's Guide for more information about obtaining and running the latest version of RCU.
Run RCU to install the required metadata for Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g.
Start RCU using the following command:
RCU_HOME/bin/rcu
In the Welcome screen, click Next.
In the Create Repository screen, select Create to load component schemas into a database and click Next.
In the Database Connection Details screen, enter connection information for your database:
Database Type: Select Oracle Database.
Host Name: Enter the name of the node that is running the database. For an Oracle RAC database, specify the VIP name, or one of the node names as the hostname: WCDBHOST1VIRTUAL.
Port: The port number for the database: 1521
Service Name: Enter the service name of the database: wcha.mycompany.com
Username: SYS
Password: Enter the password for the SYS user.
Role: SYSDBA
Click Next.
If you receive the following warning message, click Ignore or Stop:
The database you are connecting is with non-UTF8 charset, if you are going to use this DB for multilingual support, you may have data loss. If you are not using for multilingual support you can continue, otherwise we strongly recommend using UTF-8 database.
In the Select Components screen, select Create a New Prefix, and enter a prefix to use for the database schemas, for example, WCHA
Write down the schema names so they are available in later procedures.
Select the following schemas:
AS Common schemas:
Metadata Services
WebCenter Infrastructure:
WebCenter Portal
Click Next.
In the Schema Passwords screen, enter passwords for the main and additional (auxiliary) schema users. Click Next.
In the Map Tablespaces screen, choose the tablespaces for the selected components. Click Next.
In the Summary screen, click Create.
In the Completion Summary screen, click Close.
See Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Concepts and Repository Creation Utility User's Guide for more information about using RCU.
To install Oracle HTTP Server on WEBHOST1:
Verify that the servers meet the following requirements:
The system, patch, kernel, and other requirements meet the those specified in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility User's Guide.
This example uses port 7777. If you choose port 7777, ensure that it is not used by any service on the nodes. Verify this by running the following command:
Unix:
netstat -an | grep LISTEN | grep ":7777"
Windows:
netstat -an | findstr "LISTEN" | findstr ":7777"
If port 7777 is in use, choose another port, or make it available.
On UNIX platforms, if the /etc/oraInst.loc or /var/opt/oracle/oraInst.loc file exists, check that its contents are correct. Specifically, check that the inventory directory is correct and that you have write permissions for that directory.
If the /etc/oraInst.loc file does not exist, skip this step.
Start Oracle Universal Installer for Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g Webtier Utilities CD installation as follows:
For UNIX, run this command: ./runInstaller.
For Windows, double-click setup.exe.
In the Specify Inventory Directory screen, enter the location for the inventory and the user group, and click OK.
Run the root privileged actions as indicated in the dialog, and click OK.
In the Welcome screen, click Next.
In the Select Installation Type screen, select Install and Configure. Click Next.
In the Prerequisite Checks screen, ensure that all prerequisites are met. Click Next.
In the Specify Installation Location screen, set the location to:
/u01/app/oracle/product/11.1.1/ohs_1
Click Next.
In the Configure Components screen:
Select Oracle HTTP Server.
Do not select Associate Selected Components with WebLogic Domain.
Click Next.
In the Specify Component Details screen, enter the following values:
Instance Home Location: app/oracle/product/11.1.1/ohs_1/instances/ohs_instance1
Instance Name: ohs_instance1
OHS Component Name: ohs1
Click Next.
In the Specify Webtier Port Details screen, do the following:
Select Specify Custom Ports. If you specify a custom port, select Specify Ports using Configuration File and then use the Browse function to select the file.
Enter Oracle HTTP Server port. For example, enter 7777.
Click Next.
Note:
For more information on setting ports, refer to Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle SOA Suite.
Click Next.
In the Configuration Summary screen, ensure that the selections are correct, and click Install.
In the Installation Progress screen:
For UNIX systems, a dialog box appears prompting you to run the oracleRoot.sh script. Open a command window and run the script, following the prompts.
Click Next.
In the Configuration screen, several configuration assistants are started in succession. When the configuration assistants are finished, the Configuration Completed screen appears.
In the Configuration Completed screen, click Finish to exit.
Use the following procedures to install Oracle Fusion Middleware components:
Oracle WebLogic Server (see "Section 6.4.3.1, "Installing Oracle WebLogic Server"")
WebCenter Portal (see Section 6.4.3.2, "Installing Oracle Fusion Middleware for WebCenter Portal"")
See "Understanding Your Installation Starting Point" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Planning Guide for the version of Oracle WebLogic Server to use with the latest version of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
To install Oracle WebLogic Server on all nodes in the application tier:
On UNIX platforms, if the /etc/oraInst.loc or /var/opt/oracle/oraInst.loc file exists, check that its contents are correct. Specifically, check that the inventory directory is correct and that you have write permissions for it.
If the /etc/oraInst.loc file does not exist, skip this step.
Start Oracle WebLogic Server Installer.
In the Welcome screen, click Next.
In the Choose Middleware Home Directory screen:
Select Create a New Middleware Home
For the Middleware Home Directory field, enter MW_HOME
Click Next.
In the Register for Security Updates screen, enter your contact information for security update notifications, and click Next.
In the Choose Install Type screen, select Custom, and click Next.
In the JDK Selection screen, select only Oracle JRockit 1.6.0_<version> SDK and click Next.
In the Choose Product Installation Directories screen, accept the following directory:
WL_HOME
Click Next.
In the Installation Summary screen, click Next.
In the Installation Complete screen, deselect Run QuickStart, and click Done.
To install Oracle Fusion Middleware for WebCenter Portal on all the nodes in the application tier:
Start the installer for Oracle Fusion Middleware for WebCenter Portal.
On UNIX, (Linux used in this example):
APPHOST1> runInstaller
On Windows:
APPHOST1> setup.exe
When Oracle Fusion Middleware 11g WebCenter Installer prompts you for a JRE/JDK location enter Oracle SDK location created in the Oracle WebLogic Server installation, for example, MW_HOME/jrockit_160_<version>.
In the Welcome screen, click Next.
In the Prerequisite Check screen, verify that the checks complete successfully, and click Next.
In the Specify Installation Location screen:
For Middleware Home, enter MW_HOME
For Oracle Home Directory, enter the directory you want to use, for example, wc
Click Next.
In the Installation Summary screen, click Install.
In the Installation Complete screen, click Finish.
Note:
Before you run the Configuration Wizard by following the instructions in Section 6.4.5, "Running Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard on APPHOST1 to Create the WebLogic Server WebCenter Domain," ensure that you have applied the latest Oracle Fusion Middleware patch set and other known patches to your Middleware Home, so that you have the latest version of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
See "Understanding Your Installation Starting Point" in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Planning Guide for the steps you must perform to get the latest version of Oracle Fusion Middleware.
For information about configuring virtual IPs for the Administration Server, see Chapter 12, "Active-Passive Topologies for Oracle Fusion Middleware High Availability."
Run Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard from the WebCenter directory in the Middleware home to create a domain containing the Administration Server and WebCenter Portal components. Verify that the database where you installed the repository is running. For Oracle RAC databases, Oracle recommends having all the instances running.
Start Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard from the ORACLE_HOME/common/bin directory using the following command:
APPHOST1> ./config.sh
In the Welcome screen, select Create a New WebLogic Domain and click Next.
In the Select Domain Source screen, select Generate a domain configured automatically to support the following products. Select the following products:
When you select WebCenter Spaces, Oracle WSM Policy Manager is selected automatically.
Oracle WebCenter Spaces - 11.1.1.0
Oracle WebCenter Services Portlets - 11.1.1.0
Oracle WebCenter Pagelet Producer - 11.1.1.0
Oracle Enterprise manager - 11.1.1.0
Oracle Portlet Producers - 11.1.1.0
Oracle WebCenter Discussion Server - 11.1.1.0
Oracle WebCenter ActivityGraph Engines - 11.1.1.0
Oracle WebCenter Personalization - 11.1.1.0
Oracle WebCenter Analytics Collector - 11.1.1.0
Oracle WSM Policy Manager
Oracle JRF - 11.1.1.1
Click Next.
Enter the Domain Name, Domain Location, and Application Location and click Next.
In the Configure Administrator Username and Password screen, enter the username and password to use for the domain's administrator. Click Next.
In the Configure Server Start Mode and JDK screen, select the following:
WebLogic Domain Startup Mode: select Production Mode
JDK Selection: select Oracle JRockit 1.6.0_<version>.
Click Next.
In the Configure JDBC Data Sources screen:
Select all component schemas in the table at the bottom of the screen.
For the RAC configuration for component schemas, select Convert to GridLink or Convert to RAC multi data source. For single database configuration, select Don't convert.
Ensure that the following data source appear on the screen. You provide a custom prefix for these schemas. Table 6-7 lists the data sources, the schemas used and the managed servers to which they are assigned.
For information about GridLink data source configuration with Oracle RAC and the MDS repository, see Section 4.1.2, "GridLink Data Sources and Oracle RAC"; for multi data source, see Section 4.1.3, "Using Multi Data Sources with Oracle RAC."
Table 6-7 Oracle WebCenter Portal Data Sources
| Data Source | User Name |
|---|---|
|
WebCenterDS |
wcha_webcenter |
|
ActivitiesDS |
wcha_activities |
|
DiscussionsDS |
wcha_discussions |
|
PersonalizationDS |
wcha_webcenter |
|
PortletDS |
wcha_portlet |
|
Portlet-ServicesProducerDS |
wcha_portlet |
|
WC-ServicesProducerDS |
wcha_webcenter |
|
WebCenterMDS |
wcha_mds |
|
PersonalizationMDS |
wcha_mds |
|
mds-PageletProducerDS |
wcha_mds |
|
mds-ServicesProducerDS |
wcha_mds |
Click Next.
In the Configure JDBC Component Schema screen, enter values for the following fields, specifying connect information for the Oracle RAC database that was seeded with RCU.
For multi data sources, enter values for these fields:
Figure 6-6 Configure RAC Multi Data Source Component Schema Screen
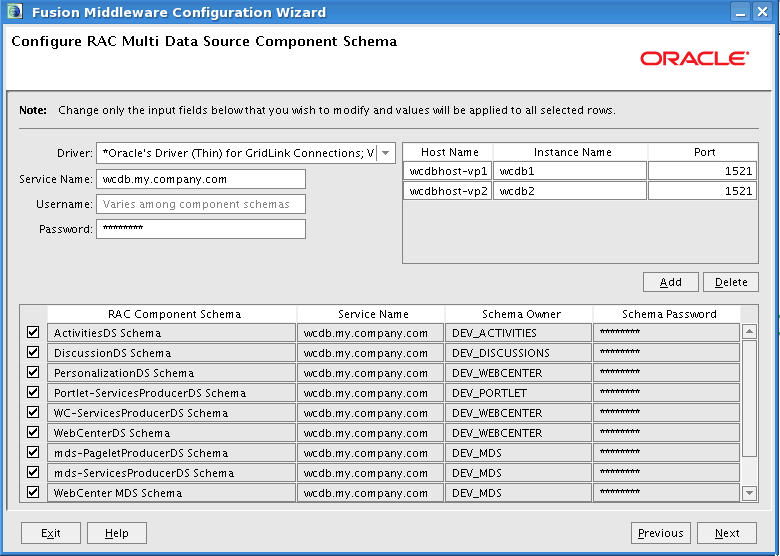
For GridLink data sources, enter values for these fields:
Figure 6-7 Configuring GridLink RAC Component Schema
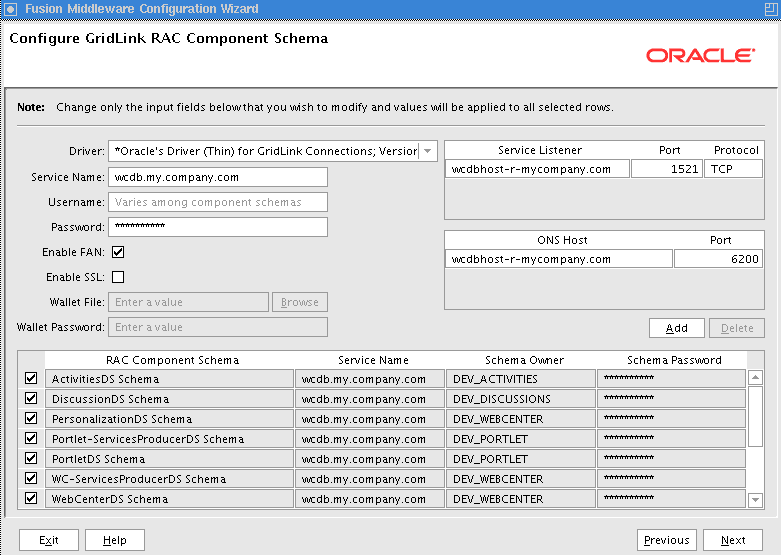
Choose a driver: For RAC: Select Oracle driver (Thin) for RAC Service-Instance connections, Versions:10, 11. For GridLink: Oracle Driver (Thin) for GridLink Connections, Versions:10 and later
Enter the Service name of the database. For a GridLink data source, you must enter the RAC service name in lower-case letters followed by the domain name example.com. For example, <mydbservice>.example.com
Note:
The Oracle RAC Service name is defined on the database; it is not a fixed name. Oracle recommends that you register/add the RAC service name with the database domain name, for example, example.com
Enter the Prefix_Username for WebCenter Portal schemas.
Enter the Password for the schemas.
For a GridLink data source, enter the SCAN address in the Listener Address field and SCAN port in the Port field. Enter the ONS host and port information in the ONS Host and Port fields, respectively.
Note:
Oracle recommends that you use SCAN addresses to specify the host and port for both the TNS listener and the ONS listener in the WebLogic console. You do not need to update a GridLink data source containing SCAN addresses if you add or remove Oracle RAC nodes. Contact your network administrator for appropriately configured SCAN urls for your environment. See SCAN Addresses in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuring and Managing JDBC Data Sources for Oracle WebLogic Server guide.
For a multi data source, click Add. Enter details for Oracle RAC instances.
Update each multi data source schema by selecting one data source at a time and adding the appropriate details.
Click Next.
In the Test JDBC Data Sources screen, the connections are tested automatically. (For GridLink data sources, ONS connections are also tested.) The Status column shows the results. Ensure that all connections were successful. If not, click Previous to return to the previous screen and correct your entries.
Click Next when all the connections are successful.
In the Select Optional Configuration screen, select the following:
Administration Server
Managed Servers, Clusters and Machines
In the Configure the Administration Server screen, enter the following values:
Name: AdminServer
Listen Address: Enter the VIP address used in Section 6.4.4.
Listen Port: 7001
SSL listen port: N/A
SSL enabled: leave unchecked
Click Next.
In the Configure Managed Servers screen, add the following managed servers:
Table 6-8 Configuring Managed Servers
| Name | Listen Address | Listen Port | SSL Listen Port | SSL Enabled |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
WC_Portlet1 |
Hostname of APPHOST1 |
8889 |
n/a |
unchecked |
|
WC_Portlet2 |
Hostname of APPHOST2 |
8889 |
n/a |
unchecked |
|
WC_Spaces1 |
Hostname of APPHOST1 |
8888 |
n/a |
unchecked |
|
WC_Spaces2 |
Hostname of APPHOST2 |
8888 |
n/a |
unchecked |
|
WC_Collaboration1 |
Hostname of APPHOST1 |
8890 |
n/a |
unchecked |
|
WC_Collaboration2 |
Hostname of APPHOST2 |
8890 |
n/a |
unchecked |
|
WC_Utilities1 |
Hostname of APPHOST1 |
8891 |
n/a |
unchecked |
|
WC_Utilities2 |
Hostname of APPHOST2 |
8891 |
n/a |
unchecked |
Click Next.
In the Configure Clusters screen, add the following clusters
Portlet_Cluster
Name: Portlet_Cluster
Cluster Messaging Mode: unicast
Cluster Address Enabled: leave blank
Spaces_Cluster
Name: Spaces_Cluster
Cluster Messaging Mode: unicast
Note:
By default, each WebCenter Portal cluster is configured as unicast. To configure your WebCenter Portal cluster for multicast, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Using Clusters for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Cluster Address Enabled: leave blank
Collaboration_Cluster
Name: Collaboration_Cluster
Cluster Messaging Mode: unicast
Cluster Address Enabled: leave blank
Utilities_Cluster
Name: Utilities_Cluster
Cluster Messaging Mode: unicast
Cluster Address Enabled: leave blank
Click Next.
In the Assign Servers to Clusters screen, assign the following servers to clusters:
Spaces_Cluster
WC_Spaces1
WC_Spaces2
Portlet_Cluster
WC_Portlet1
WC_Portlet2
Collaboration_Cluster
WC_Collaboration1
WC_Collaboration2
Utilities_Cluster
WC_Utilities1
WC_Utilities2
Click Next.
In the Configure Machines screen:
Delete the LocalMachine that appears by default.
Click the Unix Machine tab, and add the following machines:
Table 6-9 Configuring Machines
| Name | Node Manager Listen Address |
|---|---|
|
APPHOST1 |
Hostname of APPHOST1 |
|
APPHOST2 |
Hostname of APPHOST2 |
Click Next.
In the Assign Servers to Machines screen, assign servers to machines as follows:
Figure 6-8 Assign Servers to Machines Screen
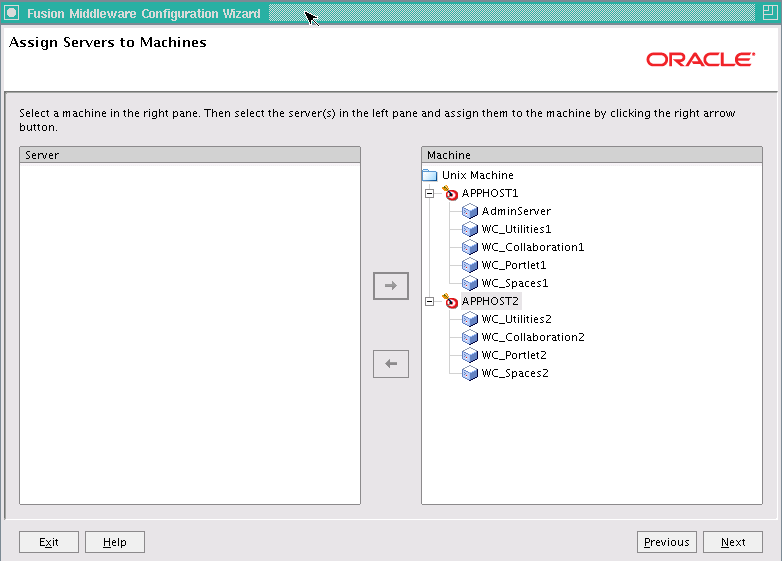
APPHOST1: WC_Spaces1, WC_Portlet1, WC_Collaboration1, WC_Utilities1
APPHOST2: WC_Spaces2, WC_Portlet2, WC_Collaboration2, WC_Utilities2
Click Next.
In the Configuration Summary screen, click Create.
In the Creating Domain screen, click Done.
This is an optional step for enabling the Administration Server to start without prompting you for the administrator username and password. Create a boot.properties file for the Administration Server and for the managed servers on APPHOST1.
For the Administration Server:
Create the following directory:
APPHOST1> mkdir -p MW_HOME/user_projects/domains/wc_domain/servers/AdminServer/security
Use a text editor to create a file called boot.properties in the directory created in the previous step, and enter the following lines in the file:
username=adminuser password=password
Note:
When you start the Administration Server, the username and password entries in the file are encrypted.
For security reasons, minimize the time the entries in the file are left unencrypted. After you edit the file, start the server as soon as possible for the entries to be encrypted.
For the WC_Spaces1 managed server:
Create the following directories:
APPHOST1> mkdir ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/user_projects/domains/wc_domain/servers/WC_Spaces1/security
Use a text editor to create a file called boot.properties in the security directory created in the previous step, and enter the following lines in the file:
username=adminuser password=password
Repeat Steps 2 and 3 for the WC_Portlet1 and WC_Collaboration1 Managed Servers on APPHOST1.
Note:
When you start the Administration Server, the username and password entries in the file are encrypted.
For security reasons, minimize the time the entries in the file are left unencrypted. After you edit the file, start the server as soon as possible in order for the entries to be encrypted.
This section describes procedures for starting the system in APPHOST1
To start the Administration Server on APPHOST1 run the following commands:
APPHOST1> cd ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/user_projects/domains/wc_domain/bin
APPHOST1> ./startWebLogic.sh
To verify that the Administration Server is properly configured:
In a browser, go to http://VIP1:7001/console.
Log in as the administrator.
Verify that all the managed servers such as WC_Spaces1, WC_Spaces2 are listed.
Verify that all clusters are listed.
Verify that you can access Enterprise Manager at http://VIP1:7001/em.
Log in to EM Console with the username and password you used in step 2.
This step is required if you have not set up SSL communication between the Administration Server and the Node Manager. If SSL is not set up, you receive an error message unless you disable hostname verification.
You can re-enable hostname verification when you have set up SSL communication between the Administration Server and the Node Manager.
To disable hostname verification:
In Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, select Servers, and then AdminServer.
Select SSL, and then Advanced.
In the Change Center, click Lock & Edit.
When prompted, save the changes and activate them.
Set Hostname Verification to None.
Select WC_Spaces1, SSL, and then Advanced.
Set Hostname Verification to None.
Repeat Steps 6 and 7 for all the Managed Servers.
Restart the AdminServers and all the Managed Servers.
Perform these steps to start Node Manager on APPHOST1:
Run the setNMProps.sh script, which is located in the ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin directory, to set the StartScriptEnabled property to true before starting Node Manager:
APPHOST1> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin
APPHOST1> ./setNMProps.sh
Note:
You must use the StartScriptEnabled property to avoid class loading failures and other problems.
Start Node Manager:
APPHOST1> cd WL_HOME/server/bin
APPHOST1> ./startNodeManager.sh
Repeat the procedures for installing WebLogic Server and WebCenter Portal for APPHOST2, start with Section 6.4.3.1, "Installing Oracle WebLogic Server". The directory paths for binary files and domains used when installing new nodes must be exactly the same as those used for first node. If these paths and domains are not exactly the same as those used for the first node, failover is does not occur.
Follow these steps to propagate the domain configuration to APPHOST2 using Pack/Unpack utilities:
Run the following pack command on APPHOST1 to create a template pack:
APPHOST1> cd WL_HOME/common/bin
APPHOST1> ./pack.sh -managed=true -domain=ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/user_projects/domains/wc_domain/
-template=wc_domaintemplate.jar
-template_name=wc_domain_template
Run the following command on APPHOST1 to copy the template file created in the previous step to APPHOST2 using, in this example, scp:
APPHOST1> scp wc_domaintemplate.jar
APPHOST2:WL_HOME/common/bin
Run the unpack command on APPHOST2 to unpack the propagated template:
APPHOST2> cd WL_HOME/common/bin APPHOST2> ./unpack.sh -domain=ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/user_projects/domains/wc_domain/ -template=wc_domaintemplate.jar
To start the Node Manager on APPHOST2, repeat the steps from Section 6.4.7.4, "Starting Node Manager on APPHOST1." on APPHOST2.
Enable Oracle HTTP Server to route to the Administration Server that contains WebCenter Portal managed servers by setting the WebLogicCluster parameter to the list of nodes in the cluster.
Add the following lines to the OHS_HOME/instances/ohs_instance1/config/OHS/ohs1/mod_wl_ohs.conf file:
# Spaces
<Location /webcenter>
WebLogicCluster apphost1.com:8888,apphost2.com:8888
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
<Location /webcenterhelp>
WebLogicCluster apphost1.com:8888,apphost2.com:8888
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
<Location /rss>
WebLogicCluster apphost1.com:8888,apphost2.com:8888
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
<Location /rest>
WebLogicCluster apphost1.com:8888,apphost2.com:8888
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
# Pagelet Producer
<Location /pagelets>
WebLogicCluster apphost1.com:8889,apphost2.com:8889
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
# Activity Graph
# The WebLogicHost below should be set to the Host on which ActivityGraph is running
<Location /activitygraph-engines>
WebLogicCluster apphost1.com:8891
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
# Portlet
<Location /portalTools>
WebLogicCluster apphost1.com:8889,apphost2.com:8889
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
<Location /wsrp-tools>
WebLogicCluster apphost1.com:8889,apphost2.com:8889
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
# SES Search
<Location /rsscrawl>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
WeblogicHost ses.example.com
WeblogicPort 7777
</Location>
<Location /sesUserAuth>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
WeblogicHost ses.example.com
WeblogicPort 7777
</Location>
# Personalization
<Location /wcps>
SetHandler weblogic-handle
WeblogicHost webcenter.example.com
WeblogicPort 8889
</Location>
# Discussions
<Location /owc_discussions>
WebLogicCluster apphost1.com:8890,apphost2.com:8890
SetHandler weblogic-handler
</Location>
#AdminServer and EM
<Location /console>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
WebLogicHost VIP1
WeblogicPort 7001
</Location>
<Location /consolehelp>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
WebLogicHost VIP1
WeblogicPort 7001
</Location>
<Location /em>
SetHandler weblogic-handler
WebLogicHost VIP1
WeblogicPort 7001
</Location>
Restart Oracle HTTP Server on WEBHOST1:
WEBHOST1> OHS_HOME/instances/ohs_instance1/bin/opmnctl restartproc ias-component=OHS_COMPONENT1
The WebCenter suite includes two applications that use / as the web context root:
Sharepoint Root - deployed on WC_Spaces
Pagelet Producer Root - deployed on WC_Portlet
To route the Sharepoint Root application without virtual hosts by using Oracle HTTP Server (OHS), add the following entry:
<Location />
SetHandler weblogic-handler
WebLogicHost webcenter.example.com
WebLogicPort 8889
</Location>
This entry grabs all context roots that are not defined explicitly. Sharepoint requires mapping, which isn't possible to do in a single OHS. For this reason, you need a virtual host configuration, a single system that runs more than one web site such as www.company1.com and www.company2.com. Virtual hosts are IP-based (a unique IP address for each web site) or name-based (multiple names run on each IP address). It is not obvious to end users that the web sites run on the same physical server. For more information on virtual hosts, see Apache HTTP Server documentation.
Oracle HTTP Server Configuration
The following entry adds two name-based hosts: one for Sharepoint Root and one for Pagelet Producer Root.
Find OHS httpd.conf in $WEBTIER_INSTANCE_HOME/config/OHS/<ohs>.
Find sample VirtualHost configuration and add the following entry:
NameVirtualHost *:7777
<VirtualHost *:7777>
ServerName webhost.example.com
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:7777>
ServerName webtier-spaces.example.com
<Location />
SetHandler weblogic-handler
WebLogicCluster apphost1:8888,apphost2:8888
</Location>
<Location /webcenter>
Deny from all
</Location>
<Location /webcenterhelp>
Deny from all
</Location>
<Location /rest>
Deny from all
</Location>
</VirtualHost>
Ensure that the new virtual hosts webtier-pageletproducer and webtier-spaces have been added to DNS.
In a Virtual Host setup, you must configure additional properties to use applications routed via virtual host.
Sharepoint
For single sign-on setups, including integration with Oracle Access Manager 10g or Oracle Access Manager 11g, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide for Oracle WebCenter Portal.
Verify the URLS to ensure that appropriate routing and failover is working from the HTTP Server to the WebCenter Portal cluster.
Start WC_Spaces1, WC_Spaces2, WC_Portlet1 and WC_Portlet2 from the WebLogic Server Administration Console as follows:
Access the Administration Console at the following URL
http://APHHOST1/console
Click Servers.
Open the Control tab.
Select WC_Spaces1, WC_Spaces2, WC_Portlet1 and WC_Portlet2.
Click Start.
Verify direct access to the managed servers using the following URLs:
apphost1:8888/webcenter
apphost2:8888/webcenter
apphost1:8889/portalTools
apphost2:8889/portalTools
While WC_Spaces2 and WC_Portlet2 are running, stop WC_Spaces1 and WC_Portlet1 from Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Access the following URLs and verify the appropriate functionality:
WebHost1:7777/webcenter
WebHost1:7777/portalTools
Start WC_Spaces1 and WC_Portlet1 from the WebLogic Server Administration Console.
Stop WC_Spaces2 and WC_Portlet2.
Access the following URLs and verify the appropriate functionality:
WebHost1:7777/webcenter
WebHost1:7777/portalTools
For information about configuring the Administration Server for high availability, see Section 12.4, "Transforming the Administration Server in an Existing Domain for Cold Failover Cluster."
The Java Object Cache (JOC) should be configured among all the servers running WebCenter Spaces. This local cache is provided to increase the performance of the Spaces application.
For instructions on configuring the Java Object Cache among all the servers running the Spaces application, see Section F.1, "Configuring the Java Object Cache."
In high availability environments, Oracle recommends that you configure distributed notifications for the MDS repository.
For instructions on configuring distributed notifications for the MDS repository, see Appendix G, "Configuring Distributed Notifications for MDS."
Use the procedures in this section to configure WebCenter Portal for replication.
Clustering Requirement
The application must be deployed to an Oracle WebLogic Cluster. This automatically establishes a replication channel for the multiple instances of the application.
Note:
In a Unicast cluster, the default replication channel is configured using the Listen address of each managed server. Therefore, the Listen address should be configured to be a specific IP address or hostname, instead of being configured to listen on Any.
Oracle ADF Replication
WebCenter Portal relies on Oracle ADF components, therefore, is it essential that you configure Oracle ADF properly. The following tag should be in the adf-config.xml file, one of the Application Resources, for a stateful application:
<adfc:adf-controller-config><adfc:adf-scope-ha-support>true</adfc:adf-scope-ha-support></adfc:adf-controller-config>
In WebCenter Portal applications, this is enabled by default.
Application Replication
Applications must also have replication enabled. Oracle WebLogic Server enables several types of persistent stores for replication. For more information on persistent stores, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Using Clusters for Oracle WebLogic Server.
WebCenter Portal applications are enabled by default with the following setting in the weblogic.xml file:
<session-descriptor> <persistent-store-type>replicated_if_clustered</persistent-store-type> </session-descriptor>
The replicated_if_clustered setting disables replication for stand-alone application environments, and uses in-memory replication within a cluster environment.
Ensure that all WebCenter Portal applications are configured for in-memory replication.
Analytics Collectors are configured out-of-the-box so all you must do is configure a connection between the Spaces application and the Analytics Collector.
Open the WLST shell:
ORACLE_HOME/common/bin/wlst.sh
Connect to WLS Server:
connect('weblogic_admin_username', 'weblogic_admin_pwd', 'APPHOST1:8888')
Note that you are connecting to the host and port of the Spaces Server.
Create the Analytics Collector connection and make it the default connection:
createAnalyticsCollectorConnection(appName='webcenter', connectionName='HAConn1', isUnicast=1, collectorHost='localhost', collectorPort=31314, isEnabled=1, timeout=30, default=1)
List the changes made:
listDefaultAnalyticsCollectorConnection(appName='webcenter')
The Activity Graph Engines application should run as a singleton. In a cluster environment, all instances of the Activity Graph Engines application should be disabled except for one.
To disable the Activity Graph Engines application:
Log on to the Oracle WebLogic Administration Console.
Shut down WC_Spaces, WC_Portlet, and WC_Utilities. Select Deployments.
In the Change Center, click Lock & Edit.
Alter the targets for each of the following deployments:
activitygraph-engines (11.1.1.6.0)
oracle.webcenter.activitygraph.enginelib (11.1.1,11.1.1)
oracle.webcenter.activitygraph.lib (11.1.1,11.1.1)
Select the deployment.
Select the Targets tab. Click on Change Targets.
Ensure that the deployment is only targeted to Part of the Cluster/one of the Managed Servers. Click OK to save the changes.
Click Activate All Changes.
Since Activity Graph runs on one node only, it is unavailable if this node is lost or the Managed Server is not available. In these cases, Oracle recommends that you deploy Activity Graph on an active Managed Server. You can automate this process by configuring Service Migration. For an example, see Section 5.13.20, "Configuring Server Migration for the WLS_SOA Servers."
This procedure requires a unicast cluster.
Before you perform this procedure, see Section 6.4.21, "Converting Discussions from Multicast to Unicast":
To convert a multicast cluster to a unicast cluster (if necessary).
To verify that an existing unicast cluster has the correct settings.
Ensure that all members of the Discussions server cluster can communicate with each other using the Discussions server Administration Console:
Log into each member of the cluster at:
http://<host>:<port>/owc_discussions/admin
Go to Cache Settings.
At the bottom of the page, in the Cache Features section, ensure that Clustering is set to Enabled.
The top of the page should now list all members of the cluster.
Again, towards the end of the page, under the Cache Tools section, do Cluster wide cache reset and the Cache warm up Task. Repeat the Cache warm up task on all members of the cluster.
You can scale out and scale up a WebCenter Portal topology. When you scale up the topology, you add new managed servers to nodes that are already running one or more managed servers. When you scale out the topology, you add new managed servers to new nodes.
In this case, you already have a node that runs a managed server configured with WebCenter portal components. The node contains a Middleware home and a WebCenter directory in shared storage.
You can use the existing installations (Middleware home and domain directories) for creating new WebCenter Portal managed servers. There is no need to install WebCenter Portal binaries in a new location, or to run pack and unpack. Running multiple managed servers on one node is only supported for the WC_Spaces servers and the WC_Portlet servers.
Follow these steps for scaling up the topology:
Using the Administration Console, clone WC_Spaces1 or WC_Portlet1 into a new managed server. The source managed server to clone should be one that already exists on the node where you want to run the new managed server.
To clone a managed server:
Select Environment -> Servers from the Administration Console.
Select the managed server that you want to clone (for example, WC_Spaces1 or WC_Portlet1).
Select Clone.
Name the new managed server SERVER_NAMEn, where n is a number to identify the new managed server.
For the listen address, assign the hostname or IP to use for this new managed server.
Ensure the port number for this managed server is available on this node.
Add the new managed server to the Java Object Cache Cluster (see Section 6.4.13, "Configuring the Java Object Cache").
Reconfigure the Oracle HTTP Server module with the new member in the cluster. See Section 6.4.11, "Configuring Oracle HTTP Server for the Administration Server and WebCenter Portal Managed Servers."
In scaling out your topology, you add new managed servers configured with WebCenter Portal applications to new nodes.
Before performing the steps in this section, check that you meet these requirements:
In your topology, there are existing nodes running managed servers configured with WebCenter Portal applications.
The new node can access the existing home directories for WebLogic Server and WebCenter Portal. You use the existing installations in shared storage for creating a new managed server. There is no need to install WebLogic Server or WebCenter Portal binaries in a new location, although you must run pack and unpack to create a managed server domain.
Follow these steps for scaling out the topology:
On the new node, mount the existing Middleware home, which should include the WebCenter Portal installation and the domain directory, and ensure that the new node has access to this directory, just like the rest of the nodes in the domain.
To attach ORACLE_HOME in shared storage to the local Oracle Inventory, run the following commands:
WCHOSTn> cd ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/wc/ WCHOSTn> ./attachHome.sh -jreLoc ORACLE_BASE/fmw/jrockit_160_<version>
To update the Middleware home list, create (or edit, if another WebLogic installation exists in the node) the MW_HOME/bea/beahomelist file and add ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw to it.
Log into the Oracle WebLogic Administration Console.
Create a new machine for the new node that will be used, and add the machine to the domain.
Update the machine's Node Manager's address to map the IP of the node that is being used for scale out.
Use the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console to clone either WC_Spaces1 or WC_Portlet1 or WC_Collaboration1 or WC_Utilities1 into a new managed server. Name it WC_XXXn, where n is a number and assign it to the new machine.
For the listen address, assign the hostname or IP to use for the new managed server. Perform these steps to set the managed server listen address:
Log into the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console.
In the Change Center, click Lock & Edit.
Expand the Environment node in the Domain Structure window.
Click Servers.
Select the managed server whose listen address you want to update in the Names column of the table.
Set the Listen Address to WCHOSTn where WCHOSTn is the DNS name of your new machine.
Click Save.
Save and activate the changes.
The changes will not take effect until the managed server is restarted.
Run the pack command on WCHOST1 to create a template pack as follows:
WCHOST1> cd ORACLE_COMMON_HOME/common/bin WCHOST1> ./pack.sh -managed=true -domain=MW_HOME/user_projects/ domains/wc_domain/ -template=webcenterdomaintemplateScale.jar -template_name=webcenter_domain_templateScale
Run the following command on WCHOST1 to copy the template file created to WCHOSTn:
WCHOST1> scp wc_domaintemplateScale.jar oracle@WCHOSTn:/ ORACLE_BASE/product/
fmw/wc/common/bin
Run the unpack command on WCHOSTn to unpack the template in the managed server domain directory as follows:
WCHOSTn> cd ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/wc/common/bin WCHOSTn> ./unpack.sh -domain=ORACLE_BASE/product/fmw/user_projects/domains/ wc_domain/ -template=wc_domaintemplateScale.jar
Start the Node Manager on the new node. To start the Node Manager, use the installation in shared storage from the existing nodes, and start Node Manager by passing the hostname of the new node as a parameter as follows:
WCHOSTn> WL_HOME/server/bin/startNodeManager <new_node_ip>
If this is a new Collaboration managed server, ensure that you have followed the steps in Section 6.4.18, "Configuring Clustering for Discussions Server" to configure clustering for the new Discussions server. Ensure also that the steps in Section 6.4.21, "Converting Discussions from Multicast to Unicast" are performed, using the hostname of the new host for the coherence.localhost parameter.
If this is a new Utilities managed server, ensure that Activity Graph is disabled by following the steps in Section 6.4.17, "Configuring Activity Graph." Ensure also that the steps for configuring a new Analytics Collector in Section 6.4.16, "Configuring Analytics" have been followed.
Start and test the new managed server from the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console:
Shut down all the existing managed servers in the cluster.
Ensure that the newly created managed server is running.
Access the application on the newly created managed server. The application should be functional.
This section describes procedures for troubleshooting WebCenter Portal.
WebCenter Portal applications deploy when the managed server first starts; use Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console first to check that all application deployments are successful:
Click Deployments in the left hand pane. The right hand pane shows the application deployments and their status. The state of all applications, assuming all the servers are running, should be ACTIVE.
If an application deployment fails, the server logs may provide some indication of why the application was not deployed successfully. The server logs are located in the DOMAIN_HOME/servers/SERVER_NAME/logs directory. Common issues include:
Unavailability of external resources, such as database resources. Examine the error, fix it, and attempt to redeploy the application.
The appropriate applications or libraries are not targeted correctly to the right managed server or cluster.
State replication is most prominent in failover scenarios. A user working on one server may discover that, upon failover:
Windows may be closed or state might be reset.
Screens may require a reset.
The application may be redirecting to the logon screen.
To troubleshoot and diagnose state replication issues.
Confirm that this is not a known replication issue.
See Section 6.3.2.8, "Expected Behavior for Application Failover" for possible expected behaviors. Before proceeding to further diagnose the issue, first confirm that the failover behavior is not an expected behavior.
Check load balancer settings.
For replication and failover to function correctly, the load balancer must be configured with the appropriate persistence settings. For more details on configuring Hardware Load Balancers for Oracle WebLogic Server, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Using Clusters for Oracle WebLogic Server.
Check the cluster status.
Replication occurs within the context of a cluster. For failover to be successful, there must be at least one other healthy member of the cluster available. You can check luster status in one of two ways:
Check the cluster status using Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console - In the Left-hand pane, click on Servers. Verify the state of all servers in the cluster.
Check the cluster status using weblogic.Admin utility The weblogic.Admin command can be used to query the state of all servers in a specific cluster. For example:
$ java weblogic.Admin -url Adminhost:7001 -username <username> -password <password> CLUSTERSTATE -clustername Spaces_Cluster
This example returns:
There are 2 server(s) in cluster: Spaces_Cluster The alive servers and their respective states are listed below: WC_Spaces1---RUNNING WC_Spaces2---RUNNING
Check cluster communications.
Although cluster members may all be running, there may be communication issues which prevent them from communicating replication information to each other. There are two types of cluster communication configurations. Troubleshooting depends on the cluster type:
Checking Unicast cluster communications - For Unicast clusters, managed servers must be able to access each other's hosts and each other's default listening port.
Ensure that all individual managed servers have their Listen Address set correctly. You can find this setting by selecting Configuration, General for each managed server.
Checking Multicast cluster communications - For multicast clusters, servers must be able to intercept the same multicast traffic. Ensure that multicast is configured correctly by running the WebLogic utility utils.MulticastTest on each machine. For example:
$ java utils.MulticastTest -H
Confirm application configuration.
WebCenter Portal applications are configured correctly by default. For user applications, in-memory replication take place only with the proper configuration in weblogic.xml:
<session-descriptor> <persistent-store-type>replicated_if_clustered</persistent-store-type> </session-descriptor>
A persistent-store-type of replicated is also acceptable.
Enable Debug.
Check the server logs for any unusual messages on managed server startup. In particular, if the managed server is unable to locate other members of the cluster. The server logs are located in the DOMAIN_HOME/servers/SERVER_NAME/logs directory.
For further debugging, enable the flags DebugCluster, DebugClusterAnnouncements, DebugFailOver, DebugReplication, and DebugReplicationDetails. Each flag can be enabled with the weblogic.Admin utility:
$ java weblogic.Admin -url Adminhost:7001 -username <username> -password <password> SET -type ServerDebug -property DebugCluster true
Policies are refreshed at an interval defined in jps-config.xml by the variable oracle.security.jps.ldap.policystore.refresh.interval. By default, this interval is ten minutes. If a server is lost, requests are routed to another server in the cluster where the original policies are cached. Recent policy changes that occurred since the last refresh may appear to be lost. For example, roles created immediately before the failover may be seen as unavailable.
The policies are still in the back-end policy store. Refresh the cache to restore policy information. Re-try after a few minutes, or log in and log out of the application to force a policy cache refresh.
If attempts to start a Managed Server that uses the Java Object Cache, such as OWSM or the Spaces application Managed Servers, fail, and the following errors appear in the logs:
J2EE JOC-058 distributed cache initialization failure J2EE JOC-043 base exception: J2EE JOC-803 unexpected EOF during read.
Another process is using the same port that JOC is attempting to obtain. To solve this problem, either stop that process, or reconfigure JOC for this cluster to use another port in the recommended port range.
To convert Discussions from multicast to unicast:
Step 1: Add the startup parameters
To add the relevant startup parameters:
In the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, select Servers, WC_Collaboration1, Configuration, and then Server Start.
In the Arguments box, add the following:
-Dtangosol.coherence.wka1=WCPHOST1 -Dtangosol.coherence.wka2=WCPHOST2 -Dtangosol.coherence.localhost=WCPHOST1 -Dtangosol.coherence.wka1.port=8089 -Dtangosol.coherence.wka2.port=8089 -Dtangosol.coherence.localport=8089
Where Host1 is where WC_Collaboration1 is running.
To use a port other than 8088 for WebCenter Coherence communications, specify a different port number using the -Dtangosol.coherence.wka1.port and -Dtangosol.coherence.wka2.port arguments in the example above.
Repeat steps 1 and 2 for WC_Collaboration2, setting the localhost parameter to Host2 instead.
Restart the WC_Collaboration servers.
Step 2: Validate the changes
To validate the changes:
Log in to the Discussions Forum Administration Console at http://<host>:<port>/owc_discussions/admin.
Select Cache Settings in the left pane.
At the bottom of the screen, ensure that Clustering is set to Enabled.
Repeat steps 1 through 3 for all members of the cluster.
As servers join the cluster they appear at the top of the screen.
WebCenter Portal Applications are deployed on servers and clusters that are provisioned with the necessary libraries. This provisioning occurs by applying a domain template to an existing WebCenter Portal domain.
The extension can be done only once per domain. This means that any WebCenter Portal application servers must be either created at one time or as clones of existing WebCenter Portal application servers.
To configure a cluster to deploy WebCenter Portal applications:
Start Oracle Fusion Middleware Configuration Wizard from the ORACLE_HOME/common/bin directory using the following command:
APPHOST1> ./config.sh
In the Welcome screen, select Extend an Existing WebLogic Domain. Click Next.
In the next screen, select your Weblogic Domain Directory.
In the next screen, choose Extend my Domain using an existing Extension template.
Choose either of these two templates, depending on whether you are creating your own Framework applications or Portlet Producer applications:
For Framework applications:
$WC_ORACLE_HOME/common/templates/applications/oracle.wc_custom_portal_
template_11.1.1.jar
For Portlet Producer applications:
$WC_ORACLE_HOME/common/templates/applications/oracle.wc_custom_services_ producer_template_11.1.1.jar
Configure the new data sources (Custom Portal Activities, Custom Portal WebCenter, Custom Portal MDS) as Oracle RAC by selecting all the data sources and then checking the RAC datasources checkbox. The applications use existing schemas.
Enter the Database connection information and then check the status of the data sources.
In the Options Configuration Screen, select Managed Servers, Clusters and Machines.
In the Managed Servers screen:
If in step 5. you selected the custom_portal template, rename the managed server WC_CustomPortal to WC_CustomPortal_Cluster1. If you selected the custom_services_producer_template, rename the managed server WC_CustomServicesProducer to WC_CustomServicesProducer_Cluster1
Click Add to create a new managed server and name it WC_CustomPortal_Cluster2. Set the Listen Port to be the same as that of WC_CustomPortal_Cluster1.
In the Configure Clusters screen, add the cluster WC_CustomServicesProducer_Cluster1.
In the Assign Servers to Clusters screen, add the two newly created servers to the Cluster.
In the Assign Server to Machines screen, place each of the two servers on separate machines.
Click Extend and then Done to Extend the Domain.
You can now start the managed server using Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console and then deploy WebCenter Portal applications. Deploy these WebCenter Portal applications to the cluster target, not the managed server target.
You can add new servers to a domain only if it has been extended by cloning an existing server:
Access the Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console at http://APPHOST1:7001/console and log in.
In the Domain Structure window, choose Environment > Servers to show all the existing managed servers on the Summary of Servers page.
Select one of the custom managed servers. Click Clone.
Enter a server name (for example, WC_CustomPortal3). Set the Listen Address and Port where this new server resides.
The new server automatically becomes a member of the cluster (for example, WC_CustomPortalCluster).
For high availability WebCenter Portal applications, Oracle recommends that you configure distributed notifications for the MDS repository. For instructions on configuring distributed notifications for the MDS repository, see Appendix G, "Configuring Distributed Notifications for MDS."