| Oracle® Fusion Applications Concepts Guide 11g Release 6 (11.1.6) Part Number E15525-06 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Fusion Applications Concepts Guide 11g Release 6 (11.1.6) Part Number E15525-06 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter describes concepts important to understanding Oracle Fusion Applications.
This chapter contains the following topics:
Section 2.2, "Patching and Upgrading Oracle Fusion Applications"
Section 2.4, "Understanding Oracle Fusion Applications Home Directories"
Provisioning is the entire set of operations required to install, configure, and deploy applications product offerings from a system point of view. It performs these operations:
Installation provides the operations related to laying down all the component needed to create an Oracle Fusion Applications environment.
Configuration tailors components based on the applications topology, the creation of Oracle WebLogic Server Managed Servers and clusters, and the updating of endpoints and virtual hosts.
Deployment starts the Managed Servers and clusters and facilitates the actual use of product offerings.
This orchestration by a single processing engine ensures that all components interact smoothly and consistently in the applications environment.
For detailed information about provisioning and installing an Oracle Fusion Applications environment, see Oracle Fusion Applications Installation Guide.
This section contains the following topics:
You choose options from the Provisioning Wizard menu to initiate one installation-related processes:
Install an empty, single-instance Enterprise database
Create a new provisioning plan
Install, configure, and deploy the product offerings in a provisioning plan
Uninstall an existing environment
You must have installed and configured a transaction database before you install product offerings. You can use the Provisioning Wizard to create an empty, single-instance database instance. This is a discrete and separate task from the other provisioning options. Alternatively, you can install the database manually without using the wizard.
In either case, you finish the database installation by running the Oracle Fusion Applications Repository Creation Utility (Applications RCU) to load applications and middleware content into the database. This process creates the applications and middleware schemas, loads seed data, and creates the tablespaces, as well all other required packages.
For more information about creating a database with Applications RCU, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Installation Guide.
The Oracle Fusion Applications patching framework assists you in patching Oracle Fusion Applications, underlying Oracle Fusion Middleware dependencies, Oracle Fusion Middleware Extensions for Applications components, and Oracle Database instances provisioned with Oracle Fusion Applications.
For more information about patching Oracle Fusion Applications and the Oracle Fusion Applications patching framework, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Patching Guide.
Oracle Fusion Applications includes tools to assist you in upgrading from one Oracle Fusion Applications release to the next. Before starting the upgrade, a series of pre-upgrade tasks must be completed to prepare the environment for the upgrade. After the upgrade has been completed, post-upgrade tasks finalize the process and prepare the environment for use.
For more information about upgrading Oracle Fusion Applications, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Upgrade Guide.
See the "What Is an Oracle WebLogic Server Domain?" section in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Administrator's Guide to understand the following concepts for Oracle WebLogic Server:
Oracle WebLogic Server domains
Managed Servers and the Administration Server
During installation, the applications for a single product family are deployed to one Oracle WebLogic Server domain. Within a single domain, an Administration Server hosts the application for Fusion Applications Control and Oracle WebLogic Server Administration Console, and the Managed Servers host the Java EE applications for the product family. The Managed Servers are grouped together into a cluster for each application of the product family. Figure 2-1 shows a domain with an Administration Server and three Managed Servers in clusters. If you want to scale out the Java EE application, you simply add new servers to the cluster. In an Oracle Fusion Applications environment, the domains are predefined so that the product families and their dependencies are always stored in a standardized arrangement.
As an example of greater detail for a product family, Figure 2-2 shows a portion of the domain for the Oracle Fusion Financials product family with an Administration Server and eight Managed Servers in a cluster. The applications are each deployed to a Managed Server within a cluster. In addition to the applications for Oracle Fusion Financials, the domain also contains an Oracle Enterprise Scheduler cluster and a SOA cluster. The Oracle Enterprise Scheduler (ESSAPP) application manages job requests for the product family. The SOA Infrastructure (soa-infra) application hosts the SOA composites for the applications in the product family.
Figure 2-2 Oracle WebLogic Server Domain for the Oracle Fusion Financials Family
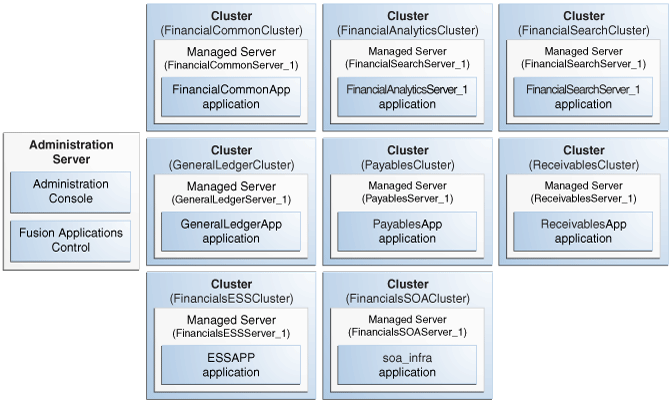
Figure 2-3 shows an Oracle Fusion Applications environment with multiple product families, each in separate Oracle WebLogic Server domains. The CommonDomain is the domain in the Oracle Fusion Setup product family.
See the "Understanding Key Concepts" chapter in the Oracle Fusion Middleware Concepts Guide for information about these home directory concepts:
Middleware home
Oracle home
Oracle Common home
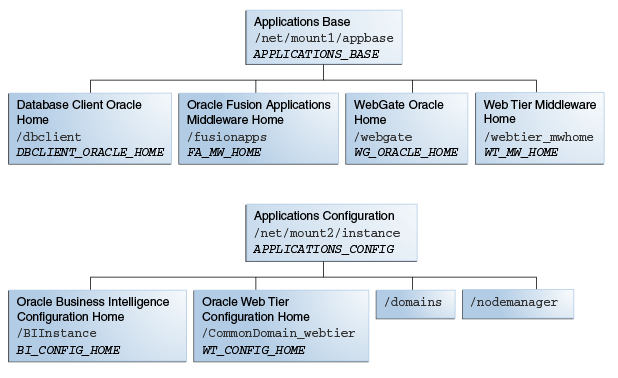
When an Oracle Fusion Applications environment is provisioned, two top-level directories are created: APPLICATIONS_BASE for the binaries and APPLICATIONS_CONFIG for the configuration files.
APPLCIATIONS_BASE contains two Middleware homes:
FA_MW_HOME contains home directories for Oracle WebLogic Server and Oracle homes for the Oracle Fusion Middleware components installed with Oracle Fusion Applications.
See the "Oracle Fusion Applications Directory Structure" section in the Oracle Fusion Applications Installation Guide for more information.
WT_MW_HOME contains system components, such as Oracle HTTP Server.
APPLICATIONS_BASE also contains the Oracle Database client home, represented as DB_CLIENT_HOME in Figure 2-4.
APPLICATIONS_CONFIG contains these home directories:
BI_CONFIG_HOME contains the configuration files for Oracle Business Intelligence.
WT_CONFIG_HOME contains the configuration files for the Oracle Web Tier.
/domains contains the DOMAIN_HOME for each product family. Each DOMAIN_HOME contains configuration files for the Administration Server and the Managed Servers for that product family.
/nodemanager contains configuration files for Node Manager.
Figure 2-4 shows the relationship of these home directories on a UNIX server.
Figure 2-4 Oracle Fusion Applications Home Directories
For more information about the directory structure and home directories, see the "Provisioned Oracle Fusion Applications Home Directories" section in the Oracle Fusion Applications Administrator's Guide.
For more information about the detailed directory structure, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Installation Guide.
An enterprise deployment is an Oracle best practice based on proven Oracle high-availability and security technologies and recommendations for Oracle Fusion Applications. The best practices span all Oracle products across the entire technology stack: Oracle Database, Oracle Applications, Oracle Fusion Middleware, Oracle Fusion Applications, Oracle Collaboration Suite, Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Middleware Control, and Oracle Enterprise Manager Fusion Applications Control, Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control, and Oracle Enterprise Manager Database Control.
For more information about enterprise deployment for Oracle Fusion Applications, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Customer Relationship Management Enterprise Deployment Guide.
Oracle Fusion Applications includes built-in security features. The default roles and security policies are designed to encompass common business needs. Role definitions, role hierarchies, data security, and segregation of duties policies can be changed or extended to meet the security needs of the enterprise.
Oracle Fusion Applications security is based on the following concepts:
Role-based access: uses job roles, duty roles, and abstract roles to assign access rights to application functions and date
Segregation of duties: separates actions, such as approving, recording, processing, and reconciling results, to limit the potential for unintentional errors and willful fraud
Consistent and transparent function and data security: makes data and application functions inaccessible to users by default, enabling access only when explicitly granted through roles necessary to access specific data or functions
Robust privacy protections: uses multiple levels of data privacy classification that work with data security policies to protect sensitive data
Native identity management and access provisioning: features Oracle Identity Management integration through Oracle Fusion Middleware allows for creating and managing user identities, creating and linking user accounts, managing user access control through user role assignment, managing workflow approvals and delegated administration
Enforcement across tools (all the tools use the same policies) and across the information lifecycle: uses common Oracle Fusion Applications security policies that are consistent across enterprise information access methods
Integration with Oracle Fusion Governance, Risk, and Compliance: provides critical business controls to manage risk multi-regulatory compliance and controls enforcement
An extensive reference implementation: uses a predefined business processes, roles, role memberships, entitlement, and policies that are secure as delivered
Standard tools to extend the footprint: uses a common set of tools to manage, edit, and expand the security features of Oracle Fusion Applications
For more information about security for Oracle Fusion Applications, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Security Guide.