11g Release 6 (11.1.6)
Part Number E16689-06
Home
Contents
Book
List
Contact
Us
|
Oracle® Fusion
Applications Security Guide 11g Release 6 (11.1.6) Part Number E16689-06 |
Home |
Contents |
Book List |
Contact Us |
|
Previous |
Next |
Enforcement Across Tools, Technologies, Data Transformations, and Access Methods: Explained
Enforcement Across Tools and Technologies: Points to Consider
Security Across Access Methods: How It Is Enforced
Enforcement of Security Policies: Points To Consider
The security infrastructures of a Oracle Fusion Applications deployment vary from one tool in the technology stack to another, however the security approach coordinates transactional and analytical security so that all security policies and controls prevail across access methods to enterprise information and transformations of enterprise information.
Oracle Fusion Applications enforces each single statement of security policy through the multiple transformations of data necessary for transactions, dimensional analysis, and search optimization.
Oracle Fusion Applications are secure no matter which technology accesses information during implementation, deployment, and maintenance.
The Oracle Fusion Applications technology stack addresses the following risks to security.
Complex combination of tools
Various technologies used by those tools
Transformations of data
Multiple access methods
User interfaces
Transactions across products
Batch processes
External Web services
Oracle Fusion Applications tools and technologies respect the security of your implementation or configuration across the changes you make to the deployment.
The changes you are likely to make involve the following:
Role definitions
Role provisioning
Data security
For example, if you remove the Accounts Payable Manager enterprise role from the roles provisioned to a user, the user should not be able to gain access to any of the resources that are provisioned by the Accounts Payable Manager role. Similarly, if you have provisioned a user with only the Accounts Payable Specialist role, the user should only have access to the resources provisioned by the Accounts Payable Specialist role.
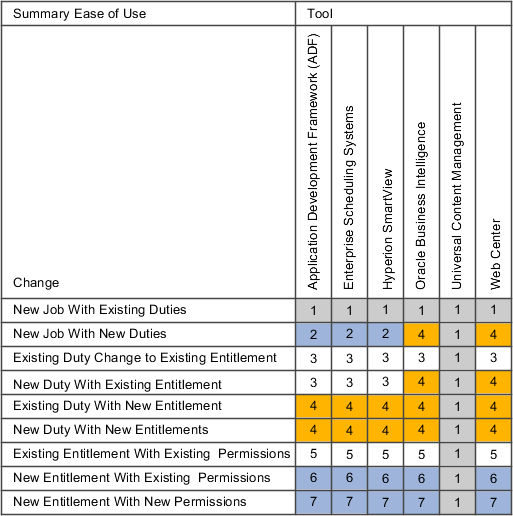
The heat map shows the ease of support from Oracle in assisting enterprises using the tools involved in reference implementation changes, where 1 is easiest and 7 most difficult. Application Development Framework represents the Oracle Fusion Applications user interface pages.
Oracle Fusion Applications includes a predefined data warehouse with some but not all dimensions secured. For example the department dimension is secured. A packaged goods enterprise with branding managers can enable security on branding resources in the product dimension. While there are no such policies predefined in the Oracle Fusion Applications reference implementation, creating such polices enforces security respected by the product dimension in the data warehouse.
Oracle Fusion Applications users access functions and data by the following means under the protection of their provisioned security policies.
Menu navigation
Worklists
Global area recent items and favorites
Oracle Fusion Search
Analytics
Tag clouds
Oracle Enterprise Scheduler jobs
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) business flows (Business Process Execution Language (BPEL))
Oracle Fusion Applications enforces security across the tools and technologies of the Oracle Fusion Applications technology stack. The Oracle Fusion Applications security approach is in effect in all tools and technologies used by Oracle Fusion Applications.
Oracle Fusion Applications uses the following tools and technologies.
Oracle WebCenter Content
Tags
Watch list
Search
Oracle Fusion Search
Enterprise Crawl and Search Framework (ECSF)
Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA)
Oracle Business Intelligence Applications (OBIA)
Oracle Transactional Business Intelligence (OTBI)
Business Intelligence (BI) Publisher
Enterprise Management
Oracle Enterprise Scheduler
Hyperion Enterprise Performance Manager (EPM)
Applications Security
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP)
Oracle Identity Manager
Content Server
Universal Content Manager (attachments to Oracle Fusion Applications objects, only)
Service Oriented Architecture (SOA) business flows (Business Process Execution Language (BPEL))
Application Development Framework (ADF)
Database Security
Extended Spread Sheet Database (ESSbase)
Hyperion SmartView
Virtual Private Directory (VPD)
Oracle Data Integrator (ODI)
Oracle Database 11g
Oracle Fusion Applications security enforcement across tools and technologies includes tags, and Watchlist in Oracle WebCenter.
The Application Development Framework (ADF) security framework handles authentication in WebCenter.
A WebCenter tag is a bookmark with user-defined keyword attributes that allow easily and repeatedly finding business objects. Tags are private or shared (public). A business object that is Oracle Fusion Search enabled can be tagged, but tagging a business objects does not make it search enabled. Users rename or delete their tags in the context of a specific resource using the tagging popup for the resource from where the tag first originated. WebCenter does not provide a user interface to users or administrators for managing all tags.
Tags in the cloud are sized according to the count of authorized documents.
Oracle Fusion Data Security secures database resources used with WebCenter tags. Oracle Fusion security enforces data security policies on the tags of each business object that is enabled for tagging. For example, Cost Center managers can view all purchase orders charged to their cost center and any tags to purchase orders that they have created or are publicly available.
Oracle Fusion Applications security enforcement across tools and technologies includes Oracle Fusion Search and Enterprise Crawl and Search Framework (ECSF).
Oracle Fusion Search is enabled on searchable business objects. If a user is entitled to view a business object in Oracle Fusion Applications, then that user can search against the business object in Oracle Fusion Search. For example, the Manage Warehouse Shipments privilege protects the Manage Warehouse Shipments task flow. The view permissions of the same privilege allow searching against the View Object that corresponds to the searchable business object Shipment Request.
Oracle Fusion Search enforces access entitlement to the data source being searched. Oracle Fusion Applications applies data security policies to search results.
The Oracle Fusion Search index does not contain personally identifiable information (PII) data. Non-PII private and sensitive attributes contained in the search index for search are protected by standard data security mechanisms
Oracle Fusion Applications security enforcement across tools and technologies includes Oracle Business Intelligence Applications (OBIA), Oracle Transactional Business Intelligence (OTBI), and BI Publisher of the Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA).
Oracle Fusion Applications data security policies protect dimensional analysis derived from transaction tables and data transformations. Analysis filters data according to the security policies that apply to the analyst's role.
Single Sign On (SSO) handles authentication in the Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA).
Both function and data security applies to OBIA and OTBI equally. OBIA and OTBI use the OBIFA security model to secure data. OBIFA View Objects are subjected to the protections of data security policies through Oracle Fusion Data Security.
OBIFA uses Oracle Fusion Applications job and abstract roles and synchronize with application roles from Oracle Platform Security Service (OPSS). Duty roles entitle access to OBIFA Subject Areas, Presentation Catalogs, Presentation Tables, Folders, Reports and Dashboards. In duty role hierarchies, the parent duty role provides assured revocation.
Virtual Private Database (VPD) policies secure personally identifiable information (PII) attributes in the Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) database.
OBIFA rarely collects metrics based on PII attributes. An extract, transfer, load (ETL) process enforces Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) Virtual Private Database (VPD) policies to protect exposed PII attributes.
Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA) mask data by first masking Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) and then running the BI extract, transfer, load (ETL) scripts that populate the BI warehouse. Since the ETL is run on a masked OLTP database, the data is masked in BI.
Oracle Fusion Applications uses OTBI for real-time operational reporting. Your enterprise can create ad hoc queries against the transactional Oracle Fusion applications schema to report the current state and analysis of your operations. OTBI serves as the content source (View Objects) for Oracle Fusion Applications embedded graphs, which are secured by the OBIFA security model.
The ADF Security framework handles authentication in Oracle BI Publisher. Oracle Platform Security enforces function security in Oracle BI Publisher. Duty roles entitled provisioned users with access to Oracle BI Publisher reports. Since the Oracle BI Publisher report prepares report data using an Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job (batch process), the privilege that secures the Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job also grants access to the report.
Data security policies protect Oracle BI Publisher content. All users provisioned with the Worker role can consume the Oracle BI Publisher generated reports to which they are authorized. However, for access to modify the layout and formatting of the report, users also must be provisioned with the BI Author role by means of their OTBI and OTBIA subject areas.
Oracle BI Publisher reports may expose PII data. Data security policies secure folders in which Oracle BI Publisher groups reports that expose PII data.
For creating or editing data models in Oracle BI Publisher, users must be provisioned with a role that is entitled with a privilege that includes the oracle.bi.publisher.developDataModel permission. While the BI Administrator role is so entitled, this role grants such broad access that it may not be prudent to provision it to users. Instead, create a new custom role that provides the entitlement of the BI Author role and additionally grants the oracle.bi.publisher.developDataModel permission.
Oracle Fusion Applications security enforcement across tools and technologies includes Oracle Enterprise Manager, Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service, and Hyperion Enterprise Performance Manager (EPM).
Single Sign On (SSO) handles authentication in Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service of the submitter of the job. Only authenticated users can submit Oracle Enterprise Scheduler jobs. For example, if user teller1 submits an Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job, the requested job runs as teller1 and is secured according to the provisioned roles and credentials of teller1.
Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service uses the Oracle Platform Security Service (OPSS) and secures its components using OPSS permissions. Oracle Fusion Applications embeds Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service components in the consuming application or invokes Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service APIs and services. The consuming application grants permission on the enclosing task flow to grant access to Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service submission requests.
Identity propagates throughout the entire life cycle of an Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job. When an Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job needs to access data to which the submitter is not entitled, the job is defined to run under an application identity that carries elevated privileges.
Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) enforce function security in Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service at the level of the submitting task flow. Access at the global level in Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service secures the job with the View Batch Jobs privilege provisioned to the Worker role. Duty roles carry entitlement to perform Oracle Enterprise Scheduler tasks. Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service also provides security on the metadata of a job, so Oracle Enterprise Scheduler permissions control the job or job set submission.
Data security policies secure database resources used with Oracle Enterprise Scheduler Service. An Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job accesses data that the submitting user is entitled to access or that the submitting application is entitled to access if the user's access is too limited. Submitting user information accompanies Oracle Enterprise Scheduler jobs for auditing purposes. Oracle Enterprise Scheduler jobs run using application identity will retain submitting user information also for auditing purpose as part of the payload. Application identity is part of Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job metadata definition.
If an Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job needs access to PII attributes, the user submitting the Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job, or the application identity running the Oracle Enterprise Scheduler job must have access to those PII attributes.
Oracle Access Manager handles authentication in Hyperion Enterprise Performance Manager (EPM).
EPM enforces function security in cube access managed through Extended Spread Sheet Database (ESSbase) Server. Access to ESSbase Server provides access to all cubes in that server. Permissions in Oracle Fusion Applications roles correspond to EPM roles.
ESSbase uses data security policies. EPM enforces data security with security filters on each cube in ESSbase.
PII attributes are not present in EPM.
Oracle Fusion Applications security enforcement across tools and technologies includes LDAP, Oracle Identity Manager, HCM security profiles, Oracle WebCenter Content, and Application Development Framework (ADF).
Oracle WebCenter Content uses SSO to authenticate access to the Content Server. When a user accesses Oracle Fusion Applications, the user's identity propagates to Oracle WebCenter Content. Security policy enforcement in Oracle WebCenter Content extends only to attachments on Oracle Fusion Applications objects, not to all content stored by Oracle WebCenter Content.
When user attaches a file to an object within the Oracle Fusion Applications, they can choose to mark the file as Shared or Not Shared. By default, text and file type attachments related to applications data are not shared and can only be viewed in Oracle Fusion Applications user interfaces. Oracle WebCenter Content user interfaces only gives access to shared files.
Note
Set the repositoryMode property to true to show the Shared column in the Attachments table.
Access to the owning table, such as for purchase orders, agreements, supplier accounts, and so on, secures the attachments. For example, by default a role that has access to the purchase order can see ALL attachments for the purchase order. As a result, users only have access to documents attached to data to which they are authorized. If a document is not viewable in the transaction system, it is also not viewable in the Content Management System
Access to attachment category additionally may secure attachments. For example, employee tax reports, payslips, and visa details are each attachment categories. Each employee can see their tax reports and payslips. A payroll professional user can see the tax reports for the people they manage but not visa details for those workers. An HR professional user can see the visa details for workers they are managing, but not payslips and tax reports for those workers.
If attachments are categorized, access may be secured by attachment category. In Procurement, data grants are based on attachment categories. For example, the Procurement Applications Administrator can only access attachments in attachment categories owned by Procurement.
Document Type security profiles protect attached HCM documents.
Data security policies protect access to privacy data based on Document Category.
Application Development Framework (ADF) is a framework of design pattern implementations and metadata-driven components used to build the Java EE Oracle Fusion Applications. ADF includes business components and faces, Web Services and attachments. ADF uses the Oracle Platform Security Service (OPSS).
The ADF instance running Oracle Fusion Applications supports the following security enforcement.
User authentication using Oracle Single Sign On (SSO)
Function security authorization using Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS)
Data security authorization using Oracle Fusion Data Security
Privacy
Oracle Fusion Data Security are used to secure database resources used with ADF and Web Services. Data security relies on the FND session to be properly initialized. The session initialization takes the user and role information from the security subject and stores it on the session. Data security uses the information from the session when deciding whether a user is authorized to access the data.
A common set of enterprise roles secures functions for Oracle Fusion Applications across all tools and technologies.
Oracle Fusion Applications security enforcement across tools and technologies includes Extended Spread Sheet Database (ESSbase), Hyperion SmartView, Oracle Database 11g, Oracle Data Integrator (ODI), and Virtual Private Directory (VPD).
SSO handles authentication in ESSbase, which accesses Hyperion SmartView on a client machine.
Oracle Fusion Applications security enforces function security on the ESSbase server, not separately on ESSbase cubes. Queries on an ESSbase cube access members of dimensions, such as business units and projects, that are authorized by Online Transaction Processing (OLTP).
Predefined duty roles that carry the EPM Admin permission provide administration access for all cubes in the server. Predefined duty roles that carry the EPM Filter permission provide read-only access to all cubes in the server and authorize view access to View Objects in SmartView.
Filters define which dimensions ESSbase secures. Data security policies enforce data access security on data stored within Essbase. SmartView in Excel and Financial Reporting access ESSbase and enforce data security policies defined with filters.
Changes to Oracle Fusion Applications data security through changes in role provisioning or data security policies propagate to ESSbase for each Oracle Fusion Applications session at the time the session is created and not through periodic synchronization.
PII attributes are not present in ESSbase.
Oracle Fusion Applications enforce security across various access methods.
The following access methods preserve the defined security of Oracle Fusion Applications functions and data.
Oracle Fusion Applications user interfaces
User sign on
User navigation
Scheduled processes
Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications
BI Publisher
External Web services
Authorization policies across all tools and technologies align with the Oracle Fusion Applications enterprise roles.
The following access methods in Oracle Fusion Applications are subject to entitlement, approvals, and policies.
Menu navigation where navigation paths are subject to an entitlement
Worklists where worklist content is subject to a privilege
Oracle Fusion Search where the data source is subject to a privilege and security policies have been applied to the results
Imbedded analytics where the data is filtered according to security policies that apply to a role
Tag clouds where a tag in the cloud is sized according to a count of authorized documents
These access methods are a valid way to access the data that you need and all respect the same security policies.
Access security is enforced using the features of the Oracle Fusion Applications security approach.
Specific enforcement details apply to the following access methods.
Single sign on (SSO)
Navigation paths
Scheduled processes
The Application Development Framework (ADF) instance running Oracle Fusion Applications supports SSO user authentication. Oracle Fusion Applications uses Oracle Access Management (OAM) for SSO.
The Policy Manager in Oracle Access Management supports the administrative tasks necessary to manage SSO and URL-based authentication and authorization policies. These policies have no relationship with OPSS policies that handle function security authorization.
SSO handles authentication in the following tools and technologies accessed by Oracle Fusion Applications.
Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications
Oracle Enterprise Scheduler
Oracle WebCenter Content
Extended Spread Sheet Database (ESSbase)
Hyperion SmartView
With SSO, a user who accesses a protected resource without having a current session cookie in the browser is redirected to the SSO server for authentication. Upon successful authentication, SSO places a session cookie in the user's browser cache.
Many targets are accessed through multiple navigation paths and roles. Oracle Fusion Applications tools and technologies secure the targets of access regardless of which navigation path is used.
Entitlement privileges secure navigation paths. For example, the common component Create Item securing the business process management (BPM) task Create Items must be navigated from different Work Areas based on the roles that execute the task.
|
User Type |
Job Role |
Navigation to Work Area (Path) |
BPM Task |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Producer |
Product Manager |
Product Management > Items |
Create Item |
|
Consumer |
Warehouse Manager |
Warehouse Operations > Inventory |
Create Item |
|
Consumer |
Cost Accountant |
Costing > Cost Accounting |
Create Item |
In the above example, for a user provisioned with the Product Manager role, the Create Item task should appear in the Items work area under the Product Management navigation path, whereas a user provisioned with the Warehouse Manager role should see the Create Item task in the Inventory work area under the Warehouse Operations navigation path.
Function and data security policies protect batch jobs.
Across the tools of the Oracle Fusion Applications deployment, the technologies may differ, but the Oracle Fusion Applications security approach enforces all security policies.
Oracle Fusion Applications security policies are respected in all tools and access methods.
Transactions
Analytics
Search
Oracle Fusion Applications data
Tag cloud
Note
With the exception of queries on personally identifiable information (PII) that are secured in the database through Virtual Private Database (VPD) policies, direct queries against the database are not secured.
For example, a manager is entitled through the privileges of provisioned roles to see expenses submitted by their direct reports. The manager sees the expenses in the expense review transactions, in the expense analytics transaction, through Oracle Fusion Search and through tag cloud navigation. The manager is not able to see expenses submitted by people who do not work for them and is prevented from seeing expenses not submitted by direct reports.
A manager sees expenses charged to their own cost center and any cost center managed by a person who reports to the manager.
Transactions, analytics, enterprise or tag navigation searches, and ad hoc queries consistently enforce security policies.
For example, if an information resource such as a purchase order is subject to the access policy that "Buyers can see purchase orders for the business units for which they are the authorized buyer," this data security policy applies to a user with that role regardless of the route the access takes, such as in metrics through Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA), in searches through Oracle Fusion Search, or in a business function through Oracle Fusion Applications.
Oracle Fusion Applications enforces access policies on the original transaction table, as well as on data transformations for dimensional analysis. For example, in reviewing payables transactions, an Accounts Payables Manager is able to view invoices by performing the View Accounts Payable Transactions action for the business units for which they are authorized. While performing the Accounts Payable Invoice Analysis action, the Accounts Payables Manager is able to analyze payables invoices for the business units for which they are authorized. An Accounts Payable Manager is able to view the same payables invoices whether they are reviewing payables invoices in the transactional system or analyzing payables invoices in the analytical system.
Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) and data security policies secure functions and data across technologies, such as ADF Entity Objects, View Objects, Page Definitions and Bindings, and search indexes securing Oracle Business Intelligence, Extended Spread Sheet Database (ESSbase), Web Center, and tag clouds.
The securing technologies of Oracle Business Intelligence Foundation Suite for Oracle Applications (OBIFA) security and Web Center authorization implement function security policies. Oracle Platform Security Services (OPSS) handles function security authorization across all tools and technologies.
View transaction privileges control view transactions across all technologies. Each privilege to secure a single real world action alone controls that action across all technologies. No other privilege secures that real world action.
The securing technology of Oracle Fusion Data Security, security plugins, and filters implement data security policies. Oracle Fusion Data Security handles data security authorization across all tools and technologies.
Documents that are not viewable in the transaction system are also not viewable in the Content Management System
The standard data security mechanisms across all Oracle Fusion Applications technology, tools, and access methods enforce security policies protecting privacy. Additional security mechanisms protect sensitive PII data.
PII data is not moved or transformed to less secure technologies. For example, PII data is not passed to Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) stores. If an Online Transaction Processing (OLTP) application is the source of the PII data, it is not passed to Oracle Business Intelligence Applications (OBIA) for exposure in metrics. If a non-OLTP application is the source of the PII data, it is passed to OBIA using extract, transfer, and load (ETL).
Oracle Identity Management (OIM) handles user and role provisioning across all tools and technologies. Oracle Fusion Applications security uses enterprise role and Oracle Identity Management to control access across all tools and technologies. All enterprise roles in Oracle Fusion Applications align with authorization policies across all tools and technologies.
Oracle Fusion Applications distinguishes between user identities and application identities (APPID). Predefined application identities serve to authorize jobs and transactions that require higher privileges than users.
Segregation of duties policies are enforced in all tools and access methods.
Oracle Fusion Applications consistently respects and enforces all security policies in the security reference implementation.
The security reference implementation can be viewed in the user interfaces where security tasks are performed or in the security reference manual (SRM) for each Oracle Fusion Applications offering.