11g Release 6 (11.1.6)
Part Number E20388-05
Home
Contents
Book
List
Contact
Us
|
Oracle® Fusion
Applications CRM Extensibility Guide 11g Release 6 (11.1.6) Part Number E20388-05 |
Home |
Contents |
Book List |
Contact Us |
|
Previous |
Next |
This chapter contains the following:
Extending CRM Applications: Top Tasks
Extending CRM Applications: How It Works
Extending CRM Applications Using Sandboxes: Highlights
Extending CRM Applications Across Application Boundaries: Explained
The Oracle Fusion CRM Application Composer is but one tool that lets you customize and extend your Oracle Fusion CRM applications. Before you start to extend and customize any application within Oracle Fusion CRM, refer first to the Oracle Fusion Applications Extensibility Guide to learn more about all the extensibility options and tools that are available to you.
The Oracle Fusion Applications Extensibility Guide walks you through the customization process for all Oracle Fusion applications, not just within Oracle Fusion CRM. After reviewing that guide, you can then review the Oracle Fusion CRM Extensibility Guide to understand in more detail how to use the Application Composer to extend and customize an application within Oracle Fusion CRM.
The Oracle Fusion CRM Application Composer is a browser-based configuration tool that enables business analysts and administrators, not just application developers, to customize and extend an Oracle Fusion CRM application. Make the type of data model changes which, for non-CRM applications, can only be made by application developers. For example, easily create a new object and related fields, then create new Enterprise pages where that object and its fields are exposed to users. The Application Composer is a design time at runtime tool, which means that you can navigate to the Application Composer directly from a CRM application, make your changes, and see most changes take immediate effect in real time, without having to sign back in to the application. Data model changes, such as the creation of custom fields, do require that you reauthenticate before you can see those changes.
The Application Composer hides the complexity of customization from business analysts by leveraging a set of standard design patterns and wizards. You focus on the application changes that your business requires (object model extensions and layout changes, for example), and the Application Composer creates the underlying object artifacts for you.
Access the Application Composer from any CRM application at runtime by using the Navigator menu, and selecting Application Composer under the Tools category. The first view of the Application Composer is the main Overview page, which is the entry point into all your customization options.

From the Application Composer's Overview page, you can make application changes such as:
Customize objects by adding new fields, or create entirely new objects.
Create foreign key-based relationships between two objects.
Customize Enterprise pages by exposing your newly created fields for an object, or create an entirely new work area for your newly created objects.
Expose object relationships on Enterprise pages in the form of subtabs or tree nodes.
Write application logic, such as triggers, validation rules, and workflows, for an object or for use across multiple objects.
Implement functional and data-level security for custom objects.
Enable objects for custom reporting.
To access the Application Composer, log in with the Customer Relationship Management Administrator job role. Then, select Application Composer under the Tools category in the Navigator menu to navigate to the main Overview page.
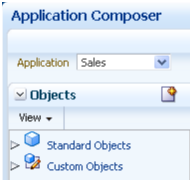
From the main Overview page, select the application you want to customize using the Application choice list. Then:
Use the object tree to select the object you want to customize, or click the New icon to create a new object.
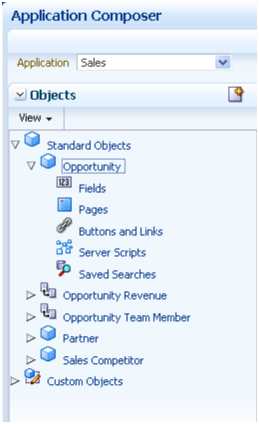
Use the links in main Overview page, also known as the local area, to select a customization task.
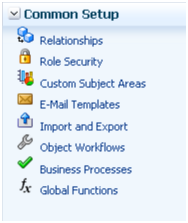
Or, use the links in the Common Setup pane.
Change the selected application in the Application choice list at any time to customize another CRM application.
The Application Composer is but one tool that lets you customize and extend your Oracle Fusion CRM applications. To learn more about extensibility options that are available to you across all Oracle Fusion applications, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Extensibility Guide.
When you customize and extend your Oracle Fusion CRM applications, you should always do so using sandboxes. Sandboxes let users make changes isolated from the mainline application, as well as from other sandboxes. (The mainline is the source of data and definitions used at the time of creating a new sandbox.) Business analysts can implement and test application customizations and, once satisfied, can publish them back to the mainline. When publishing a sandbox, the application customizations that you made in that sandbox overwrite the mainline application's existing configuration.
Before you start to extend and customize any application within Oracle Fusion CRM, refer first to the Oracle Fusion Applications Extensibility Guide to learn more about all the extensibility options and tools that are available to you, including sandboxes. After reviewing that guide, you can then review Customizing Oracle Fusion CRM Applications Using Sandboxes (1487832.1) on My Oracle Support at https://support.oracle.com.
Note
Whenever possible, always make your application customizations in sandboxes first, and then publish your changes back to the mainline application. In general, you should not make software changes directly in the mainline unless sandboxes are not available for your particular customization.
When you customize and extend your Oracle Fusion CRM applications, you always do so within the context of a Web application, such as Oracle Fusion Sales or Oracle Fusion Marketing. This is a critical selection that you must remember, because the customizations that you make reside within that application only. For example, to create a new custom object, you first select an application on the main Overview page of the Application Composer. The new custom object will belong only to the application that you select.
Note
When you first open the Application Composer, the default application is always Common. If you previously made customizations in another application, such as Sales, then you must manually change the application using the Application choice list to Sales, before you can review and update those customizations.
Web applications are also referred to as application containers.
The types of changes that you can make in the Application Composer can be categorized into three areas:
User interface extensions
Object model extensions
Scripting extensions
The concept of application containers directly impacts what you can do when making the above types of changes using the Application Composer.
User interface extensions
For example, can I add a subtab to an opportunity's page that displays sales lead records?
Object model extensions
For example, can I create relationships between objects that exist in different Web applications?
Scripting extensions
For example, for the opportunity object, can I create a trigger whose underlying expression references an object in Oracle Fusion HCM?
The special considerations that you must be aware of when extending and customizing across Web application containers are described in Oracle Fusion Applications CRM Extensibility: Special Considerations (1490074.1) on My Oracle Support at https://support.oracle.com.