 Overview
Overview
This appendix provides an overview and features of the Regulatory Reporting Center and discusses the generation of PeopleSoft exported files for FRS products.
 Overview
Overview
PeopleSoft has an interface from Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) to FRS, a third party profitability and regulatory reporting solution. The FRS regulatory reporting system takes data from a bank's System of Record (SOR) and converts it to the required format and structure for reporting to regulatory agencies.
With this module, PeopleSoft delivers a set of components that allow you to map general ledger account and instrument balances into legal/regulatory reporting business units (RBUs) and assign FRS product and type (profit/loss) codes. The resultant mapped records then are available to FRS via a PeopleSoft generated file.
The following high-level diagram highlights the overall data processing flow and functionality. The objects in gray represent new elements comprising this new module.
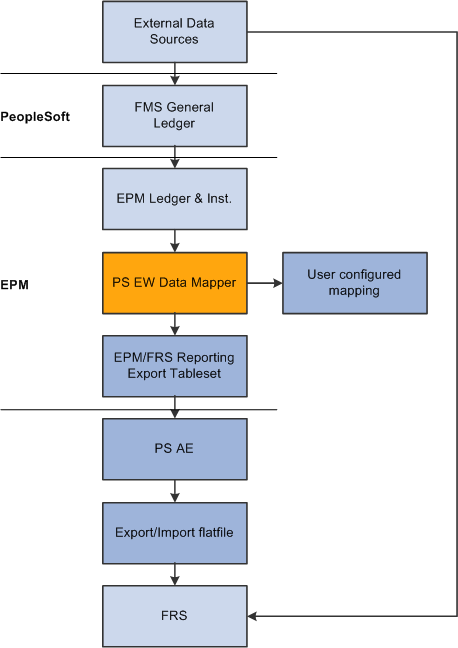
Data processing flow overview
The External Data Sources object represents the System of Record as well as any other external sources of financial and relationship data.
The User Configured Mapping represents the module that allows you to define the mapping of your ledger and instrument balances into FRS product, type (profit/loss) codes and regulatory reporting business units.
PeopleSoft supplies a set of export tables suitable for import into FRS.
 Features
Features
The features of the Regulatory Reporting Center allow you to:
Map to PS ledger accounts and instrument balances into legal/regulatory reporting business units, and into FRS product and type (profit/loss) codes.
Use Application Engine programs to populate PS defined Report Export tables with data from PS ledger accounts and instrument balances based on implementation defined maps.
Generate ASCII flat files suitable for import into FRS.
Use pages to enter and maintain FRS product and type (profit/loss) codes.
Use a set of pages to review the results prior to posting to FRS.
Assign records for either 1:1 mapping or aggregation by legal/regulatory reporting business units which may, or may not, correspond to the business unit used for internal purposes.
The following flowchart displays the data flow in greater detail.
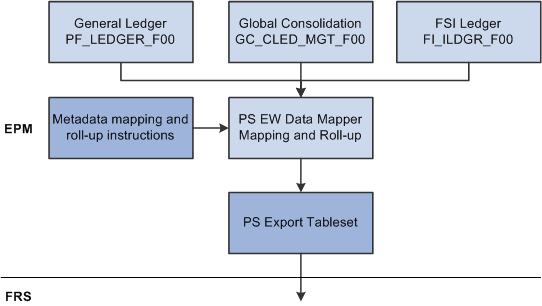
Detailed data flow
The system processes only one of the following source tables for a given run:
PS General Ledger (PF_LEDGER_F00)
Global Consolidation (GC_CLED_MGT_F00)
FSI Ledger (FI_ILDGR_F00)
 The Regulatory Reporting Center
The Regulatory Reporting CenterAccess the Regulatory Reporting Center page from Main Menu, Financial Services Industries, Regulatory Reporting Center.
Product Codes
The PeopleSoft Regulatory Reporting Center includes all 635 FRS Product Codes pre-loaded. To accommodate new codes and changes, the system allows you to edit the codes.
Access the Product Codes page from Main Menu, Financial Services Industries, Regulatory Reporting Center, Product Codes.
Note. You can retrieve FRS product codes by product: code, category, or class.
Note. All product codes are effective-dated.
Profit/Loss Codes
Like the FRS Product Codes, PeopleSoft has already loaded all 126 FRS Profit/Loss codes. And like the product codes, the FRS P/L code list can be edited.
Access the FRS Profit/Loss Codes page from Main Menu, Financial Services Industries, Regulatory Reporting Center, Profit/Loss Codes.
Note. You can retrieve FRS P/L Codes by product: code or class.
Note. Like FRS Product Codes, FRS Profit/Loss Codes are effective-dated.
Regulatory Reporting Business Units (RBUs)
Access the Reporting Business Unit page from Main Menu, Financial Services Industries, Regulatory Reporting Center, Reporting Business Unit.
Select the Add a New Value tab to add a new regulatory reporting business unit. For the purposes of this example, you'll create a new regulatory reporting business unit to track one of your legal entities, in this case a RBU called 001 Sheet Corp.
Click the Save button to save your newly-defined entry.
Access the Instrument Level page from Main Menu, Financial Services Industries, Regulatory Reporting Center, Results, Instrument Level.
Note. You can click the Previous in List and Next in List buttons to move through the list.
Performance Ledger
Access the Performance Ledger page from Main Menu, Financial Services Industries, Regulatory Reporting Center, Results, Performance Ledger.
Access the Global Consolidations Ledger page from Main Menu, Financial Services Industries, Regulatory Reporting Center, Results, Global Consolidation.

 Generating Regulatory Reporting Export Files
Generating Regulatory Reporting Export FilesThe FRS Connector is essentially a set of three stage AE processes consisting of a Data Mapper stage, an AE job to roll-up accounts by regulatory reporting business units, and an AE job to generate the resulting import files. Basically the job begins with one of the three views as input and results in one of three import flat files.
In the following diagram, items in gray text are predefined. Items in black text need to be defined as part of an implementation.
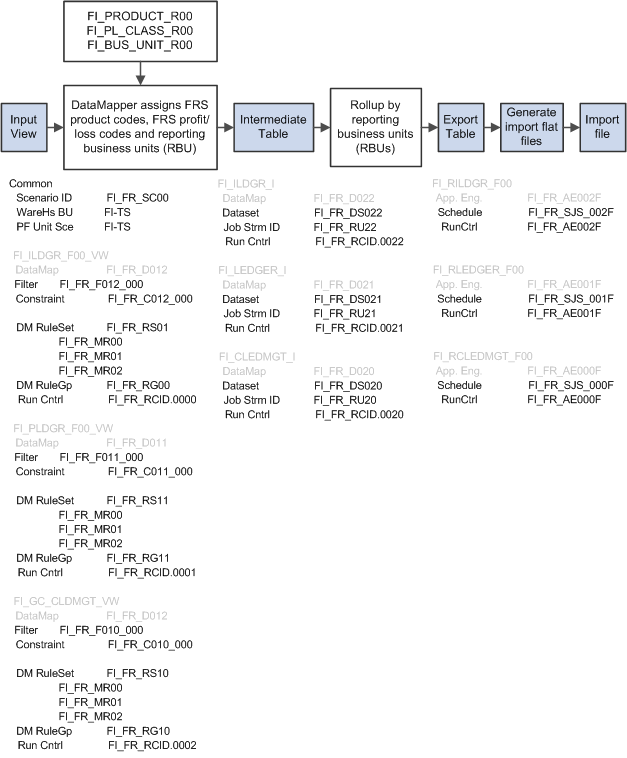
The FRS Connector process flow and implementation-required metadata definitions.
|
Predefined |
||
|
Ledger Type |
Source View |
Output Files |
|
FSI Instrument Ledger |
FI_ILDGR_F00_VW |
FI_RILDGR_F00.CSV |
|
PS General Ledger |
FI_PLDGR_F00_VW |
FI_RLEDGER_F00.CSV |
|
Global Consolidation |
FI_GC_CLDMGT_VW |
FI_RCLEDMGT_F00.CSV |
|
Example of Implementation—Defined Run Controls |
|||
|
Ledger Type |
Data Mapper Job |
RBU Roll-Up Job |
Output File Generator |
|
FSI Instrument Ledger |
FI_FR_RCID.0000 |
FI_FR_RCID.0022 |
FI_FR_AE002F |
|
PS General Ledger |
FI_FR_RCID.0001 |
FI_FR_RCID.0021 |
FI_FR_AE001F |
|
Global Consolidation |
FI_FR_RCID.0002 |
FI_FR_RCID.0020 |
FI_FR_AE000F |
Steps to generating export files for regulatory reporting systems
Initial Implementation and infrequent changes:
Ensure that FRS Product and Profit/Loss code lists are current for your implementation.
Define regulatory RBUs.
Ensure that any and all Performance and Warehouse business units are defined.
Define any and all scenarios that will be associated with the export runs.
Define any and all filters and constraints for: PS General Ledger (DataMap: FI_FR_D011), Global Consolidation (DataMap: FI_FR_D010) and FSI Ledger (DataMap: FI_FR_D012).
Define Data Mapper Rule Sets.
Define Data Mapper Value Mappings (if required).
Define Data Mapper Rule Groups.
Define all metadata Data Sets for roll-ups by RBU.
Define Run Control Templates for Data Mapper and RBU roll-ups.
Set Data Mapper Run Control Values corresponding to the Run Control Templates.
Set Regulatory Reporting Center Runtime Parameters corresponding to the RBU roll-up Run Control Templates.
Define Process Scheduler processes and jobs for generating import files from the export tables.
For each run:
Run the Data Mapper job for the source table, period, regulatory RBU and ledger (that is, FI_FR_RCID.0000, FI_FR_RCID.0001 or FI_FR_RCID.0002).
Note. Since non-RBUs (performance business units) might have a many-to-one relationship to the RBU, you might have to run the Data Mapper more than once (that is, once for each BU in a RBU) prior to running the RBU roll-up job.
Run the corresponding RBU roll-up (that is, FI_FR_RCID.0022, FI_FR_RCID.0021 or FI_FR_RCID.0020).
Review the resulting RBU roll-ups. (optional)
Run the corresponding import file generating AE (that is, FI_FR_AE002F, FI_FR_AE001F or FI_FR_AE000F).
For the purposes of illustration, this document will provide an example covering steps 6 - 13 (in the Initial Implementation and infrequent changes section) and 1 - 4 (in the For each run section). The example will not cover steps 1 - 5 (in the Initial Implementation and infrequent changes section) as they are covered in detail in other PeopleSoft documents.
For each of the following predefined datamaps, at least one constraint must be defined:
|
Predefined |
||
|
Ledger Type |
Source DataMap |
Target DataMap |
|
FSI Instrument Ledger |
FI_FR_D012 |
FI_FR_RCID.0022 |
|
PS General Ledger |
FI_FR_D011 |
FI_FR_RCID.0021 |
|
Global Consolidation |
FI_FR_D010 |
FI_FR_RCID.0020 |
Defining Data Mapper Rule Sets
Access the Data Mapper Rule Set page from Main Menu, EPM Foundation, Data Enrichment Tools, Data Mapper, Rule Set, Data Mapper Rule Sets.
For FSI Instrument Ledger, select the predefined FI_FR_D012 and FI_FR_D022 datamaps for the Source Datamap and Target Datamap fields, respectively.
|
Predefined |
||
|
Ledger Type |
Source Datamap |
Target Datamap |
|
FSI Instrument Type |
FI_FR_D012 |
FI_FR_D022 |
|
PS General Ledger |
FI_FR_D011 |
FI_FR_D021 |
|
Global Consolidation |
FI_FR_D010 |
FI_FR_D020 |
Note. Since the Reporting business unit, FRS Product Code, and FRS profit/loss class fields in the Target Column do not have a corresponding Source Column, you need to specify either a mapping rule or a list. You can select the Field Mapping Rule tab to define a mapping rule.
Access the Field Mapping Rule page from Main Menu, EPM Foundation, Data Enrichment Tools, Data Mapper, Rule Set, Field Mapping Rule.
For this example, you'll associate the FRS Product Code field in the Target Columns field with the Account field from the Source Columns. Later you will map specific values between the two columns. Then click the + to continue and do the same to associate FRS Profit/Loss Classes and Reporting Business Units with columns from the source datamap. Finally, click Save to save the Data Mapper Rule Set definition.
Defining Data Mapper Rule Sets
Access the Data Mapper Value Mappings page from Main Menu, EPM Foundation, Data Enrichment Tools, Data Mapper, Value Mappings.
Value Mappings assign specific Target Column values based on values present in the Source Column.
Note. Looking up your previously defined Map Rules in your Map Rule Set, select FI_FR_MR00.
In this instance, the system associates a value of 10000 in the Account column of the source datamap to a value of 110000 in the FRS Product Code column of the target datamap. The Data Mapper processes rows every time it encounters a row with a value of 10000 in the Account field of the source table and it places a value of 110000 in the FRS Product Code field of the target table. Continue this pattern, mapping all expected Account values in the Source datamap to FRS Product Code values in the target datamap.
Defining Data Mapper Rule Groups
After defining Rules, Rule Sets and any necessary value maps, you must define rule groups.
Access the Data Mapper Rule Group from Main Menu, EPM Foundation, Data Enrichment Tools, Data Mapper, Rule Group, Data Mapper Rule Group.
Note. You define a new Data Mapper Rule Group FI_FR_RG00. This rule group contains the previously defined Rule Set FI_FR_RS01.
.
Defining MetaData Sets to be Used to Generate Roll-Ups by RBU
Access the DataSet page from Main Menu, EPM Foundation, Foundation Metadata, Metadata Creation and Editing, DataSet.
Use datasets to specify how records are totalled into corresponding RBUs based on your previously defined Data Mapper definitions.
See Using Data Sets.
For FSI Instrument Ledger, you select the predefined FI_FR_C022_000 constraint for the Constraint field. This brings up a list of all predefined fields. You then assign Aggregate Types to set the RBU summation policy.
Note. You need to select every field for inclusion.
|
Ledger Type |
Predefined Constraint |
|
FSI Instrument Ledger |
FI_FR_C022_000 |
|
PS General Ledger |
FI_FR_C021_000 |
|
Global Consolidation |
FI_FR_C020_000 |
Defining Run Control Templates for Data Mapper and RBU Roll-Up Stages
Access the Run Jobstream page from Main Menu, EPM Foundation, Job Processing, Update/Run Jobstreams, Run Jobstream.
Assign the Run Control for the Data Mapper job. Set the Unit to the previously defined regulatory reporting business unit (RBU). Set the Scenario ID to the previously defined scenario. Set the Fiscal Year to the fiscal year of the data to be mapped. Set Period to the period to be used to filter source records for summation into the RBU.
Note. Set the Jobstream ID to the predefined FI_FR_JM00 job stream. Use this job stream for all three ledger types.
Now that you have defined the Run Control for the Data Mapper, you will need to define a Run Control for RBU roll-up. Define the Run Controls for the RBU roll-up on the Run Jobstream page.
Set the Unit, Scenario ID, Fiscal Year, and Period fields to the same values as the previously defined Run Control to be used by the Data Mapper. Unlike the Run Control used by the Data Mapper, you specify a different Jobstream depending on the ledger you're processing. For this FSI Instrument Ledger example, you specify FI_FR_RU22 for the Jobstream.
|
Ledger Type |
Predefined Jobstream |
|
FSI Instrument Ledger |
FI_FR_RU22 |
|
PS General Ledger |
FI_FR_RU21 |
|
Global Consolidation |
FI_FR_RU20 |
Setting Data Mapper Run Control Values
Access the Run Group page from Main Menu, EPM Foundation, Data Enrichment Tools, Data Mapper, Run Control Values, Run Group.
Here you assign the previously defined Rule Group to the Run Control that will be used to run the Data Mapper.
Setting Regulatory Reporting Center Runtime Parameters
Access the Roll-up runtime parameters page from Main Menu, Financial Services Industries, Regulatory Reporting Center, Reporting Setup, Roll-up runtime parameters.
Assign the previously defined DataSet FI_FR_DS022 to the Run Control that will be used to run the RBU Roll-up stage.
Defining Process Scheduler Processes and Jobs
Access the Process Definition page from Main Menu, PeopleTools, Process Scheduler, Processes, Process Definition.
Define a new Application Engine process FI_FR_AE002F.
Access the Process Definition Options page from Main Menu, PeopleTools, Process Scheduler, Processes, Process Definition Options.
Select on the Process Definition Options tab, assign ALLPNLS to Process Groups.
|
Ledger Type |
Predefined AE Job |
|
FSI Instrument Ledger |
FI_FR_AE002F |
|
PS General Ledger |
FI_FR_AE001F |
|
Global Consolidation |
FI_FR_AE000F |
Access the Job Definition page from Main Menu, PeopleTools, Process Scheduler, Jobs, Job Definition.
Assign Application Engine to Process Type and the predefined Application Engine program FI_FR_AE002F to Process Name.
Access the Job Definitions Options page from Main Menu, PeopleTools, Process Scheduler, Jobs, Job Definition Options.
Select the Job Definition Options tab, assign ALLPNLS to Process Groups.
Access the Schedule JobSet Definition page from Main Menu, PeopleTools, Process Scheduler, Schedule JobSet, Schedule JobSet Definition.
Specify the previously defined job: FI_FR_02.

 Generating Instrument Level Export File
Generating Instrument Level Export FileTo generate the Instrument Level Export File, run the following implementation defined jobs:
FI_FR_RCID.0000 – Data Mapper job for the source table, period, regulatory reporting business unit and ledger.
Note. Since non-RBUs (performance business units) might have a many-to-one relationship to the RBU you might have to run the Data Mapper more than once (that is, once for each BU in a RBU) prior to running the RBU roll-up job.
FI_FR_RCID.0022 – The corresponding RBU roll-up.
FI_FR_AE002F – The corresponding import file generating AE.

 Generating Performance Ledger Export File
Generating Performance Ledger Export FileTo generate the Performance Ledger Export File, run the following implementation defined jobs:
FI_FR_RCID.0001 – Data Mapper job for the source table, period, regulatory reporting business unit and ledger.
Note. Since non-RBUs (performance business units) might have a many-to-one relationship to the RBU you might have to run the Data Mapper more than once (that is, once for each BU in a RBU) prior to running the RBU roll-up job.
FI_FR_RCID.0021 – The corresponding RBU roll-up.
FI_FR_AE001F – The corresponding import file generating AE.

 Generating Global Consolidation Export File
Generating Global Consolidation Export FileTo generate the Global Consolidation Export File, run the following implementation defined jobs:
FI_FR_RCID.0002 – Data Mapper job for the source table, period, regulatory reporting business unit and ledger.
Note. Since non-RBUs (performance business units) might have a many-to-one relationship to the RBU you might have to run the Data Mapper more than once (that is, once for each BU in a RBU) prior to running the RBU roll-up job.
FI_FR_RCID.0020 – The corresponding RBU roll-up.
FI_FR_AE000F – The corresponding import file generating AE.