2 Getting Started with the Oracle SES Administration GUI
This chapter provides a brief introduction to using Oracle Secure Enterprise Search (Oracle SES). More information about the Oracle SES Administration GUI is provided later in this book and in the online Help.
This chapter contains the following topics:
Getting Started Basics for the Oracle SES Administration GUI
After you have successfully installed Oracle SES, you can define your data sources and start crawling them. The following are general procedures.
To open the Oracle SES Administration GUI:
-
Open a browser and enter the URL for the Oracle SES Administration GUI. This URL is provided after the installation and has the form
http://host:port/search/admin/index.jsp -
Log in with the user name
searchsysand the password specified during installation.
To administer Oracle SES:
-
Define one or more sources for the data you want to search.
For example, if your data is stored in Web pages, then select Web source.
-
Check the crawler progress and status on the Home - Schedules page. Click Refresh Status. From the status page, you can view the statistics of the crawl.
-
Monitor the search statistics on the Home - General page and the Home - Statistics page.
The following procedures expand these steps.
Note:
For specific information about a source, see Part I, "Creating Data Sources".To create a source:
-
On the home page, select the Sources secondary tab to display the Sources page.
-
Select a source type.
-
Click Create to display the Create Source page.
-
Complete the page. Click Help for a description of each item.
-
Click Create or Create & Customize.
A crawl schedule is automatically created along with the source. If you select Start Crawling Immediately, then the crawler starts crawling when you click Create.
To customize a source:
-
When creating a source, click Create & Customize on the Create Source page to display the Customize Source page.
or
After creating a source, click the Edit icon for the source on the Home - Sources page.
-
Click the subtabs and make the desired changes.
-
Click Apply.
To crawl and index an existing source:
-
On the home page, select the Schedules secondary tab to display the Crawler Schedules page.
-
Select the schedule.
-
To set up the frequency and other crawling options for one or more sources, click Edit. (Optional)
-
Click Start to start crawling.
-
To test whether users can search a source, click the Search link in the upper right of any page.
This link displays the search page in a new window. The URL for Search has the form
http://host:port/search/query/search.
Understanding the Oracle SES Administration GUI
The Oracle SES Administration GUI provides many options for managing and customizing Oracle SES to suit your enterprise. This section describes some tasks you can accomplish using the Oracle SES Administration GUI.
Home Tab
The Home tab consists of the General, Sources, Schedules, and Statistics secondary tabs.

Description of the illustration ''home.gif''
-
Home - General
This is the home page for Oracle SES. The Summary section shows an overview of the system's search performance, both quality and speed, over the past seven days. The Failed Schedules section lists all schedules that have failed. A failed schedule is one in which the crawler encountered an irrecoverable error, such as an indexing error or a source-specific login error, and cannot proceed. A failed schedule could be because of a partial collection and indexing of documents.
-
Home - Sources
A collection of information is called a source. Each source has a type, such as a Web site or a database table. User-defined source types are created on the Global Settings - Source Types page. The list includes any available user-defined source types. You can create as many sources as you want.
-
Home - Schedules
This page lets you view, edit, create, delete, stop, or start a schedule. Schedules define the frequency at which the index is updated with information about each source.
-
Home - Statistics
This page provides numerous search and crawler statistics, such as most popular queries and crawler progress.
Some statistics constantly show up-to-date information, while others are cached hourly to improve performance. The Last Refreshed time shows the actual time of the statistics displayed. Check the online help for each statistics page to confirm if the statistics are up-to-date or cached hourly.
Search Tab
The Search tab consists of the Relevancy, Suggested Links, Suggested Content, Alternate Words, and Source Groups secondary tabs. These pages help you improve search quality.

Description of the illustration ''search.gif''
-
Search - Relevancy
Make important documents easier to find with relevancy boosting. Oracle SES lets you influence the order of documents in the result list for a particular search. For example, your company Web site could have a home page for documentation that should appear high in the results of any search for
documentation. -
Search - Suggested Links
Direct users to a particular Web site for a search string. For example, when users search for "Oracle SES documentation" or "Enterprise Search documentation" or "Search documentation", you could suggest
http://www.oracle.com/technology. In the default search page, suggested links are displayed at the top of the search result list. This is especially useful to provide links to important Web pages that are not crawled by Oracle SES. -
Search - Suggested Content
Suggest actual content (as opposed to links) to be displayed along with the result list. For example, when an end user searches for contact information on a coworker, Oracle SES fetches the content from the suggested content provider and returns the contact information (e-mail address, phone number, and so on) for that person with the result list. Suggested content results appear in tabbed panes above the query results.
-
Search - Alternate Words
Use alternate words to suggest alternative search queries to users. This is useful for fixing common errors that users make in searching (for example, entering Oracel instead of Oracle). Also, synonyms can provide more relevant results; for example, cellular phones for cell phones or wireless phones. Additional uses for alternate keywords are for product code names and abbreviations.
-
Search - Source Groups
Source groups are groups of sources that can be searched together. A source group consists of one or more sources, and a source can be assigned to multiple source groups. On the basic Search page, users can browse source groups that the administrator created. If no source group is selected, then all documents are searched.
Global Settings Tab
The Global Settings tab includes links to configure settings for your Oracle SES environment.
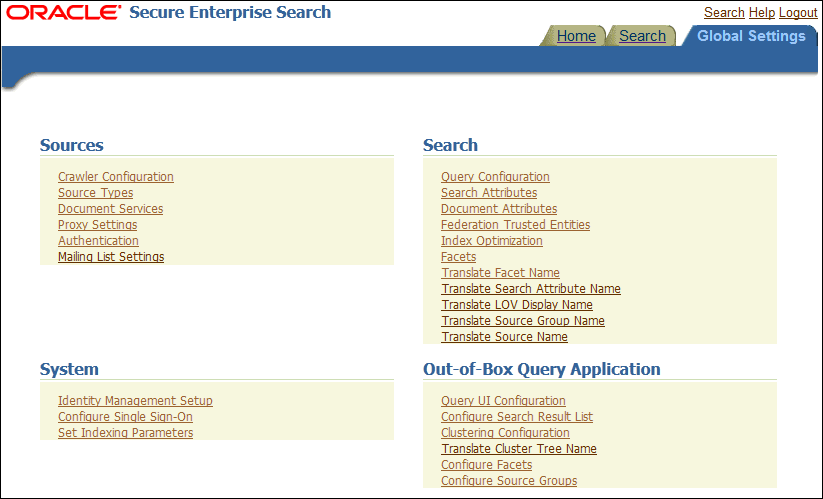
Description of the illustration ''global10182.gif''
This section describes some global configuration pages.
-
This page configures global crawler settings, such as crawling depth, language, and maximum document size.
After a source has been created, you can define crawling parameters, such as URL boundary rules and crawling depth, for that source by editing that source on the Home - Sources page.
-
This page includes several options, including the following: maximum number of results returned, display URL, spell checking, statistics collection, URL submission, federated search, and secure search.
-
Identity Management Setup
This page lets you set up connections between Oracle Secure Enterprise Search and any identity management system to validate and authenticate users. This is necessary for secure searches. Oracle SES uses an identity plug-in as an interface to an identity management system.
-
Configure Search Results List
This page lets you customize the look and feel of the search result list using XSLT and CSS style sheets.
-
Configure Clustering in Search Results
Real-time clustering organizes search results into various groups to provide end users with different views on the top results. Clustered documents within one group (called a cluster node) share the same common topics or property values. A cluster node with a large document set can be categorized into child cluster nodes, and a hierarchy cluster result tree is built. Users can navigate directly to a specific cluster node or refine their query by combining the original query and cluster results.
-
Configure Facets in Search Results
The facets are used in refining the query results in the query application by using the facet panel and the facet navigation bar. The faceted search provides the mechanism for filtering data in a search result based on the categorization and sub-categorization of data. The various categories of data can be considered as facets, and for each category, the sub-categories are called facet nodes. Thus, a hierarchy of facet tree is built. Users can navigate directly to a specific facet node or refine their query by combining the original query with the facet search results.
The pages - Facets, Translate Facet Name, and Configure Facet Name - let you configure facets by providing the facet related operations, such as, creating, updating, deleting, enabling and disabling, setting visibility parameters, and translating facet names to different languages.
-
Configure Source Groups
This page lets you configure the display properties of facets, cluster trees, top-n sortable attributes, top-n groupable attributes, and Absolute sorting criteria (default sort conditions and sortable attributes) for a source group that is enabled to be displayed in the query application.
-
Configure Single Sign-On
This page configures one of the following Single Sign-On (SSO) authentication mechanisms for Oracle SES:
-
Oracle Access Manager (OAM)
-
Oracle Single Sign-On (OSSO)
-
Windows Native Authentication (WNA)
-
See Also:
-
Oracle SES Administration Tutorial for help with common administrator tasks
-
Oracle SES Administration GUI context sensitive online Help
-
Oracle SES home page for updated information on known issues, code samples, and best practices:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/search/oses/overview/index.html
Starting and Stopping Oracle SES Instance
You can start and stop the Oracle SES instance (Oracle SES server, Oracle ESS server, WebLogic server, and Database server) using any of the following methods:
Note:
In the previous Oracle SES releases, the Oracle SES home was referred to asORACLE_HOME. In this release, the Oracle SES home is referred to as ses_home. The ses_home directory is created under the mw_home directory. When Oracle SES 11.2.2.2 is installed along with the WebLogic Server middle tier, the ses_home directory is mw_home/Oracle_SES1.
In this release oracle_home refers to the directory where the database component specific to Oracle SES software is installed.
Refer to "Conventions" for more information.
Using WebLogic Administration Console
You can start and stop the Oracle SES middle tier components (WebLogic Server, Oracle ESS Server, and Oracle SES Server) using the WebLogic Administration Console.
Using WebLogic Server Scripts
You can use the following WebLogic Server scripts to start and stop the Oracle SES middle tier components (WebLogic Server, Oracle ESS Server, and Oracle SES Server):
| Description | WebLogic Server Script |
|---|---|
| Start WebLogic Server | wls_domain_home/ses_domain_name/startWebLogic.sh |
| Stop WebLogic Server | wls_domain_home/ses_domain_name/bin/stopWeblogic.sh |
| Start Oracle SES server | wls_domain_home/ses_domain_name/bin/startManagedWebLogic.sh ses_servar_name |
| Stop Oracle SES server | wls_domain_home/ses_domain_name/bin/stopManagedWebLogic.sh ses_server_name admin_URL user_name password |
| Start Oracle ESS server | wls_domain_home/ses_domain_name/bin/startManagedWebLogic.sh ess_server_name |
| Stop Oracle ESS server | wls_domain_home/ses_domain_name/bin/stopManagedWebLogic.sh ess_server_name admin_URL user_name password |
Using searchctl Command
You can use the searchctl command for starting and stopping the Oracle SES instance, only when both the Database and the WebLogic Server middle tier are installed as part of the Oracle SES software installation.
The searchctl executable is located in the ses_home/bin directory:
$ses_home/bin/searchctl
The searchctl command syntax is as follows.
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
searchctl start |
Start Oracle SES server |
searchctl stop |
Shut down Oracle SES server |
searchctl restart |
Restart Oracle SES server |
searchctl start_midtier |
Start WebLogic Server middle tier |
searchctl stop_midtier |
Shut down WebLogic Server middle tier |
searchctl restart_midtier |
Restart WebLogic Server middle tier |
searchctl start_backend |
Start Database server |
searchctl stop_backend |
Shut down Database server |
searchctl restart_backend |
Restart Database server |
searchctl startall |
Start Oracle SES server, WebLogic Server middle tier, and Database server |
searchctl stopall |
Stop Oracle SES server, WebLogic Server middle tier, and Database server |
searchctl restartall |
Restart Oracle SES server, WebLogic Server middle tier, and Database server |
On Linux and UNIX systems, you must provide the Oracle SES administrator password when running the searchctl command. If the middle tier port is less than 1024, then the searchctl command for starting or stopping the WebLogic Server middle tier, must be run by the root user.
Note:
Thesearchctl stopall command does not close active background tasks before initiating an immediate shutdown. This may raise internal errors, which you can ignore.