A server pool consists of at least one, but usually multiple Oracle VM Servers. All Oracle VM Servers in a server pool should have CPUs in the same CPU family and of the same type. If they are not in the same CPU family and type, some operations such as live migration may fail. Though the CPUs should be in the same CPU family, they may have differing configurations, such as different number of cores. Other hardware components on the host computer may also differ, such as the amount of RAM, the number and size of disk drives, and so on.
Although the host computers may have differing configurations, Oracle recommends that all Oracle VM Servers in a server pool are identical. Oracle VM Manager contains rules for processor compatibility groups. If live migration is attempted between incompatible processors, an error message is displayed.
Before creating a server pool, you must have:
IP addresses for the Oracle VM Servers.
IP address to use as the virtual IP address.
Password to access the Oracle VM Agent installed on the Oracle VM Server(s).
NoteThe Oracle VM Agent password should be the same on each Oracle VM Server in a server pool. For information on changing the Oracle VM Agent password on your Oracle VM Servers, see Section 6.9.6, “Changing Oracle VM Agent Passwords on Oracle VM Servers”.
A clustered server pool must have a dedicated file system (either a NAS export, or a LUN) to use as the server pool's file system. Oracle recommends that you create this storage with a size of at least 10 GB.
If any errors are encountered when you create a server pool, the Oracle VM Servers are returned to the unconfigured state.
To create a server pool:
Click the Servers and VMs tab.
Click Create Server Pool
 in the toolbar to start the Create
Server Pool wizard.
in the toolbar to start the Create
Server Pool wizard.
The Create Server Pool step is displayed in the wizard.
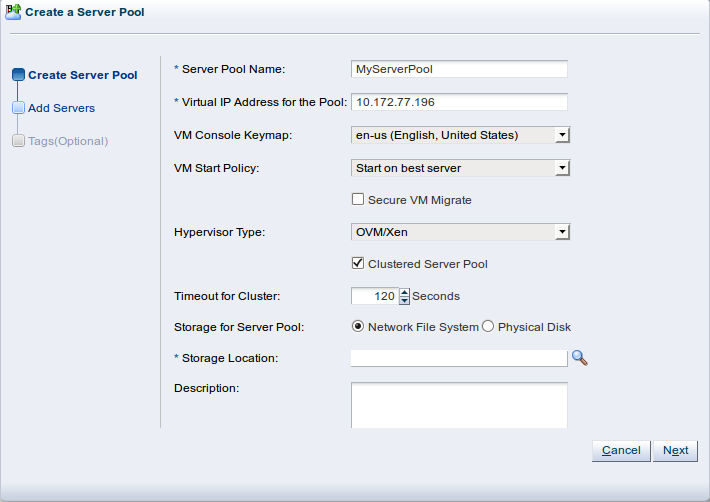
Enter the server pool information:
Server Pool Name: The name of the server pool. The maximum length of a server pool name is 256 characters and may contain any character.
Virtual IP Address for the Pool: An IP address used to identify the master Oracle VM Server, which controls the other Oracle VM Server in the server pool. In the event that the master Oracle VM Server fails or is placed into maintenance mode, another Oracle VM Server is selected to perform the master role, and this IP address is then assigned to the new host.
VM Console Keymap: The key mapping to be used when connecting to a virtual machine's console.
VM Start Policy: For each server pool you can define the default startup policy for all of your virtual machines. Options include the ability to start the virtual machine on the current server (the server to which the virtual machine has been assigned) and the ability to start the virtual machine on the best available server (determined using the same algorithms as DRS and DPM). It is possible to override the default policy within the configuration of each virtual machine. See Section 7.7, “Creating a Virtual Machine” for information on setting the start policy for an individual virtual machine.
Secure VM Migrate: Select whether to enable encrypted migration of virtual machines. When Secure VM Migrate is checked, virtual machines are migrated using SSL to protect the data during the migration process. Secure migration of a virtual machine may effect the time taken to perform the migration as the encryption and decryption of data requires more system resources and time.
Hypervisor Type: Select the hypervisor type to use for the server pool.
Clustered Server Pool: Select whether to enable clustering of the Oracle VM Servers in the server pool to enable HA. See Section 6.4, “High Availability (HA)” for more information on HA policies and configuration.
NoteThis option is greyed out if the Hypervisor Type is set to
OVM/SPARC.Timeout for cluster: If clustering is enabled for the server pool, this option allows you to set the timeout parameter. The maximum cluster timeout setting is 300 seconds. The minimum cluster timeout is 12 seconds. The default cluster timeout is 120 seconds. The Disk heartbeat and network heartbeat are automatically derived from the cluster timeout value.
The cluster timeout can only be changed when there are no servers in the server pool, therefore it is usually good to set this during the creation of your server pool. See Section 6.4, “High Availability (HA)” for more information on HA policies and configuration.
NoteThis option is greyed out if the Hypervisor Type is set to
OVM/SPARC.Storage for Server Pool: Select the file system type to use for the server pool, either a Network File System, or a Physical Disk. The server pool file system is used to hold the server pool and cluster data, and is also used for cluster heartbeating. Oracle recommends that you create this storage with a size of at least 12 GB, as a NAS export or LUN.
A server pool file system is exclusive, just like other storage. That is, in the same way that you cannot create two storage repositories on the same export path, the server pool file system cannot be shared with other server pools, or with storage repositories. Each fully qualified export path (for example, /export/myexport/one, /export/myexport/two) must be used for one, and only one, purpose, that is, for a storage repository, or a server pool file system.
For information on creating storage, see Chapter 4, Managing Storage.
Network File System: The file system to use as the pool file system. Click Search
 in the Storage Location
field to search for a network file system. This field is
displayed if you select Network File System in the
previous field.
in the Storage Location
field to search for a network file system. This field is
displayed if you select Network File System in the
previous field.
Physical Disk: The file system to use as the pool file system. Click Search
 in the Storage Location
field to search for a physical disk. This field is
displayed if you select Physical Disk in the previous
field.
in the Storage Location
field to search for a physical disk. This field is
displayed if you select Physical Disk in the previous
field.
Description: A description of the server pool. This field is optional.
Click Next.
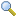
The Add Servers step is displayed in the wizard.
Select the Oracle VM Servers to add to the server pool from the Available Servers column and move them to the Selected Servers column.
If you have defined tags and wish to add any to the server pool, click Next. Otherwise, click Finish.
The Tags step is optional and displays in the wizard if you clicked Next in the previous step.
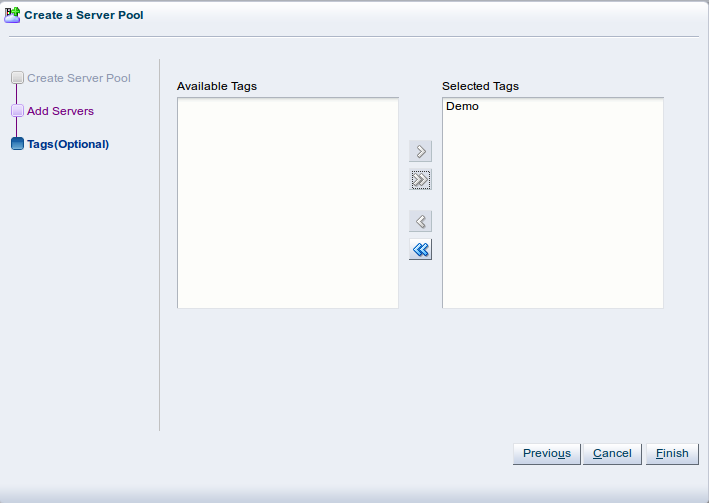
If you have defined tags previously they will appear in the Available Tags column. You can select the tags that you wish to apply to the server pool and move them to the Selected Tags column.
See Section 3.15, “Tags” for more information on creating and managing tags.
Click Finish.
The server pool is created.