This topic discusses cluster architecture in the development and production environments.
In the development environment, you can start with a simple single-node cluster configuration and expand it by adding more nodes.
A single-node cluster in the development environment
In a development environment, the simplest version of a cluster may consist of just one server hosting a Dgraph process for a data store, thus representing a single node. This node is by definition the leader node — in a single-node cluster, the only node is considered the leader node by default.
This diagram represents a single-node cluster in a development environment:
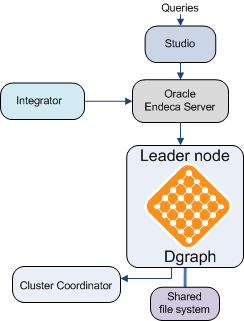
- The Oracle Endeca Server is installed and is hosting a single data store with the Dgraph process running. The Oracle Endeca Server is receiving query requests from Studio (or any other front-end application that is powered by the Oracle Endeca Server).
- The Oracle Endeca Server's host and port are included in the configuration for connectors from Integrator which can send various kinds of data and updates to the Oracle Endeca Server.
- The Dgraph process that is designated as the leader node must have write access to a shared file system on which the data for the specific data store is maintained. All other follower nodes that you add later must have read access to this file system.
- Finally, the cluster is managed by the Cluster Coordinator. In a single-node cluster, the Cluster Coordinator service runs on the same server on which the Dgraph process is running.
A multiple-node cluster in the development environment
In the development environment, many cluster configurations are possible; they depend on the requirements for your application. For example, while a single leader node is always required, the number of additional follower nodes (represented by the Oracle Endeca Server that is hosting the same data store and running the Dgraph process for it) may vary.
This diagram represents a possible multiple-node cluster in a production environment:
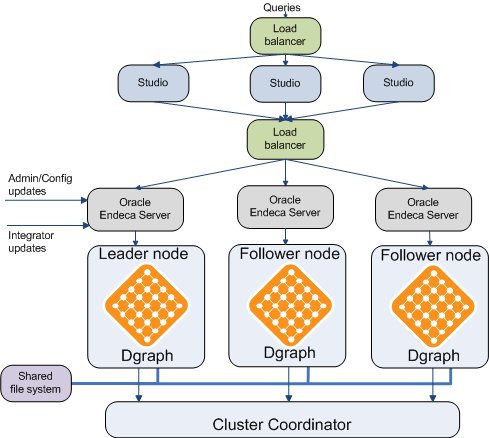
- The queries are sent to the load balancer that is configured in front of several servers hosting Studio instances.
- The instances of Studio point to a second load balancer between Studio and the Oracle Endeca Server cluster.
- Integrator is configured to communicate with the host and port of the Oracle Endeca Server hosting the leader node to ensure a point of communication for sending data and updates.
- All nodes in the cluster (Dgraph processes) communicate with each other through the Cluster Coordinator. The Cluster Coordinator service must be running on the leader node.
- All nodes in the cluster have access to a shared file system on which data files for the data store are stored.
A multiple-node cluster in the production environment
When you move to a production environment, you can duplicate a multi-node development cluster.
