| Oracle® Communications Services Gatekeeper OAuth Guide Release 5.1 E37521-01 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Communications Services Gatekeeper OAuth Guide Release 5.1 E37521-01 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter explains the options you have for customizing the Open Authorization Protocol (OAuth) functionality for use with Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper (Services Gatekeeper).
This section contains information on customizing Service Gatekeeper's OAuth functionality.
You can delegate authentication to a third-party authentication service provider instead of with the default Subscriber Management Service. The authentication provider is responsible for the resource owner identity validation and handling the grant collection flow.
A delegated authentication service used with Services Gatekeeper is responsible for:
Hosting the Authentication Endpoint.
Presenting the expanded scope and authenticating a resource owner.
Redirecting the resource owner to the grant endpoint hosted by Services Gatekeeper upon successful authentication of the resource owner.
See "Understanding the OAuth Endpoints" for more information.
This section describes the flow of requests between Services Gatekeeper and a delegated authentication service. Sample responses to the requests along with a description of the flow are provided.
An application sends a standard OAuth2.0 Authorization request to Services Gatekeeper in a format that looks like this:
GET /oauth2/authorize?client_id=client123&redirect_uri=https://www.google.com/asdf&response_type=code&scope=POST-/payment/acr:Authorization/transactions/amount&state=123 HTTP/1.1
After receiving the OAuth2 authorization request, Services Gatekeeper add more detailed information to it using the client_id and scope request parameters. This additional information is appended to the location header in the 302 redirect response directed to the configured authentication endpoint.
The location header contains these elements:
The delegating authentication endpoint
The original OAuth2.0 Authentication request parameters
The Grant endpoint
Detailed information for the client_id and scope parameters.
An example 302 response is provided here:
HTTP/1.1 302 Moved Temporarily Location: https://authentication_url?client_id=client123&redirect_uri=https://www.google.com/asdf&response_type=code&scope=POST-/payment/acr:Authorization/transactions/amount&state=123&grant_url=grant&client_info=%7B%22clientId%22%3A%22client123%22%2C%22clientName%22%3A%22client123%22%2C%22clientDescription%22%3A%22client123+desc%22%7D&scopes_info=%5B%7B%22scopeId%22%3A%22POST-%2Fpayment%2Facr%3AAuthorization%2Ftransactions%2Famount%22%2C%22scopeDescription%22%3A%22Charge+or+refund%22%2C%22parameters%22%3A%5B%7B%22code%22%3A%22billable+item+id%22%7D%5D%7D%5D
In addition to the original OAuth2.0 authorization request parameters, the detailed format specs of all additional parameters are defined in Table 4-1:
Table 4-1 OAuth 2.0 Authorization Request Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
grant_url |
The URL can be submitted later according resource owner's approval. See "Understanding the OAuth Endpoints" for more information. |
|
client_info |
Client information will be constructed into a JSON Object as shown below. Encoding complies with the following specification:
{
"clientId":"client123",
"clientName":"Oracle",
"clientDescription":"Oracle Description"
}
|
|
scopes_info |
scope information will be constructed into a JSON Object as shown below. Encoding complies with the following specification:
[
{
"scopeId":"POST- payment acr:Authorization transactions amount",
"scopeDescription":"Charge+or+refund",
"parameters":[{"code":"billable+item+id"}]
}
]
|
The resource owner's browser continues to access the authentication endpoint identified in the Location Header.
The Authentication endpoint should accept the redirected request, authenticate the resource owner for proper credentials and render an interactive graphical interface for authorization. The resource owner can use the information in the interface to understand the scope and client information of the authorization request and determine if the request should be authorized.
After the resource owner authorizes the scope the Authentication endpoint redirects the resource owner to the Grant endpoint with following parameters through an HTTP POST operation. The OAuth flow continues normally after redirecting the resource owner toward the grant endpoint. The client then receives the authorization code at the Redirect endpoint.
Table 4-2 lists the OAuth 2.0 grant endpoint POST parameters.
Table 4-2 OAuth 2.0 Grant Endpoint POST Parameters
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
|
user_address |
Address of resource owner |
|
grant_scopes |
The scope that the resource owner grants to the application. The value of the scope parameter is expressed as a list of space-delimited strings. Each string adds an additional access range to the selected scope parameter. According to the resource owner decisions at the Authentication endpoint, the granted scope can be narrower than the originally requested scope. Services Gatekeeper will reject a granted scope that is wider than originally requested scope. Based on the implementation of the Authentication endpoint and the resource owner interaction, additional parameter may be appended to each scope id. These scope parameters will be available to an interceptor so that stricter enforcement can be applied according to different parameters. The scope format is: scopeId?[<param>=<value>[&<param>=<value>]*]. For example: grant_scopes=chargeAmount?maxAmount=100&minAmount=100 getLocation?requestedAccuracy=100 sendSMS |
|
response_type |
As in the first authorization request |
|
client_id |
As in the first authorization request |
|
redirect_uri |
As in the first authorization request |
|
state |
As in the first authorization request |
|
scope |
As in the first authorization request |
This section describes the basic principles for creating a custom OAuth interceptor.
As described in "Implementing a Third-Party Authentication Service", it is possible to add additional parameters to the scope-token so that custom interceptors can be created for fine-grained resource access and traffic control.
Table 4-3 lists the OAuth parameters available in the RequestContext object for an OAuth2.0 enabled communication service. Customized interceptors can make use of these parameters to further fine tune authorized access to protected resources.
For information on creating custom interceptors, see Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper Platform Development Studio Developer's Guide.
Table 4-3 OAuth 2.0 RequestContext Parameters
| Attribute Name | Access | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
|
OAUTH2_SCOPE_PARAMETER |
read only |
java.util.Map |
Contains all parameters of the current request scope. |
|
CONTEXT_OAUTH2_RESOURCE_OWNER |
read only |
java.lang.String |
The resource owner of the token, which is usually the same as the address in the request. When the resource owner is a group URI or the scheme of address in request is ACR, they may be different. |
|
CONTEXT_OAUTH2_PARAMETER |
read only |
java.util.Map |
Contains all endpoint parameters of this request. This parameter must start with “oracle_” or “ocsg_”. |
|
CONTEXT_OAUTH2_STATE |
read/write |
java.util.Map |
Values of this attribute will be available during the lifecycle of one OAuth access token. |
Below is an example for retrieving and using OAuth associated information from the requestContext within a customized interceptor.
To retrieve the MSIDN of an OAuth resource owner:
/**
* The following example shows a way to retrieve Oauth2 resource owner MSIDN
*/@Override
public Object invoke(final Context context) throws Exception {
String currentResourceOwner = (String) context.getRequestContext().get(“CONTEXT_OAUTH2_RESOURCE_OWNER”);
If (currentResourceOwner == null)
throw new DenyPluginException(“Not a OAuth based request!”);
else
System.out.println(“Current Oauth2 resource owner is:” + currentResourceOwner);
context.invokeNext(this);
}
To control the maximum charged value using an additional scope parameter called maxAmount:
/**
* The following example shows a way to control the maximum charged value using additional scope parameter* "maxAmount".
*/
@Override
public Object invoke(final Context context) throws Exception {
if (context.getType().equals(AmountCharingPlugin.class)) { Map<String, String> scopeParameters = (Map<String, String>)context.getRequestContext().get("OAUTH2_SCOPE_PARAMETER");
int maxAmount = Integer.parseInt(scopeParameters.get("maxAmount").toString());
if (((ChargeAmount)context.getArguments()[0]).getAmount() > maxAmount) throw new DenyPluginException("Specified chargeAmount request exceed limitation.");
}
context.invokeNext(this);}
Service Gatekeeper offers the flexibility to integrate with custom subscriber repositories for user authentication. You can develop a customized Subscriber Manager to authenticate users against external subscriber repositories such as LDAP.
Developing a custom Subscriber Manager involves the following steps:
Implementing oracle.Services Gatekeeper.subscriber.SubscriberManager, and customizing the implementation of this interface
Registering the custom implementation with the OAuth security framework with this method.
void oracle.Services Gatekeeper.subscriber.SubscriberManager.registerInstance("default", SubscriberManager instance);
For additional information on customizing the default Subscriber Manager, including method details, see the Services Gatekeeper JavaDoc.
Services Gatekeeper supports a rich set of credential types that OAuth uses for security. However, if your implementation uses new or evolving credential standards that Services Gatekeeper does not support, you have the option to create a customized extension handler to use them. The Platform Development Studio enables you to customize endpoint parameters, grant types, response types, or errors using the OAuth2 Extension Handlers wizard.
For details see Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper Platform Development Studio Developer's Guide
Services Gatekeeper enables you to add your own customized tests to OAuth resource requests. For example, you may want to restrict access to a resource to just subscribers from a specific block of email addresses. There are two ways to add the customized tests:
Using an auth.jsp file which you then reference using a REGEX_MATCH parameter in the resource XML file. Services Gatekeeper then perform any tests (regular expressions) that you have added to the jsp file. Each subscriber must pass the tests in this file to get access to the resource.
Creating a custom services interceptor.
For details on both of these methods, see Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper Platform Development Studio Developer's Guide.
This section contains information helpful to Application Developers using OAuth2.0 with Services Gatekeeper.
This section describes what OAuth endpoints are available, what steps are involved in obtaining an access token and how an application can use an access token to access a REST resource in Services Gatekeeper.
The following endpoints are available in the OAuth2.0 Service:
Authorization endpoint
Token endpoint
Authentication endpoint
Grant endpoint
Figure 4-1 demonstrates the end to end flow to obtain an access token and use the access token to access the resource.
Figure 4-1 OAuth Endpoints and Functional Responsibility
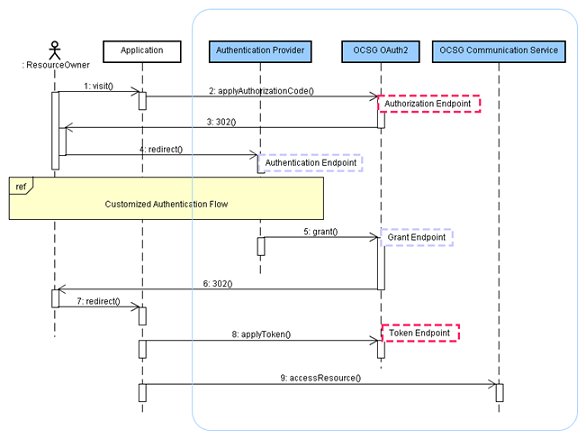
The following procedure describes the OAuth access flow:
A resource owner visits an application Web site and initiates a request that requires granting access to protected resources to an application.
The application redirects the resource owner to the Authorization Endpoint with the application information including the client id and scope id.
For example, the application can provide a link to trigger a HTTP GET request where the following information is included in the HTTP query string:
HTTP Request: GET
URI: https://host:port/oauth2/authorize
Parameters:
response_type -- Supported values are code or token
client_id. -- The client identifier
redirect_uri -- Required
scope -- The scope of the access request expressed as a list of space-delimited, case sensitive strings. The Services Gatekeeper Authorization Server accepts zero to multiple scope-tokens in the following format for scope-token:
<scopeId>[?<param>=<value>[&<param>=<value>]*]+
where scopeId is the resource identifier and param is the name of one of the allowed parameters defined as part of resource.
For example:
chargeAmount?code=1976
An example scope would look like:
GET /oauth2/authorize?response_type=code&client_id=app123&state=xyz &redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fclient%2Eexample%2Ecom%2Fcb HTTP/1.1
Host: server.Services Gatekeeper.com
Services Gatekeeper validates the resource owner identity and obtains the resource owner's consent on the requested scope.
The application exchanges the authorization code for an authorization token using the Token Endpoint. Services Gatekeeper server returns the token directly.
The request can be described as follows:
HTTP Request: POST
URI: https://<AT_HOST>:<AT_PORT>/oauth2/token
Parameters:
grant_type: Value can be set to authorization_code, if the request is not a SAML assertion.
code: The authorization code received from the Authorization Server.
redirect_uri: The redirection URI used by the Authorization Server to return the authorization response in the previous step.
client_id: The client identifier.
client_secret: The client password.
Authorization Header:
The client application may use the http Basic authentication scheme as defined in RFC2617 to authenticate with the Services Gatekeeper server. The client_id is used as the username and the client_secret is used as the password.
For example:
Authorization: Basic czZCaGRSa3F0MzpnWDFmQmF0M2JW
Alternatively, the Authorization Server may support including the client credentials in the request body using the following parameters:
client_id: The client identifier.
client_secret: The application password.
HTTP Response:
access_token: The authorization code generated by Services Gatekeeper.
token_type: The Bearer or MAC authorization code received from Services Gatekeeper.
expires_in: The duration in seconds of the access token lifetime.
refresh_token: The refresh token which you use to obtain new access tokens using the same authorization grant.
scope: The scope of the access request expressed as a list of space-delimited, case sensitive strings.
anonymous_id: Uniquely identifies the resource owner.
mac_key: The MAC key verifies the later request of access protect resource. (MAC-Type access token).
mac_algorithm: The MAC algorithm used to calculate the request MAC. The value must be either hmac-sha-1 or hmac-sha-256.
The response will be different depending on the token type submitted in the request.
This is an example for a Bearer-Type Access Token with HTTP Basic Authentication:
Request:
POST /oauth2/token HTTP/1.1 Host: localhost:7999 Content-length: 128 Authorization: Basic YXBwMTIzOmFwcDEyMw== Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Connection: Close grant_type=authorization_code&code=75dfe1c9-9784-4545-846f-e1493f087017&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%2Fapp%2Fredirect.php
Response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OKCache-Control: no-storeConnection: closeContent-Length: 327Content-Type: application/json{"access_token":"44fb85f8-e400-41b3-9bd4-68617d131039","token_type":"MAC","expires_in":3600,"scope":"POST-/payment/acr:Authorization/transactions/amount","mac_algorithm":"hmac-sha-1","mac_key":"-3677656698299327487","secret":"-3677656698299327487","anonymous_id":"1debde44-f9d4-41d6-88fe-bbb77fea37c8","algorithm":"hmac-sha-1"}
The following example is for a MAC-Type Access Token with included client credentials in the request body.
Request:
POST /oauth2/token HTTP/1.1 Host: server.Services Gatekeeper.com Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=authorization_code&client_id=app123&client_secret=app123&code=i1WsRn1uB1&redirect_uri=https%3A%2F%2Fclient%2Eexample%2Ecom%2Fcb
Response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Content-Type: application/json
Cache-Control: no-store
{ "access_token":"SlAV32hkKG", "token_type":"mac", "expires_in":3600, "refresh_token":"8xLOxBtZp8", "secret":"23sasd#adf@#" "algorithm":"hmac-sha-1"}
The application now access the protected resource.
The application needs to add an HTTP Authorization Header when accessing the granted resource. The value of authorization head depends on the access token type.
For a Bearer token, the application can directly transmit the access token using an HTTP authorization header in the request.
For a MAC token, the application constructs the HTTP authorization header using a MAC key with the access token. For more information, see: http://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-ietf-oauth-v2-http-mac-00.
Below is a sample PHP code snippet illustrating the insertion of the token in the HTTP Authorization Header:
$body_hash=base64_encode(hash('sha1',$http_body,true));
$payload=$nonce."\n".$http_method."\n".$request_path."\n".$host_name."\n".$host_port."\n".$body_hash."\n".$ext."\n";
$mac = base64_encode(hash_hmac('sha1', $payload, $mac_key, true));
$oauth2_header='MAC id="'.$mac_key_id."\",nonce=\"".$nonce."\",bodyhash=\"".$body_hash."\",mac=\"".$mac.'"';
Following is an example of a request containing a Bearer authorization token:
POST /oneapi/1/payment/acr%3AAuthorization/transactions/amount HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:7999
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
Authorization: Bearer vF9dft4qmT
{"amountTransaction":{"endUserId":"acr:Authorization", "paymentAmount":{"chargingInformation":{"description":"chargeAmount", "currency":"USD", "amount":"2","code":""}, "chargingMetaData":{"onBehalfOf":"Example Games Inc", "purchaseCategoryCode":"Game", "channel":"", "taxAmount":"0", "mandateId":"", "serviceId":"", "productId":""}}, "transactionOperationStatus":"Charged", "referenceCode":"REF-12345", "clientCorrelator":""} }
Following is an example of a request containing a MAC authorization token:
POST /oneapi/1/payment/acr%3AAuthorization/transactions/amount HTTP/1.1
Host: localhost:7999
Content-length: 415
Authorization: MAC id="176c04f0-d4d4-4385-b2d6-b19649f21b78", nonce="273156:di3hvdf8", bodyhash="junEVZu4M9q1qVaxAByY7lYQun8=", mac="TudmT3bM5UgqvkL8nq1EuhcZ6O8="
Content-Type: application/json
X-Session-ID: app:-7562122823730178188
Connection: Close
{"amountTransaction":{"endUserId":"acr:Authorization", "paymentAmount":{"chargingInformation":{"description":"chargeAmount", "currency":"USD", "amount":"2", "code":""}, "chargingMetaData":{"onBehalfOf":"Example Games Inc", "purchaseCategoryCode":"Game", "channel":"", "taxAmount":"0", "mandateId":"", "serviceId":"", "productId":""}}, "transactionOperationStatus":"Charged", "referenceCode":"REF-"
}