| Oracle® Communications Services Gatekeeper System Administrator's Guide Release 5.1 E37531-01 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
| Oracle® Communications Services Gatekeeper System Administrator's Guide Release 5.1 E37531-01 |
|
|
PDF · Mobi · ePub |
This chapter describes how to manage and configure Event Data Records (EDRs), Charging Data Records (CDRs), and alarms in Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper.
Event Data Records (EDRs), are generated in the following ways:
Automatically, using aspects at various locations in a network protocol plug-in.
Manually, anywhere in the code using the EDRService directly.
EDRs are the base component of both CDRs and alarms.
In order to categorize the objects in the EDR flow as either pure EDRs, alarms or CDRs, the EDR service uses an EDR configuration file:
Domain_Home/config/custom/wlng-edr.xml
The configuration file contains a set of sections:
<edr-config> contains descriptors that describe pure EDRs.
<alarm-config> contains descriptors that describe EDRs that should be considered alarms.
<cdr-config> contains descriptors that describe EDRs that should be considered CDRs.
The default Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper installation comes with a set of predefined descriptors. Changing and adapting the descriptors is done as a part of an integration project.
The XML configuration file can be edited and reloaded using the EDR Configuration pane: see "Managing EDR, CDR, and alarms configuration files using the EDR Configuration Pane".
Example 8-1 illustrates the structure of wlng-edr.xml. See “Creating an EDR Listener and Generating SNMP MIBs” in Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper Platform Development Studio Developer's Guide for more information.
Example 8-1 structure of wlng-edr.xml
<edr-config xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.bea.com/ns/wlng/30 edr-config.xsd"> <edr id="ID" description="description"> <filter> <method> <name>message response message</name> <class>fully qualified class name</class> </method> </filter> </edr> ..... </edr-config>
The following values are always available in an EDR when it is generated in the standard way:
Class name
Method name
Direction (application-facing, network-facing), if the request is travelling from Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper to the network or from the network to Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper.
Position (before, after), if the EDR was emitted before or after the method was invoked or the exception was thrown
Interface (application-facing or network-facing), if the EDR was emitted from the application-facing interface or from the network-facing interface of the plug-in
Source (method, exception), if the EDR is related to a method invocation or to an exception
In addition to these values, the EDR may also contain values relevant to the context of the request.
Figure 8-1 Application Tier and Network Tier EDR Generation
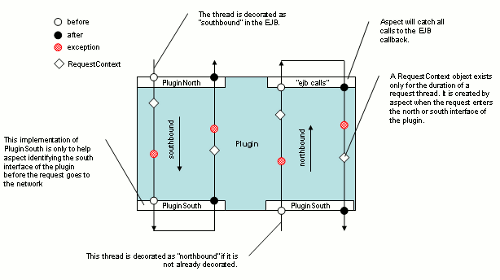
Table 8-1 describes the contents of an EDR. Individual value fields in an EDR are retrieved by name using a key in a name/value pair.
| String value of name (key) in name/ value pair | Description |
|---|---|
|
EdrId |
Defined in wlng-edr.xml. |
|
ServiceName |
The name or type of the service |
|
ServerName |
Name of server where the EDR was generated |
|
Timestamp |
The time at which the EDR was triggered Milliseconds since midnight, January 1, 1970 UTC |
|
ContainerTransactionId |
WebLogic Server transaction ID (if available) |
|
Class |
Name of the class that logged the EDR |
|
Method |
Name of the method that logged the EDR |
|
Direction |
Direction of the request |
|
Source |
The type of source that logged the EDR |
|
Position |
Position of the EDR relative to the method that logged the EDR |
|
State |
Where the EDR was dispatched |
|
Interface |
Interface where the EDR is logged |
|
Exception |
Name of the exception that triggered the EDR |
|
SessionId |
Session ID |
|
ServiceProviderId |
Service provider account ID |
|
ApplicationId |
Application account ID |
|
AppInstanceId |
Application account identifier |
|
TransactionId |
Transaction Id. Correlates completed traffic among all three EDR states |
|
Facade |
Facade (REST or SOAP). |
|
OrigAddress |
The originating address with scheme included. For example: tel:1212771234 |
|
DestAddress |
The destination address, or addresses, with scheme included. May contain multiple addresses. |
|
<custom> |
Any additional context-specific information |
|
PluginID |
The unique ID of the plug-in instance |
|
URL |
The URL of the current web service |
|
WebAppName |
Name of the current web application |
|
HttpMethod |
HTTP request method. For example "POST", or "GET". |
|
RequestContext |
Attributes in the request context map. (Name/Value pairs) |
|
InterceptorChain |
List of all of the interceptors that are triggered |
|
SubscriberID |
Subscriber identifier (using route address) |
All EDRs are passed through the EDRService. All EDRs are dispatched to a JMS- distributed topic so external clients can receive them over JMS.
EDRs are not persisted in the database.
Alarms are EDRs that are mapped to alarms using the alarm.xml configuration file: see "EDR categories and XML markup".
Alarms can be configured to be persisted, see "Alarms".
CDRs are EDRs that are mapped to CDRs using the wlng-edr.xml configuration file, see "EDR categories and XML markup".
CDRs can be configured to be persisted, see "Attribute: StoreCDRs".
External EDR listeners are JMS topic subscribers. See “Creating an EDR Listener and Generating SNMP MIBs” in Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper Platform Development Studio Developer's Guide for information on how to create a EDR listeners.
The following section describes the EDRService.
To configure the behavior of the EDRService, in the EdrService managed object:
Specify Attribute: PublishToJMS.
Specify Attribute: StoreAlarms.
Specify Attribute: StoreCDRs.
The following section describes how to manage the EDRService.
To configure the maximum number of EDRs sent in a batch to a JMS EDR listener and the maximum time to wait before the EDRs in the buffer are sent to listeners:
Specify Attribute: BatchTimeout.
Specify Attribute: BatchSize.
Managed object: Container Services−>EdrService
MBean: com.bea.wlcp.wlng.edr.management.EdrServiceMBean
Following is a list of attributes and operations for configuration and maintenance:
Scope: Cluster
Format: int
Unit: milliseconds
Specifies the timeout value for a JMS batch.
Scope: Cluster
Format: boolean
Specifies if statistics is enabled for EDRService. Must be enabled for Operation: displayStatistics to be relevant.
Scope: Cluster
Format: int
Unit: number of EDRs
Specifies the size of the JMS batch.
Scope: Cluster
Format: Boolean
Specifies if EDRs shall be published in the JMS topic or not. Needs to be true if external EDR listeners are used.
Scope: Cluster
Format: boolean
Specifies if alarms shall be stored in the database or not.
Scope: Cluster
Format: boolean
Specifies if CDRs shall be stored in the database or not.
Scope: Cluster
Displays a snapshot of the current statistics for EDRService. Attribute: StatisticsEnabled must be true for this operation to be relevant.
The following information is displayed:
Number of EDRs
Smallest EDR message size in bytes
Biggest EDR message size in bytes
Average EDR message size in bytes
Signature:
displayStatistics()
Scope: Cluster
Resets the statistics for the EDRService.
Signature:
resetStatistics()
Scope: Cluster
Configures the type of EDRs that should be sent from the EDRService.
Signature:
setEdrType(Programmable: boolean, Facade: boolean, Enabler, boolean, ProtocolStack: boolean, Others: boolean)
| Parameters | Description |
|---|---|
|
Programmable |
true: send EDRs created manually through EdrDataHelper |
|
Facade |
true: send EDRs created in the AT layer. Default is false. |
|
Enabler |
true: send EDRs created in PluginNorth or PluginSouth via AspectJ |
|
ProtocolStack |
true: send EDRs created in PluginNorthCallback, ProtocolServiceNorth, or ProtocolServiceSouth via AspectJ |
|
Others |
true: send EDRs created via AspectJ |
The Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper EDR Configuration pane allows the administrator to load new EDR, CDR, and alarm configuration files.
Open the pane by selecting OCSG > Server Name > EDR Configuration from the Domain Structure in the Administration Console.
Note:
Lock and Edit must be used.Table 8-3 describes the inputs for the entry fields in the configuration pane.
Table 8-3 Oracle Communications Services Gatekeeper EDR Configuration pane
| Entry field | Input |
|---|---|
|
EDR descriptor |
The EDR configuration file, see "EDR categories and XML markup". |
|
CDR descriptor |
The CDR configuration file: see "EDR categories and XML markup". |
|
Alarm descriptor |
The alarms configuration file: see "EDR categories and XML markup". |