The piston assembly consists of five components, and the cylinder assembly consists of two, each with certain nominal dimensions. These components are then stacked to create the assembly. The difference in length between the two, called the assembly gap, must be between 0.003 and 0.02 inches. This might seem like a simple problem, but since milling processes are not exact and quality control has a direct effect on prices, components have an error associated with each, called tolerance. When stacked, these errors compile or add together to create a cumulative tolerance.
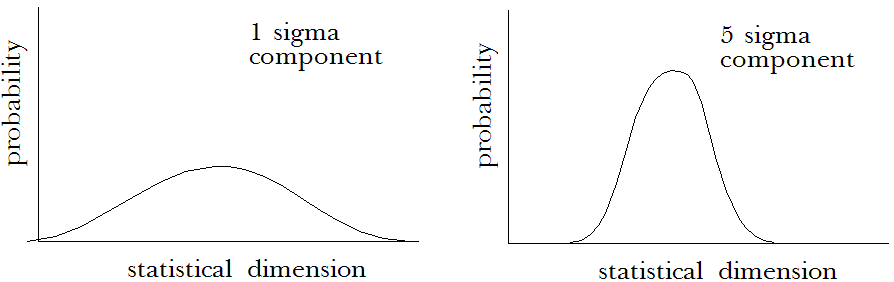
When a batch of components is milled and measured, the components’ actual dimensions form a distribution around the desired, or nominal, dimension. Standard deviation, or sigma, is a measure of the variation present in a batch of components. The components then have a statistical dimension based on this distribution. The quality of the component and the associated tolerance is described in terms of sigmas, with 1 sigma component having the largest tolerance and a 5 sigma component the smallest. This is called the quality specification.
One simplified solution takes the total tolerance allowed and divides it by the number of components. But, due to individual component complexity and process differences in manufacturing, each component of the assembly has a different cost function associated with the quality specification. This then becomes a juggling act to balance cumulative tolerance and associated cost.
Crystal Ball supports quality programs such as Six Sigma by calculating a set of process capability metrics for forecasts when the process capability features are activated and at least one specification limit (LSL or USL) is entered for the forecasts. OptQuest then includes these metrics in the list of statistics that can be optimized. For more information, see OptQuest and Process Capability.
This example assumes that the process capability metrics have been activated in Crystal Ball. Then, the capability metrics are available in the Forecast Statistic list of the Objectives panel.