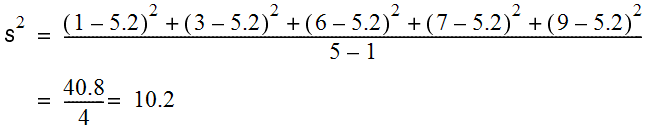Variance is a measure of the dispersion, or spread, of a set of values about the mean. When values are close to the mean, the variance is small. When values are widely scattered about the mean, the variance is larger.
Formula:
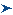 To calculate the variance of a set of values:
To calculate the variance of a set of values:
Find the mean or average.
For each value, calculate the difference between the value and the mean.
Square the differences.
Divide by n - 1, where n is the number of differences.
For example, suppose your values are 1, 3, 6, 7, and 9. The mean is 5.2. The variance, denoted by s2 , is calculated as follows:
Note: | The calculation uses n - 1 instead of n to correct for the fact that the mean was calculated from the data sample, thus removing one degree of freedom. This correction makes the sample variances slightly larger than the variance of the entire population. |
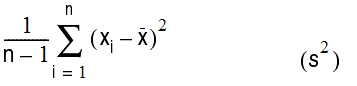
 To calculate the variance of a set of values:
To calculate the variance of a set of values: