Essbase can be deployed to work in SSL and non-SSL modes. Essbase Agent listens on a non-secure port; it can be configured to listen on a secure port also. All connections accessing the secure port are treated as SSL connections. If a client connects to the Essbase Agent on the non-SSL port, the connection is treated as a non-SSL connection. Components can establish concurrent non-SSL and SSL connections to an Essbase Agent.
You can control SSL on a per-session basis by specifying the secure protocol and port when you log in. See Establishing a Per-Session SSL Connection.
If SSL is enabled, all communication within an Essbase instance is encrypted to ensure data security.
Default deployments of Essbase components in secure mode uses self-signed certificates to enable SSL communication, mainly for testing purposes. Oracle recommends that you use certificates from well-known third-party CAs to SSL-enable Essbase in production environments.
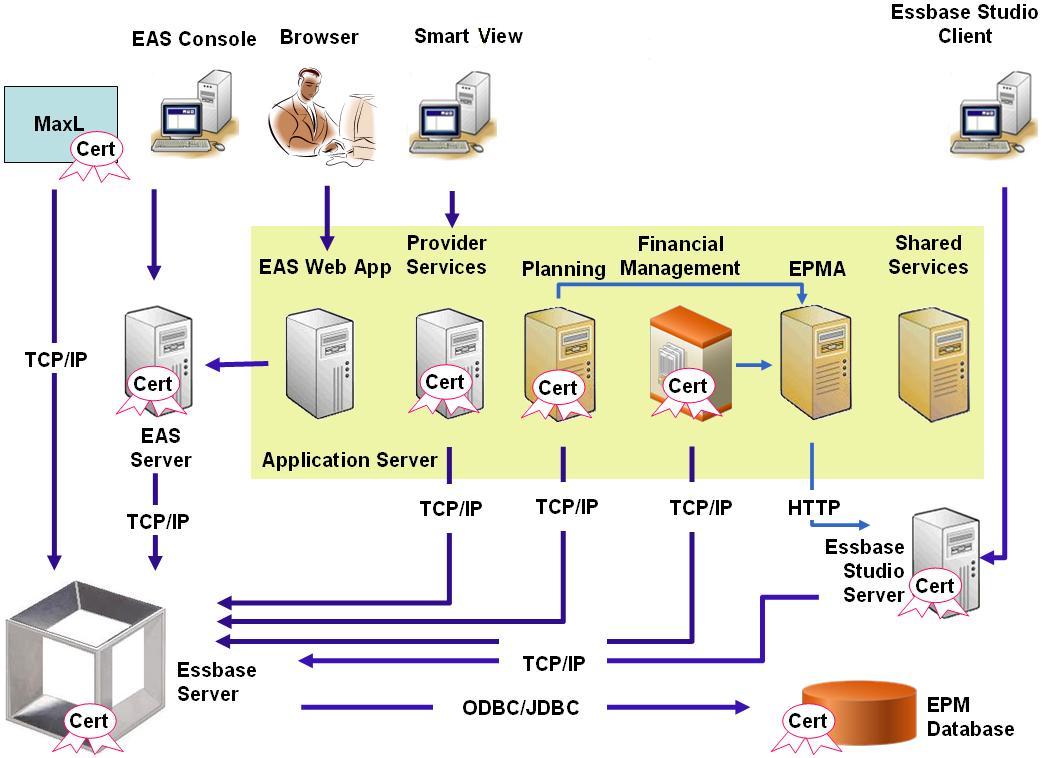
Typically, an Oracle Wallet stores the certificate that enables SSL communication with clients that use Essbase RTC (C APIs) and a Java keystore stores the certificate that enables SSL communication with components that utilize JAPI for communication. To establish SSL communication, Essbase clients and tools store the root certificate of the CA that signed the Essbase Server and Agent certificates. See Required Certificates and Their Location.