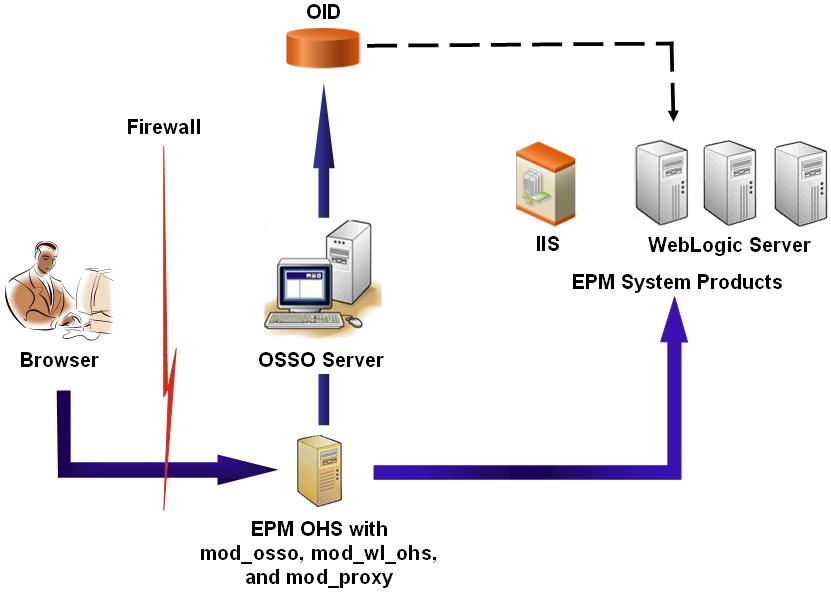
The OSSO process:
Using an EPM System URL, for example, http://OSSO_OHS_Server_NAME:OSSO_OHS_Server_PORT/interop/index.jsp, users access an EPM System component that is defined as an OSSO protected application.
Because the URL is under OSSO protection, mod_osso, deployed on Oracle HTTP Server, intercepts the request. Using mod_osso, Oracle HTTP Server checks for a valid cookie. If a valid cookie is not available in the request, Oracle HTTP Server redirects users to the OSSO Server, which challenges users for credentials, which it authenticates against OID.
OSSO Server creates the obSSOCookie and returns control to the mod_osso module on the Oracle HTTP Server, which sets the obSSOCookie in the browser. It also redirects the request to the EPM System resource through mod_wl_ohs (WebLogic Server) or mod_proxy (IIS Server). Before forwarding the request to an EPM System resource, Oracle HTTP Server sets the Proxy-Remote-User header which EPM System security uses to enable SSO.
The EPM System component verifies that the user whose identity is retrieved from Proxy-Remote-User is present in OID. For this process to work, the OID that is configured with the OSSO Server should be configured as an external user directory in Shared Services.