A context handle represents a single, valid login by a user onto the system. A successful call to EsbLogin() returns a context handle, which can be passed to other API calls which require a context handle as an argument.
Using Context Handles in Applications
Context handles are defined as type ESB_HCTX_T in Visual Basic programs.
In general, a context handle is valid for as long as the user remains logged in to that server (that is, until after a successful EsbLogout() call). However, in case such as a server shutdown, a context handle can become invalid. Your program should therefore provide some way for the user to log back in during a session (for example, via a menu option or function key).
Note: | A context handle is specific to an instance of the API, and contains an implied reference to the resources and settings for the appropriate instance. |
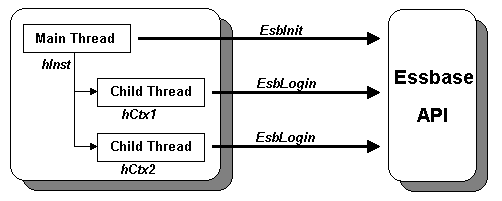
A single instance of an API program may make multiple calls to EsbLogin(), using the same user name or different user names on one or more Essbase Servers. Each call to EsbLogin() returns a unique context handle, and your program must keep track of each context handle returned. You may have up to 255 context handles per client application in use simultaneously, but if a program performs all its processing on a single server, in general it is easier to use only one context handle and to switch between different applications and/or databases as required, using either the EsbSetActive() function or the EsbAutoLogin() function.
Operations on local objects and files (objects on the client) can use a local context handle. See Using Local Context Handles and Local Contexts.
In general, it is not advisable to share context handles between multiple programs, processes, or threads, unless such use is guaranteed to be exclusive. A better approach is to use the same instance handle and log in each process separately. Essbase ensures that multiple logins using the same user name on the same server will only occupy one port on that server.