Consolidation is the process of gathering data from dependent entities and aggregating the data to parent entities. After you enter or load data into base-level entities, you run a consolidation for a selected Scenario and Period to aggregate the data through the organization. As data consolidates, the system performs the necessary currency translation and intercompany eliminations, and equity adjustments or minority ownership calculations if needed.
Financial Management provides a default consolidation method. To enable statutory consolidations, you can customize the consolidation process. When you create an application, you can set the Consolidation Rules attribute. By default, when this setting is OFF, the system performs the default consolidation and eliminations. When this setting is ON, the system performs consolidation according to the rules written in the Sub Consolidate() routine, as defined by the user. See the Oracle Hyperion Financial Management Administrator’s Guide.
You launch the consolidation process from data grids on the Desktop or on the Web. Launching consolidation runs the consolidation rules for the specified scenario, year, period, entity, and value. As part of that process, consolidation is run for all descendent entities and all prior time periods within the same year. The consolidation process runs all Calculate functions for each affected entity and value. Translation is run as required to convert from child entity currency to parent entity currency. If the child and parent entity are using the same currency, translation is not run.
After you select the parent into which the dependent entities consolidate, this process takes place:
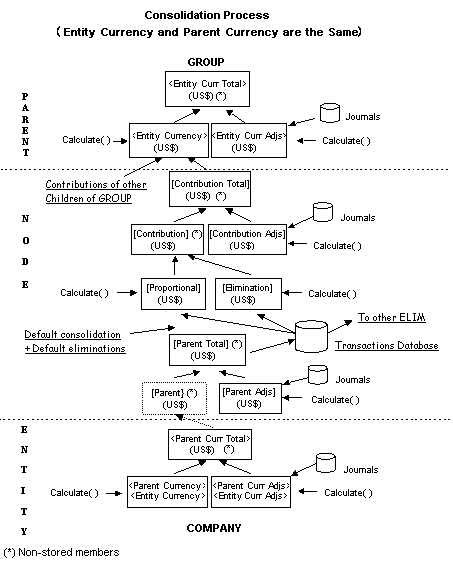
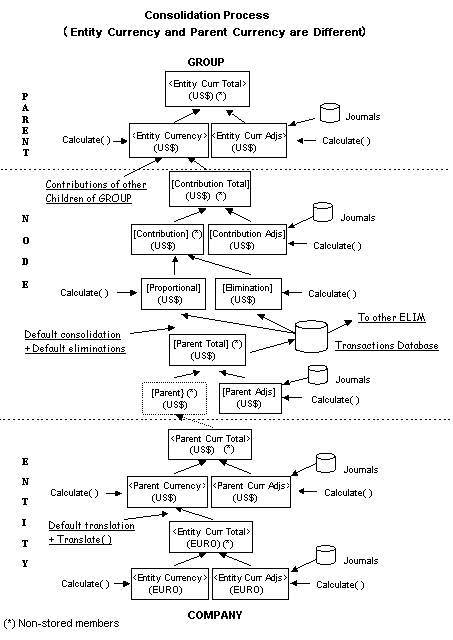
The system executes chart rules, and aggregates input and adjustment data in the local currency.
The system performs translation, if it has not been previously executed. The system also aggregates input and adjustment data by currency for a given entity.
The consolidation process begins. The system generates proportion and elimination detail, and creates contribution data. You can make further adjustments to contribution data through journals.
At the entity level of the consolidation process, you enter data in input accounts and enter adjustments through journals in the entity currency. The system executes chart rules at the entity level, resulting in adjusted data for the entity.
Following are examples of the consolidation process.
The first example shows the process when the entity currency and the parent currency are different.
The following example shows the process when the entity currency and the parent currency are the same.