Describes the fields in a flat (delimited or fixed-width) data file.
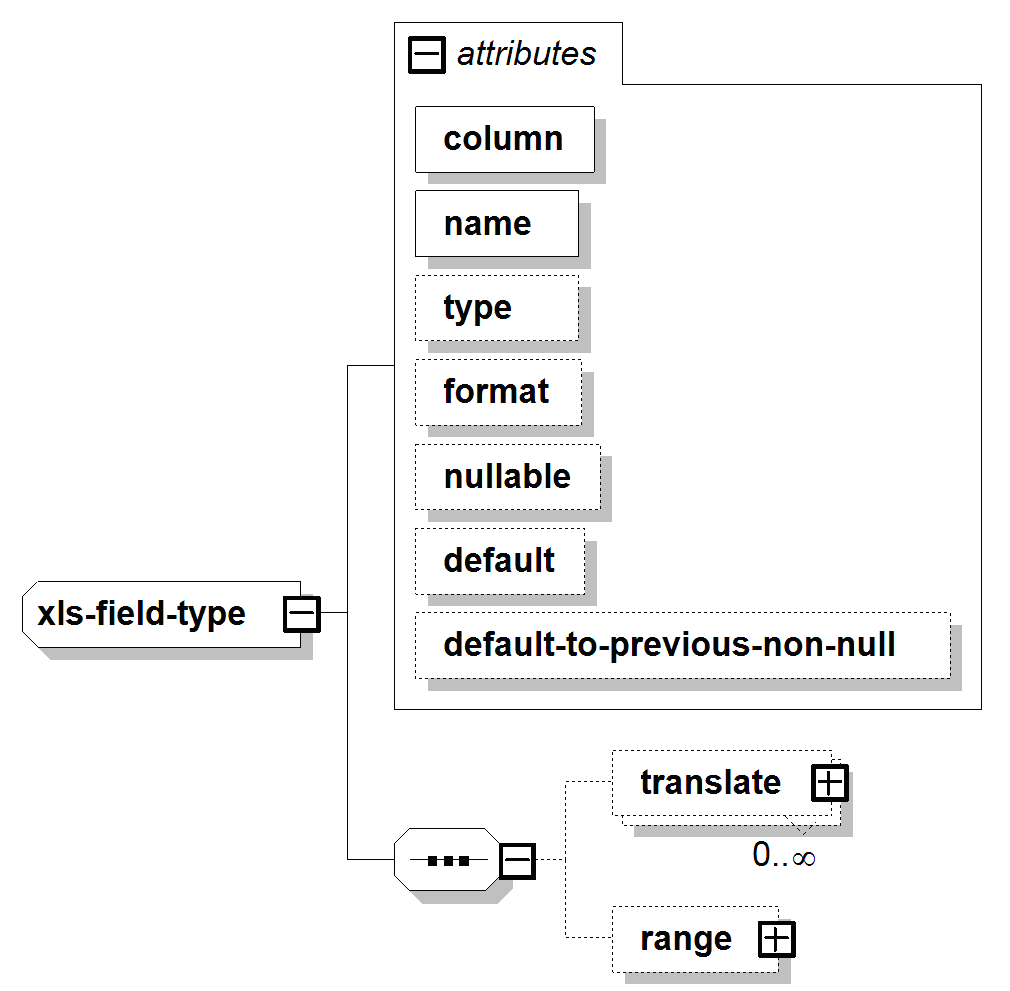
Required: Excel column identifier. For example, “A”, “AB”.
Required: Name of the field. Give each field a unique name; for example, name="part number".
Data type of the field. Valid types are: string, int, long, double, date, duration, and boolean. (Default=string)
Used for type="date" fields to tell the loader how to parse the date string. The format specification is as follows:
yy—two-digit year
yyyy—four-digit year
MM—two-digit month (01 to 12)
MMM—3three-letter month (JAN, FEB, etc)
dd—two-digit day of month
For example, format="MM/dd/yyyy" equals 11/04/2004 and format="yyyy-MM-dd" equals 2004-11-04. Note that yy also matches four-digit years.
Whether the field can be null. If nullable="false", the loader treats a null value as an error. (Default=true)
Value to substitute if the field value is null. (Default=null)
Whether to use the previous non-null value if the current value of the field is null. The default applies if there is no previous non-null value. (Default=false)