Depending on how you plan to view your data, you can select to preaggregate data at the database server. Preaggregation (also called server aggregation) is a querying strategy that uses functions to summarize data as it is retrieved from the database. Instead of returning a line-item list of every row that meets the criteria on your Request line, you can order the database to group related information. This results in one row representing the combined (aggregate) value of each distinct group.
You use data functions (provided by your RDBMS) to preaggregate data in a query. When a data function is applied to a Request item, the data related to that item is aggregated when the query is processed. If you need both summary data and increasing levels of detail breakdown in your reporting or analysis, do not preaggregate the data. Report sections will automatically provide an aggregated summary view, and component levels of detail data can be reached using drill-down tools.
If your data set is potentially very large, or incorporates very discrete levels of transactional data that do not apply to your analysis, it may be best to preaggregate the data at the server to return a more manageable data set. Preaggregating data in your query assumes that you have a clear idea of the data to look at and a good conceptual understanding of relational databases. If you are unsure about preaggregation, process the query without applying data functions. If you find that it would be better to preaggregate, return to the Query section and apply data functions to the query.
Use data functions to preaggregate data as it is retrieved from the database. The following table lists the prebuilt data functions that you can apply to items in the Request line.
When using data functions, remember that with the exception of counts, data functions are applied almost entirely to numeric data items and the results are computed with respect to dimensional, nonnumeric items on the Request line, such as name and date items as in the following examples.
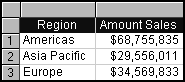
Query 1 includes only items for Region and Amount_Sales. The data function Sum is applied and the data returned consists of one row for each region with an aggregate sum for that region in the Amount Sales column.

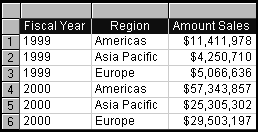
In Query 2, the item Fiscal_Year is added to Query 1, breaking out rows for each state/fiscal year combination with Units totaled on a per state, per year basis.

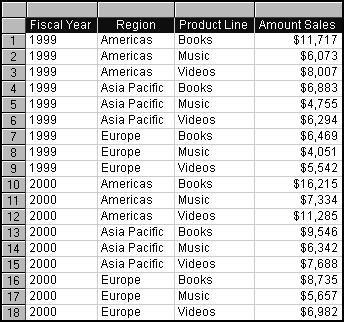
In Query 3, the Product_Line Name has been included and the data function is changed to Average. The number of rows increased, with data summarized as an average per state, per year, per product line.

 To apply a data function in the Query section:
To apply a data function in the Query section: