11g Release 7 (11.1.7)
Part Number E37979-01
Home
Contents
Book
List
Contact
Us
|
Oracle® Fusion Applications Project Execution Management Implementation Guide 11g Release 7 (11.1.7) Part Number E37979-01 |
Home |
Contents |
Book List |
Contact Us |
|
Previous |
Next |
This chapter contains the following:
Project Execution Management Offering: Overview
Define Common Applications Configuration for Project Execution Management: Overview
Getting Started with an Implementation: Overview
Manage Application Implementation
In the Project Management business process area, your enterprise can configure how you execute projects, including how to manage requirements, schedule and collaborate on tasks, staff resources, maximize utilization, resolve issues, and complete deliverables.
Before you begin, use the Getting Started page in the Setup and Maintenance work area to access reports for each offering, including full lists of setup tasks, descriptions of the options and features that you can select when you configure the offering, and lists of business objects and enterprise applications that are associated with the offering.
The first implementation step is to configure the offerings in the Setup and Maintenance work area by selecting the offerings, options, and features that you want to make available to implement. For the Project Execution Management offering, you can select the following features and options:
Project Execution Management
The following table lists feature choices for the Project Execution Management offering.
|
Feature |
Feature Description |
|---|---|
|
Implementation Project Task Lists |
Indicate whether to display the minimum or a complete list of setup tasks in implementation projects.
|
|
Local Installation of Help |
Define help settings if help is locally installed. |
|
Access to Internet-Based Help Features |
Set options for using Internet-based help features. |
|
Help Customization |
Set help options for privileged users to edit help and add custom help. |
|
Custom Help Security |
Enables addition of links to internet sites from help, and sharing of ratings. |
Project Resource Management
Indicate whether Oracle Fusion Project Resource Management will be deployed.
Next, create one or more implementation projects for the offerings, options, and features that you want to implement first, which generates task lists for each project. The application implementation manager can customize the task list and assign and track each task.
If you select the Complete feature choice for the Implementation Project Task Lists feature, and enable all additional features, the generated task list for this offering will contain the groups of tasks listed in the following table:
|
Task List |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Define Common Applications Configuration for Project Execution Management |
Define the configuration for common setup such as users, enterprise and HR structures, security, and common reference objects for Oracle Fusion Project Execution Management. You can find other information that supports the common implementation tasks in the Oracle Fusion Applications Concepts Guide. |
|
Define Common Project Execution Options |
Configure Oracle Fusion Project Management products to manage project users, project roles, and calendars. |
|
Define Project Management Configuration |
Configure Oracle Fusion Project Management to manage projects, tasks, requirements, deliverables, and resources, and to track and resolve issues. |
|
Define Project Resource Management Configuration |
Configure Oracle Fusion Project Resource Management to manage the availability and staffing of resources, fulfill project resource requests, and monitor resource utilization. |
|
Define Extensions for Project Execution Management |
Configure specific extensions for customization of Project Execution Management. |
You can also customize and extend applications using other tools. For more information, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Extensibility Guide.
In the Define Common Applications Configuration for Project Execution Management activity, you perform common setup steps such as populating the product tables containing user and role information and defining security and common reference objects for Project Execution Management applications in Oracle Fusion Project Portfolio Management. This activity contains advanced setup tasks that are not required for a typical implementation of Project Execution Management applications.
Setup tasks in the Define Common Applications Configuration for Project Execution Management activity are grouped into the following task lists:
|
Task List |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Define Synchronization of Users and Roles from LDAP |
Run a process to populate the product tables containing user and role information with the users and roles held in LDAP. This process is typically the first implementation task but can also run periodically to keep the product tables synchronized with subsequent updates to LDAP. |
|
Define Social Networking |
Review options related to social networking and update as necessary. |
|
Define Security for Project Execution Management |
Enable users to perform functions related to their job roles. |
|
Define Approval Management for Project Execution Management |
Define approval routing structures and controls to match the needs of the organization. |
|
Define Help Configuration |
Define what users can see and do in a local deployment of Oracle Fusion Applications Help. |
|
Maintain Common Reference Objects |
Review and manage objects, for example currencies and reference data sets, that are shared across applications. Perform setup that applies to Oracle Fusion Applications as a whole, for example Navigator menu customization and maintenance of common messages that can be used in any application. |
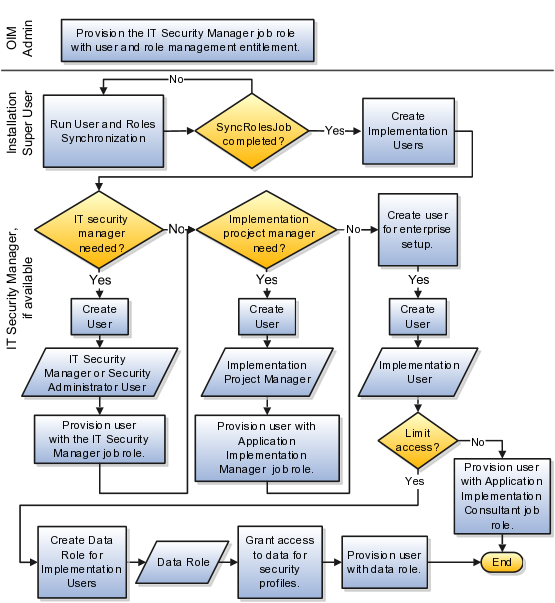
To start an Oracle Fusion Applications implementation, you must set up one or more initial users using the super user that was created during installation and provisioning of the Oracle Fusion Applications environment, or using the initial administrator user provided by Oracle for Oracle Cloud Application Services implementations. Because Oracle Fusion Applications is secure as delivered, the process of enabling the necessary setup access for initial users requires several specialized steps when getting started with an implementation.
The following high level steps are required for starting an implementation.
If you are not starting an Oracle Cloud Application Services implementation, sign into Oracle Identity Manager (OIM) as the OIM Administration users and provision the IT Security Manager job role with roles for user and role management. This enables the super user account, which is provisioned with the IT Security Manager job role, to create implementation users.
For starting all implementations, sign in as the user with initial access: either the Oracle Fusion Applications installation super user or the initial Oracle Cloud Application Services administrator user.
Select an offering to implement, and generate the setup tasks needed to implement the offering.
Perform the following security tasks:
Synchronize users and roles in the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) store with HCM user management by using the Run User and Roles Synchronization Process task.
Create an IT security manager user by using the Create Implementation Users task.
Provision the IT security manager with the IT Security Manager role by using the Provision Roles to Implementation Users task.
As the newly created IT security manager user, sign in to Oracle Fusion Applications and set up at least one implementation user for setting up enterprise structures.
Create an implementation user by using the Create Implementation Users task.
Provision the implementation user with the Application Implementation Manager job role or the Application Implementation Consultant job role by using the Provision Roles to Implementation Users task. The Application Implementation Consultant job role inherits from all product-specific application administrators and entitles the necessary View All access to all secured object.
Optionally, create a data role for an implementation user who needs only the limited access of a product-specific Application Administrator by using the Create Data Role for Implementation Users. Then assign the resulting data role to the implementation user by using the Provision Roles to Implementation Users task.
The figure shows the task flow from provisioning the IT Security Manager job role with the user and role management entitlement to creating and provisioning implementation users for enterprise setup.
The Manage Applications Implementation business process enables rapid and efficient planning, configuration, implementation, deployment, and ongoing maintenance of Oracle Fusion applications through self-service administration.
The Setup and Maintenance work area offers you the following benefits:
Prepackaged Lists of Implementation Tasks
Task lists can be easily configured and extended to better fit with business requirements. Auto-generated, sequential task lists include prerequisites and address dependencies to give full visibility to end-to-end setup requirements of Oracle Fusion applications.
Rapid Start
Specific implementations can become templates to facilitate reuse and rapid-start for comparable Oracle Fusion applications across many instances.
Comprehensive Reporting
A set of built-in reports helps to analyze, validate and audit configurations, implementations, and setup data of Oracle Fusion applications.
With Oracle Fusion Functional Setup Manager you can:
Learn about and analyze implementation requirements.
Configure Oracle Fusion applications to match your business needs.
Achieve complete visibility to setup requirements through guided, sequential task lists downloadable into Excel for project planning.
Enter setup data through easy-to-use user interfaces available directly from the task lists.
Export and import data from one instance to another for rapid setup.
Validate setup by reviewing setup data reports.
Implement all Oracle Fusion applications through a standard and consistent process.
The following documentation resources are available for learning how to configure Oracle Fusion Applications.
Functional Setup Manager Developer's Guide
Common Implementation Guide
Customer Data Management Implementation Guide
Enterprise Contracts Implementation Guide
Marketing Implementation Guide
Sales Implementation Guide
Fusion Accounting Hub Implementation Guide
Financials Implementation Guide
Compensation Management Implementation Guide
Workforce Deployment Implementation Guide
Workforce Development Implementation Guide
Incentive Compensation Implementation Guide
Procurement Implementation Guide
P6 EPPM Administrator's Guide for an Oracle Database
P6 EPPM Administrator's Guide for Microsoft SQL Server Database
An implementation project is the list of setup tasks you need to complete to implement selected offerings and options. You create a project by selecting the offerings and options you want to implement together. You manage the project as a unit throughout the implementation lifecycle. You can assign these tasks to users and track their completion using the included project management tools.
You can also create an implementation project to maintain the setup of specific business processes and activities. In this case, you select specific setup task lists and tasks
Implementation projects are also the foundation for setup export and import. You use them to identify which business objects, and consequently setup data, you will export or import and in which order.
When creating an implementation project you see the list of offerings and options that are configured for implementation. Implementation managers specify which of those offerings and options to include in an implementation project. There are no hard and fast rules for how many offerings you should include in one implementation project. The implementation manager should decide based on how they plan to manage their implementations. For example, if you will implement and deploy different offerings at different times, then having separate implementation projects will make it easier to manage the implementation life cycles. Furthermore, the more offerings you included in an implementation project, the bigger the generated task list will be. This is because the implementation task list includes all setup tasks needed to implement all included offerings. Alternatively, segmenting into multiple implementation projects makes the process easier to manage.
Offerings are application solution sets representing one or more business processes and activities that you typically provision and implement as a unit. They are, therefore, the primary drivers of functional setup of Oracle Fusion applications. Some of the examples of offerings are Financials, Procurement, Sales, Marketing, Order Orchestration, and Workforce Deployment. An offering may have one or more options or feature choices.
The configuration of the offerings will determine how the list of setup tasks is generated during the implementation phase. Only the setup tasks needed to implement the selected offerings, options and features will be included in the task list, giving you a targeted, clutter-free task list necessary to meet your implementation requirements.
Offerings and their options are presented in an expandable and collapsible hierarchy to facilitate progressive decision making when specifying whether or not an enterprise plans to implement them. An offering or its options can either be selected or not be selected for implementation. Implementation managers decide which offerings to enable.
The Provisioned column on the Configure Offerings page shows whether or not an offering is provisioned. While you are not prevented from configuring offerings that have not been provisioned, ultimately the users are not able to perform the tasks needed to enter setup data for those offerings until appropriate enterprise applications (Java EE applications) are provisioned and their location (end point URLs) is registered.
Each offering in general includes a set of standard functionality and a set of optional modules, which are called options. For example, in addition to standard Opportunity Management, the Sales offering includes optional functionality such as Sales Catalog, Sales Forecasting, Sales Prediction Engine, and Outlook Integration. These optional functions may not be relevant to all application implementations. Because these are subprocesses within an offering, you do not always implement options that are not core to the standard transactions of the offering.
Offerings include optional or alternative business rules or processes called feature choices. You make feature selections according to your business requirements to get the best fit with the offering. If the selected offerings and options have dependent features then those features are applicable when you implement the corresponding offering or option. In general, the features are set with a default configuration based on their typical usage in most implementations. However, you should always review the available feature choices for their selected offerings and options and configure them as appropriate for the implementation.
You can configure feature choices in three different ways:
If a feature can either be applicable or not be applicable to an implementation, a single checkbox is presented for selection. Check or uncheck to specify yes or no respectively.
If a feature has multiple choices but only one can be applicable to an implementation, multiple choices are presented as radio buttons. You can turn on only one of those choices.
If the feature has multiple choices but one or more can be applicable to an implementation then all choices are presented with a checkbox. Select all that apply by checking the appropriate choices.