11g Release 7 (11.1.7)
Part Number E37979-01
Home
Contents
Book
List
Contact
Us
|
Oracle® Fusion Applications Project Execution Management Implementation Guide 11g Release 7 (11.1.7) Part Number E37979-01 |
Home |
Contents |
Book List |
Contact Us |
|
Previous |
Next |
This chapter contains the following:
Defining Security After Enterprise Setup: Points to Consider
Security Tasks and Oracle Fusion Applications: How They Fit Together
Define Users for Project Execution Management
Manage HCM Role Provisioning Rules
Security tasks include the following.
Security setup
Security implementation and administration
Note
Security setup and administration tasks typically use integrated user interface pages that are provided by the following products.
Oracle Identity Manager (OIM)
Oracle Authorization Policy Manager (APM)
Oracle Fusion Human Capital Management (HCM) products
Oracle Application Access Control Governor (AACG) in Oracle Enterprise Governance, Risk and Compliance (GRC)
Security setup and administrative tasks performed by product administrators and implementation consultants, such as managing HCM security profiles, are presented in the documentation for those products.
Provision the IT Security Manager job role with roles for user and role management.
Sign into Oracle Fusion Applications for the first time with the Installation Super User account to synchronize LDAP users with HCM user management and create an IT security manager user account and provision it with the IT Security Manager role. For environments that are not in Oracle Cloud, use the super user account that was created during installation to sign in for the first time.
Establish at least one implementation user and provision that user with sufficient access to set up the enterprise for all integrated Oracle Fusion Middleware and all application pillars or partitions.
Once initial security administration is complete and your enterprise is set up with structures such as business units, additional security administration tasks are optional and based on modifying and expanding the predefined security reference implementation to fit your enterprise. See points to consider for defining security, data security and trading partner security after enterprise setup.
After the implementation user has set up the enterprise, further security administration depends on the requirements of your enterprise.
The Define Security activity within the Information Technology (IT) Management business process includes the following tasks.
Import Worker Users
Import Partner Users
Manage Job Roles
Manage Duties
Manage Application Access Controls
If no legacy users, user accounts, roles, and role memberships are available in the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) store, and no legacy workers are available in Human Resources (HR), the implementation user sets up new users and user accounts and provisions them with roles available in the Oracle Fusion Applications reference implementation.
If no legacy identities (workers, suppliers, customers) exist to represent people in your enterprise, implementation users can create new identities in Human Capital Management (HCM), Supplier Portal, and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Self Service, respectively, and associate them with users.
Oracle Identity Management (OIM) handles importing users.
If legacy employees, contingent workers, and their assignments exist, the HCM Application Administrator imports these definitions by performing the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task. If user and role provisioning rules have been defined, the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load process automatically creates user and role provisioning requests as the workers are created.
Once the enterprise is set up, performing the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task populates the enterprise with HR workers in records linked by global user ID (GUID) to corresponding user accounts in the LDAP store. If no user accounts exist in the LDAP store, the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task results in new user accounts being created. Worker email addresses as an alternate input for the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task triggers a search of the LDAP for user GUIDs, which may perform more slowly than entering user names.
In the security reference implementation, the HCM Application Administrator job role hierarchy includes the HCM Batch Data Loading Duty role, which is entitled to import worker identities. This entitlement provides the access necessary to perform the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task in HCM.
Note
The Import Person and Organization task in the Define Trading Community Import activity imports the following resources, creates users, and links the resources to users for use in CRM.
Internal employees
Contingent workers
External partner contacts
Partner companies
Legal entities
Customers
Consumers
If role provisioning rules have been defined, the Import Person and Organization task automatically provisions role requests as the users are created.
If legacy users (identities) and user accounts exist outside the LDAP store that is being used by the Oracle Fusion Applications installation, the IT security manager has the option to import these definitions to the LDAP store by performing the Import Worker Users and Import Partner Users tasks.
If no legacy users or user accounts can be imported or exist in an LDAP repository accessible to Oracle Identity Management (OIM), the IT security manager creates users manually in OIM or uses the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task to create users from imported HR workers.
Once users exist, their access to Oracle Fusion Applications is dependent on the roles provisioned to them in OIM or Human Capital Management. Use the Manage HCM Role Provisioning Rules task to define rules that determine what roles are provisioned to users.
Importing user identities from other applications, including other Oracle Applications product lines, is either a data migration or manual task. Migrating data from other Oracle Applications includes user data. For more information about importing users, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager.
In the security reference implementation, the IT Security Manager job role hierarchy includes the HCM Batch Data Loading Duty and the Partner Account Administration Duty. These duty roles provide entitlement to import or create users. The entitlement Load Batch Data provides the access necessary to perform the Import Worker Users task in OIM. The entitlement Import Partner entitlement provides the access necessary to perform the Import Partner Users task in OIM.
Job and abstract roles are managed in OIM. This task includes creating and modifying job and abstract roles, but not managing role hierarchies of duties for the jobs.
Note
Manage Job Roles does not include provisioning job roles to users. Provisioning users is done in OIM, HCM, CRM or Oracle Fusion Supplier Portal.
Roles control access to application functions and data. Various types of roles identify the functions performed by users.
The Oracle Fusion Applications security reference implementation provides predefined job and abstract roles. In some cases, the jobs defined in your enterprise may differ from the predefined job roles in the security reference implementation. The predefined roles and role hierarchies in Oracle Fusion may require changes or your enterprise may require you to create new roles. For example, you need a job role for a petty cash administrator, in addition to an accounts payable manager. The security reference implementation includes a predefined Accounts Payable Manager, and you can create a petty cash administrator role to extend the reference implementation.
In the security reference implementation, the IT Security Manager job role hierarchy includes the Enterprise Role Management Duty role, which is entitled to manage job and abstract roles (the entitlement is Manage Enterprise Role). This entitlement provides the access necessary to perform the Manage Job Roles task in OIM.
A person with a job role must be able to perform certain duties. In the Oracle Fusion Applications security reference implementation, enterprise roles inherit duties through a role hierarchy. Each duty corresponds to a duty role. Duty roles specify the duties performed within applications and define the function and data access granted to the enterprise roles that inherit the duty roles.
Managing duties includes assigning duties to job and abstract roles in a role hierarchy using Authorization Policy Manager (APM). If your enterprise needs users to perform some actions in applications coexistent with Oracle Fusion applications, you may wish to remove the duty roles that enable those actions. For details about which duty roles are specific to the products in an offering, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Security Reference Manual for each offering.
OIM stores the role hierarchy and the spanning of roles across multiple pillars or logical partitions of applications.
In cases where your enterprise needs to provide access to custom functions, it may be necessary to create or modify the duty roles of the reference implementation.
Tip
As a security guideline, use only the predefined duty roles, unless you have added new applications functions. The predefined duty roles fully represent the functions and data that must be accessed by application users and contain all appropriate entitlement. The predefined duty roles are inherently without segregation of duty violations of the constraints used by the Application Access Controls Governor.
In the security reference implementation, the IT Security Manager job role hierarchy includes the Application Role Management Duty role, which is entitled to manage duty roles (the entitlement is Manage Application Role). This entitlement provides the access necessary to perform the Manage Duties task in APM.
Note
Product family administrators are not entitled to create role hierarchies or manage duty roles and must work with the IT security manager to make changes such as localizing a duty role to change a role hierarchy. Setup for localizations is documented in HCM documentation.
Prevent or limit the business activities that a single person may initiate or validate by managing segregation of duties policies in the Application Access Controls Governor (AACG) .
Note
In AACG, segregation of duties policies are called access controls or segregation of duties controls.
In the security reference implementation, the IT Security Manager job role hierarchy includes the Segregation of Duties Policy Management Duty role, which is entitled to manage segregation of duties policies (the entitlement is Manage Segregation of Duties Policy). This entitlement provides the access necessary to perform the Manage Application Access Controls task in AACG.
The major security tasks and their order within the context of an overall Oracle Fusion Applications implementation extend from security setup through production deployment audits.
The Oracle Fusion business process model (BPM) provides a sequence of security implementation tasks that includes the following.
Security setup (Define Common Applications Configuration activity)
Define Implementation Users task group (optional)
Create Implementation Users task
Create Data Role for Implementation Users task
Provision Roles to Implementation Users task
Define security - tasks vary depending on deployed Oracle Fusion product family
Revoke Data Role from Implementation Users task
Import Worker Users task
Import Partner Users task
Manage Duties task
Manage Job Roles task
Manage Application Access Controls task
Define Automated Governance, Risk, and Performance Controls activity
Manage Application Access Controls task (AACG settings)
Manage Application Preventive Controls task
Manage Application Transaction Controls task
Manage Application Configuration Controls task
User and role provisioning tasks
Implement Role Request and Provisioning Controls activity
Import Worker Users task
Import Partner Users task
Self Request User Roles task
Approve User and Role Provisioning Requests task
Assign User Roles task
Manage Supplier User Roles and User Role Usages task
Map and Synchronize User Account Details task
Tasks for viewing account details for self or others
Tasks for applying and managing various role provisioning rules
Tasks for running synchronization processes
Security implementation and ongoing maintenance after setup (Manage IT Security activity)
Implement Function Security Controls
Create Job Role task
Import Worker Users task
Import Partner Users task
Manage Duties task
Manage Job Roles task
Manage Users task
Implement Data Security Controls
Manage Data Security Policies task
Manage Role Templates task
Manage Encryption Keys task
Manage Segment Security task
Manage Data Access Sets task
Define Security Profiles task group
Auditing tasks
Manage Security Audit, Compliance and Reporting activity
Manage Application Access Controls task
Note
Go live deployment does not require lockdown or specific security tasks because security is enforced across the test to production information life cycle.
The following enterprise roles are provisioned to a single super user that is set up by the Oracle Fusion Applications installation process, and to the initial user set up by Oracle for Oracle Cloud Application Services:
Application Implementation Consultant
IT Security Manager
Application Administrators for the provisioned products
Initial security administration also includes provisioning the IT Security Manager role with Oracle Identity Management (OIM) roles for user and role management.
Identity User Administrator
Role Administrator
Additionally, the Xellerate Users organization must be assigned to the IT Security Manager role.
Important
As a security guideline, provision a dedicated security professional with the IT Security Manager role at the beginning of an implementation, and revoke that role from users provisioned with the Application Implementation Consultant role.
Security tasks are supported by tools within both Oracle Fusion Applications and Oracle Fusion Middleware.
The figure lists the tasks associated with each of the integrated products and pillars of an Oracle Fusion Applications deployment.
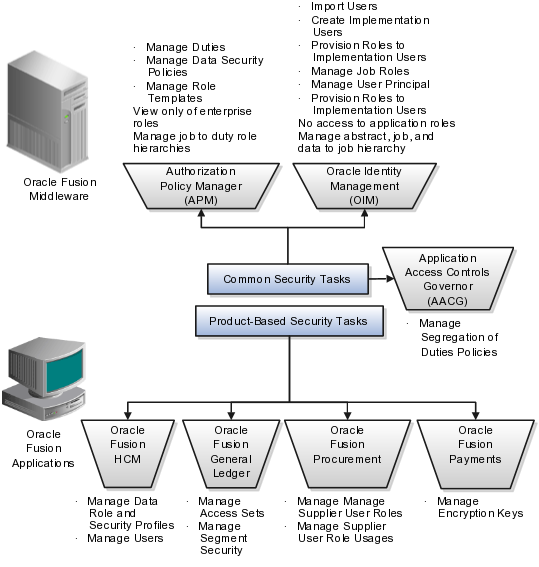
Security tasks span multiple business processes and are performed by various roles using numerous integrated tools.
The following table shows the business process model (BPM) tasks and tools used to support securing Oracle Fusion Applications.
|
Example Task |
Oracle BPM Task |
Supporting Tools |
Details |
|---|---|---|---|
|
View duty roles inherited by a job role |
Manage Duties |
|
Each logical partition or pillar contains a collection of application roles, and function and data security policies. |
|
View entitlement or policies carried by a job role |
Manage Duties |
|
In LDAP, the policy store stores application roles and the identity store stores enterprise roles. |
|
Add a job role to a role hierarchy |
Manage Job Roles |
|
The identity store in LDAP stores enterprise roles. |
|
Add a duty role to a role hierarchy |
Manage Duties |
|
LDAP stores the role hierarchy and the spanning of roles across multiple pillars or logical partitions. |
|
Create a hierarchy of enterprise (abstract, job, data) roles |
Manage Job Roles |
|
|
|
Create a hierarchy of (application) duty roles |
Manage Duties |
|
|
|
Create a new job role |
Manage Job Roles |
|
The identity store in LDAP stores enterprise roles. |
|
Change duty roles inherited by a job or abstract role |
Manage Duties |
|
The policy store stores duty roles. The identity store stores enterprise roles. Some duty roles may enable actions and their associated users interface features that your enterprise does not want users to perform in Oracle Fusion applications. |
|
Create a new duty role |
Manage Duties |
|
All functions and actions in Oracle Fusion Applications that need to be secured are covered by the reference implementation. In some cases, especially with function customizations, a new duty role may be needed. |
|
View Segregation of Duties (SOD) policies respected by a duty role |
Manage Application Access Controls |
|
The Security Reference Manuals (SRM) document the segregation of duties (SOD) policies respected within each job role |
|
View SOD policy violations carried by the duty roles inherited by a job role |
Manage Application Access Controls |
|
The Security Reference Manuals (SRM) document the SOD policies respected within each job role |
|
View SOD policy violations |
Manage Segregation of Duties Policies |
|
The SRM documents the SOD conflicts for each job role |
|
View the data security policies carried by a job, abstract, and data roles |
Manage Data Security Policies |
|
Oracle Fusion Data Security stores data security policies in the policy store. Data security can also be defined in application pages provided by Oracle Middleware Extensions for Applications (FND) |
|
Create and update HCM security profiles |
Manage Data Role and Security Profiles |
|
This task does not include assigning data roles to the users, which is supported by user provisioning tasks. |
|
Create (generate) a data role |
|
|
Data roles are generated automatically based on data role templates and enterprise setup. Changes to data role templates generate new or changed data roles. Create data roles in HCM using the Manage Data Roles and Security Profiles task. |
|
Create a new data security policy (not through generated data roles based on data role templates or HCM security profiles) |
Manage Data Security Policies |
|
Data security can also be defined in application pages provided by Oracle Middleware Extensions for Applications (FND) |
|
View data role templates defined by a product |
Manage Role Templates |
|
|
|
Create or edit an existing data role template |
Manage Role Templates |
|
|
|
Secure common objects such as attachment categories or profile options |
Manage Data Security Policies |
|
Data security can also be defined in application pages provided by Oracle Middleware Extensions for Applications (FND) |
|
View, create, update encryption keys used to secure attributes of personally identifiable information |
Manage Encryption Keys |
|
|
|
View, create, update Data Access Sets used to secure Ledgers and Ledger Sets |
Manage Data Access Sets |
|
|
|
View, create, update accounting flexfield segment security rules |
Manage Security Segments |
|
|
|
View or update the set of job roles that can be provisioned to supplier users |
Manage Supplier User Role |
|
These tools are in the Oracle Fusion Procurement product family |
|
Determine the supplier job roles that the supplier self service administrator can provision to supplier users |
Manage Supplier User Role Usages |
|
These tools are in the Oracle Fusion Procurement product family |
|
Set default supplier job roles based on the set of supplier roles that are defined by performing the Manage Supplier User Roles task |
Manage Supplier User Role Usages |
|
These tools are in the Oracle Fusion Procurement product family |
|
Create a new implementation user |
Create Implementation Users |
|
|
|
Import legacy users |
|
|
|
|
Create a new user |
Manage Users |
|
HCM creates a new user and identity when a new worker is created. The Hire Employee and Add Contingent Worker tasks also result in new user creation requests. Creating a new user automatically triggers role provisioning requests based on role provisioning rules. |
|
Provision roles to a user |
|
|
Implementation users are provisioned through OIM since HCM is not setup at the start of the implementation. The Provision Roles to Implementation Users is not needed once implementation is complete. Once HCM is setup, HCM is used to provision roles to non-implementation users by performing the Manage Users task. Human Resources (HR) transaction flows such as Hire and Promote also provision roles. Once supplier users are setup, Supplier Model can be used by internal users to maintain supplier user accounts or supplier users can maintain their accounts in Supplier Portal. |
|
View the job, abstract, and data roles provisioned to a user |
|
|
LDAP stores users, roles and provisioning information. The Manage User Principal and Provision Roles to Implementation Users tasks are not needed once implementation is complete. |
|
Revoke role from user. |
Manage Users |
|
You can revoke roles from various Human Resources task flows, the HCM Manage Users task and OIM. User termination includes role revocation. |
|
Approve role provisioning or user account request. |
Approve User and Role Provisioning Requests |
|
|
|
View audit logs |
Not applicable |
|
Viewing audit logs is a Oracle Fusion Middleware function and not represented by an Oracle Fusion Applications BPM task. |
For more information about provisioning identities and configuring audit policies, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Administrator's Guide.
There may be more than one navigation path to the graphical user interface in which the task is performed. You can access most security tasks by starting in the Setup and Maintenance Overview page and searching for security tasks and task lists.
Identity covers all aspects of an entity's existence within the contexts in which it is used. The identity of an enterprise user consists of HR attributes, roles, resources, and relationships.
HR attributes include identifying information about a user that is relatively static and well understood, such as first and last name, title, and job function.
Roles are part of a user's identity and define the user's purpose and responsibilities.
Within identity management, resources define what a user can and does do. In an enterprise, this typically translates into what resources a user has access to, what privileges they have on that resource, and what they have been doing on that resource. Resources can be application accounts or physical devices such as laptops or access cards. The enterprise owns the resources, secures them, and manages access to the resources by managing the user's identity and access.
Relationships establish the portion of user identities that involve organizational transactions such as approvals.
An Oracle Fusion Applications user and corresponding identity are usually created in a single transaction, such as when a worker is created in Human Resources (HR). That transaction automatically triggers provisioning requests for the user based on role provisioning rules.
User accounts for some identities that are not employees, such as partner contacts, may be created in a later transaction using an identity that is already created in the identity store. Supplier contacts are created in the Supplier Model, not HR.
Various locations store identity and user data.
Identity data consists of the following.
HR person records
Oracle Fusion Trading Community Model party records
In Oracle Fusion Applications, identities and users correspond one to one, but not all identities correspond to a user, and not all users are provisioned with an identity. Some identities stored in HR and Trading Community Model may not be provisioned to user accounts and therefore are not synchronized with Oracle Identity Management (OIM). For example, a contact for a prospective customer is an identity in Trading Community Model but may not be provisioned with a user account in OIM. Some users stored in the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) store may not be provisioned with identities. For example, system user accounts used to run Web services to integrate third party services with Oracle Fusion Applications are not associated with a person record in HR or Trading Community Model. Some identifying credentials such as name, department, e-mail address, manager, and location are stored with user data in the LDAP store.
You can import users or user attributes in bulk from existing legacy identity and user stores.
Your tasks may include the following.
Create users in bulk
Update specific attributes for all users, such as postal code
Link users to HR or Trading Community Model persons
Monitor progress of the import process
Correct errors & re-import
Export users in bulk
Import and export users using a standard plain text data interchange format like Lightweight Data Interchange Format (LDIF)
You can reserve a specific user name not currently in use for use in the future, or release a reserved username from the reservation list and make it available for use. Between a user registration request and approved registration, Oracle Fusion Applications holds the requested user name on the reservation list, and releases the name if an error occurs in the self-registration process or the request is rejected. Self-registration processes check the reservation list for user name availability and suggest alternative names.
New identities, such as new hires, trigger user and role provisioning events. In addition to user creation tasks, other tasks, such as Promote Worker or Transfer Worker, result in role provisioning and recalculation based on role provisioning rules.
When an identity's attributes change, you may need to provision the user with different roles. Role assignments may be based on job codes, and a promotion triggers role provisioning changes. Even if the change in the identities attributes requires no role assignment change, such as with a name change, OIM synchronizes the corresponding user information in the LDAP store.
Deactivating or terminating an identity triggers revocation of some roles to end all assignments, but may provision new roles needed for activities, such as a pay stub review. If the corresponding user for the identity was provisioned with a buyer role, terminating the identity causes the user's buyer record in Procurement to be disabled, just as the record was created when the user was first provisioned with the buyer role.
Oracle Fusion Applications provides mechanisms for notifying and auditing requests or changes affecting identities and users.
Oracle Fusion Applications notifies requestors, approvers, and beneficiaries when a user account or role is provisioned. For example, when an anonymous user registers as a business-to-customer (B2C) user, the B2C user must be notified of the registration activation steps, user account, password and so on once the approver (if applicable) has approved the request and the user is registered in the system.
User ID and GUID attributes are available in Oracle Fusion Applications session information for retrieving authenticated user and identity data.
End user auditing data is stored in database WHO columns and used for the following activities.
Setting up sign-in audit
Using the application monitor
Notifying of unsuccessful sign ins
Sign-in audit reports
You can conduct real time audits that instantiate a runtime session and impersonate the target user (with the proxy feature) to test what a user has access to under various conditions such as inside or outside firewall and authentication level.
For information on configuring audit policies and the audit store, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Administrator's Guide.
You can designate local administrators as delegated administrators to manage a subset of users and roles.
Delegated administrators can be internal or external persons who are provisioned with a role that authorizes them to handle provisioning events for a subset of users and roles.
For example, internal delegated administrators could be designated to manage users and roles at the division or department level. External delegated administrators could be designated to manage users and roles in an external organization such as a primary supplier contact managing secondary users within that supplier organization.
You can also define delegated administration policies based on roles. You authorize users provisioned with specific roles named in the policy to request a subset of roles for themselves if needed, such as authorizing a subset of roles for a subset of people. For example, the policy permits a manager of an Accounts Payables department to approve a check run administrator role for one of their subordinates, but prohibits the delegated administrator from provisioning a budget approver role to the subordinate.
You activate or change credentials on users by managing them in Oracle Identity Management (OIM)
Applications themselves must be credentialed to access one another.
Oracle Fusion Applications distinguishes between user identities and application identities (APPID). Predefined application identities serve to authorize jobs and transactions that require higher privileges than users.
For example, a payroll manager may submit a payroll run. The payroll application may need access to the employee's taxpayer ID to print the payslip. However, the payroll manager is not authorized to view taxpayer IDs in the user interface as they are considered personally identifiable information (PII).
Calling applications use application identities (APPID) to enable the flow of transaction control as it moves across trust boundaries. For example, a user in the Distributed Order Orchestration product may release an order for shipping. The code that runs the Pick Notes is in a different policy store than the code that releases the product for shipment. When the pick note printing program is invoked it is the Oracle Fusion Distributed Order Orchestration Application Development Framework (ADF) that is invoking the program and not the end user.
A user's access to data and functions depends on the user's roles: users have one or more roles that enable them to perform the tasks required by their jobs or positions. Roles must be provisioned to users; otherwise, users have no access to data or functions.
Roles can be provisioned to users:
Automatically
Manually, using delegated administration:
Users such as line managers and human resource specialists can provision roles manually to other users.
Users can request roles for themselves.
For both automatic and manual role provisioning, you create a role mapping to identify when a user becomes eligible for a role.
Oracle Identity Management (OIM) can be configured to notify users when their roles change; notifications are not issued by default.
Data roles, abstract roles, and job roles can be provisioned to users. Roles available for provisioning include predefined roles, HCM data roles, and roles created using OIM.
A role is provisioned to a user automatically when at least one of the user's assignments satisfies the conditions specified in the relevant role-mapping definition. The provisioning occurs when the assignment is either created or updated. For example, when a person is promoted to a management position, the line manager role is provisioned automatically to the person if an appropriate role mapping exists. Any change to a person's assignment causes the person's automatically provisioned roles to be reviewed and updated as necessary.
Automatically provisioned roles are deprovisioned automatically as soon as a user no longer satisfies the role-mapping conditions. For example, a line manager role that is provisioned to a user automatically is deprovisioned automatically when the user ceases to be a line manager.
Automatically provisioned roles can be deprovisioned manually at any time.
Manually provisioned roles are deprovisioned automatically only when all of the user's work relationships are terminated; in all other circumstances, users retain manually provisioned roles until they are deprovisioned manually.
When a person's line manager is changed, the roles of both new and previous line managers are updated as necessary. For example, if the person's new line manager now satisfies the conditions in the role mapping for the line manager role, and the role is one that is eligible for autoprovisioning, then that role is provisioned automatically to the new line manager. Similarly, if the previous line manager no longer satisfies the conditions for the line manager role, then that role is deprovisioned automatically.
When a work relationship is terminated, all automatically provisioned roles for which the user does not qualify in other work relationships are deprovisioned automatically. Manually provisioned roles are deprovisioned automatically only if the user has no other work relationships; otherwise, the user retains all manually provisioned roles until they are deprovisioned manually.
Automatic deprovisioning can occur either as soon as the termination is submitted or approved or on the day after the termination date. The user who is terminating the work relationship selects the appropriate deprovisioning date.
Role mappings can provision roles to users automatically at termination. For example, the locally defined roles Retiree and Beneficiary could be provisioned to users at termination based on assignment status and person type values.
If a termination is later reversed, roles that were deprovisioned automatically at termination are reinstated and post-termination roles are deprovisioned automatically.
Automatic role provisioning and deprovisioning are based on current data. For a future-dated transaction, such as a future promotion, role changes are identified and role provisioning occurs on the day the changes take effect, not when the change is entered. The process Send Pending LDAP Requests identifies future-dated transactions and manages role provisioning and deprovisioning at the appropriate time. Note that such role-provisioning changes are effective as of the system date; therefore, a delay of up to 24 hours may occur before users in other time zones acquire the access for which they now qualify.
User access to data and functions is determined by abstract, job, and data roles, which are provisioned to users either automatically or manually. To enable a role to be provisioned to users, you define a relationship, known as a mapping, between the role and a set of conditions, typically assignment attributes such as department, job, and system person type. In a role mapping, you can select any role stored in the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) directory, including Oracle Fusion Applications predefined roles, roles created in Oracle Identity Management (OIM), and HCM data roles.
The role mapping can support:
Automatic provisioning of roles to users
Manual provisioning of roles to users
Role requests from users
Immediate provisioning of roles
A role is provisioned to a user automatically if:
At least one of the user's assignments satisfies all conditions associated with the role in the role mapping.
You select the Autoprovision option for the role in the role mapping.
For example, for the HCM data role Sales Manager Finance Department, you could select the Autoprovision option and specify the following conditions.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Department |
Finance Department |
|
Job |
Sales Manager |
|
Assignment Status |
Active |
The HCM data role Sales Manager Finance Department is provisioned automatically to users with at least one assignment that satisfies all of these conditions.
Automatic role provisioning occurs as soon as the user is confirmed to satisfy the role-mapping conditions, which can be when the user's assignment is either created or updated. The provisioning process also removes automatically provisioned roles from users who no longer satisfy the role-mapping conditions.
Note
The automatic provisioning of roles to users is effectively a request to OIM to provision the role. OIM may reject the request if it violates segregation-of-duties rules or fails a custom OIM approval process.
Users such as human resource (HR) specialists and line managers can provision roles manually to other users; you create a role mapping to identify roles that can be provisioned in this way.
Users can provision a role to other users if:
At least one of the assignments of the user who is provisioning the role (for example, the line manager) satisfies all conditions associated with the role mapping.
You select the Requestable option for the role in the role mapping.
For example, for the HCM data role Quality Assurance Team Leader, you could select the Requestable option and specify the following conditions.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Manager with Reports |
Yes |
|
Assignment Status |
Active |
Any user with at least one assignment that satisfies both of these conditions can provision the role Quality Assurance Team Leader manually to other users, who are typically direct and indirect reports.
If the user's assignment subsequently changes, there is no automatic effect on roles provisioned by this user to others; they retain manually provisioned roles until either all of their work relationships are terminated or the roles are manually deprovisioned.
Users can request roles when reviewing their own account information; you create a role mapping to identify roles that users can request for themselves.
Users can request a role if:
At least one of their own assignments satisfies all conditions associated with the role mapping.
You select the Self-requestable option for the role in the role mapping.
For example, for the Expenses Reporting role you could select the Self-requestable option and specify the following conditions.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Department |
ABC Department |
|
System Person Type |
Employee |
|
Assignment Status |
Active |
Any user with at least one assignment that satisfies all of these conditions can request the role. The user acquires the role either immediately or, if approval is required, once the request is approved. Self-requested roles are classified as manually provisioned.
If the user's assignment subsequently changes, there is no automatic effect on self-requested roles. Users retain manually provisioned roles until either all of their work relationships are terminated or the roles are manually deprovisioned.
When you create a role mapping, you can apply autoprovisioning from the role mapping itself.
In this case, all assignments and role mappings in the enterprise are reviewed. Roles are:
Provisioned immediately to all users who do not currently have roles for which they are eligible
Deprovisioned immediately from users who are no longer eligible for roles that they currently have
Immediate autoprovisioning from the role mapping enables bulk automatic provisioning of roles to a group of users who are identified by the role-mapping conditions. For example, if you create a new department after a merger, you can provision relevant roles to all users in the new department by applying autoprovisioning immediately.
To provision roles immediately to a single user, the user's line manager or an HR specialist can autoprovision roles from that user's account.
The names of role mappings must be unique in the enterprise. You are recommended to devise a naming scheme that reveals the scope of each role mapping. For example:
|
Name |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Autoprovisioned Roles Sales Department |
Mapping includes all roles provisioned automatically to anyone in the sales department |
|
Benefits Specialist Autoprovisioned |
Mapping defines the conditions for autoprovisioning the Benefits Specialist role |
|
Line Manager Requestable Roles |
Mapping includes all roles that a line manager can provision manually to direct and indirect reports |
Roles must be provisioned to users explicitly, either automatically or manually; no role is provisioned to a user by default. This topic provides some examples of typical role mappings to support automatic and manual role provisioning.
You want all employees in your enterprise to have the Employee role automatically when they are hired. In addition, employees must be able to request the Expenses Reporting role when they need to claim expenses. Few employees will need this role, so you decide not to provision it automatically to all employees.
You create a role mapping called All Employees and enter the following conditions.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|---|---|
|
System Person Type |
Employee |
|
Assignment Status |
Active |
In the role mapping you include the:
Employee role, and select the Autoprovision option
Expenses Reporting role, and select the Self-requestable option
You could create a similar role mapping for contingent workers called All Contingent Workers, where you would set the system person type to contingent worker.
Note
If the Employee and Contingent Worker roles are provisioned automatically, pending workers acquire them when their periods of employment or placements start. If they need roles before then, you create a separate role mapping for the pending worker system person type.
Any type of worker can be a line manager in the sales business unit. You create a role mapping called Line Manager Sales BU and enter the following conditions.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Business Unit |
Sales |
|
Assignment Status |
Active |
|
Manager with Reports |
Yes |
You include the Line Manager role and select the Autoprovision option. This role mapping ensures that the Line Manager role is provisioned automatically to any worker with at least one assignment that matches the role-mapping conditions.
In the same role mapping, you could include roles that line managers in this business unit can provision manually to other users by selecting the roles and marking them as requestable. Similarly, if line managers can request roles for themselves, you could include those in the same role mapping and mark them as self-requestable.
Retirees in your enterprise need a limited amount of system access to manage their retirement accounts. You create a role mapping called All Retirees and enter the following conditions.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|---|---|
|
System Person Type |
Retiree |
|
Assignment Status |
Inactive |
You include the locally defined role Retiree in the role mapping and select the Autoprovision option. When at least one of a worker's assignments satisfies the role-mapping conditions, the Retiree role is provisioned to that worker automatically.
Grade 6 sales managers in the sales department need the Sales Manager role. In addition, sales managers need to be able to provision the Sales Associate role to other workers. You create a role mapping called Sales Managers Sales Department and enter the following conditions.
|
Attribute |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Department |
Sales |
|
Job |
Sales manager |
|
Grade |
6 |
|
Assignment Status |
Active |
In the role mapping, you include the:
Sales Manager role, and select the Autoprovision option
Sales Associate role, and select the Requestable option
After the implementation user has set up the enterprise, further security administration depends on the requirements of your enterprise.
The Define Security activity within the Information Technology (IT) Management business process includes the following tasks.
Import Worker Users
Import Partner Users
Manage Job Roles
Manage Duties
Manage Application Access Controls
If no legacy users, user accounts, roles, and role memberships are available in the Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) store, and no legacy workers are available in Human Resources (HR), the implementation user sets up new users and user accounts and provisions them with roles available in the Oracle Fusion Applications reference implementation.
If no legacy identities (workers, suppliers, customers) exist to represent people in your enterprise, implementation users can create new identities in Human Capital Management (HCM), Supplier Portal, and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Self Service, respectively, and associate them with users.
Oracle Identity Management (OIM) handles importing users.
If legacy employees, contingent workers, and their assignments exist, the HCM Application Administrator imports these definitions by performing the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task. If user and role provisioning rules have been defined, the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load process automatically creates user and role provisioning requests as the workers are created.
Once the enterprise is set up, performing the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task populates the enterprise with HR workers in records linked by global user ID (GUID) to corresponding user accounts in the LDAP store. If no user accounts exist in the LDAP store, the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task results in new user accounts being created. Worker email addresses as an alternate input for the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task triggers a search of the LDAP for user GUIDs, which may perform more slowly than entering user names.
In the security reference implementation, the HCM Application Administrator job role hierarchy includes the HCM Batch Data Loading Duty role, which is entitled to import worker identities. This entitlement provides the access necessary to perform the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task in HCM.
Note
The Import Person and Organization task in the Define Trading Community Import activity imports the following resources, creates users, and links the resources to users for use in CRM.
Internal employees
Contingent workers
External partner contacts
Partner companies
Legal entities
Customers
Consumers
If role provisioning rules have been defined, the Import Person and Organization task automatically provisions role requests as the users are created.
If legacy users (identities) and user accounts exist outside the LDAP store that is being used by the Oracle Fusion Applications installation, the IT security manager has the option to import these definitions to the LDAP store by performing the Import Worker Users and Import Partner Users tasks.
If no legacy users or user accounts can be imported or exist in an LDAP repository accessible to Oracle Identity Management (OIM), the IT security manager creates users manually in OIM or uses the Initiate HCM Spreadsheet Load task to create users from imported HR workers.
Once users exist, their access to Oracle Fusion Applications is dependent on the roles provisioned to them in OIM or Human Capital Management. Use the Manage HCM Role Provisioning Rules task to define rules that determine what roles are provisioned to users.
Importing user identities from other applications, including other Oracle Applications product lines, is either a data migration or manual task. Migrating data from other Oracle Applications includes user data. For more information about importing users, see the Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Identity Manager.
In the security reference implementation, the IT Security Manager job role hierarchy includes the HCM Batch Data Loading Duty and the Partner Account Administration Duty. These duty roles provide entitlement to import or create users. The entitlement Load Batch Data provides the access necessary to perform the Import Worker Users task in OIM. The entitlement Import Partner entitlement provides the access necessary to perform the Import Partner Users task in OIM.
Job and abstract roles are managed in OIM. This task includes creating and modifying job and abstract roles, but not managing role hierarchies of duties for the jobs.
Note
Manage Job Roles does not include provisioning job roles to users. Provisioning users is done in OIM, HCM, CRM or Oracle Fusion Supplier Portal.
Roles control access to application functions and data. Various types of roles identify the functions performed by users.
The Oracle Fusion Applications security reference implementation provides predefined job and abstract roles. In some cases, the jobs defined in your enterprise may differ from the predefined job roles in the security reference implementation. The predefined roles and role hierarchies in Oracle Fusion may require changes or your enterprise may require you to create new roles. For example, you need a job role for a petty cash administrator, in addition to an accounts payable manager. The security reference implementation includes a predefined Accounts Payable Manager, and you can create a petty cash administrator role to extend the reference implementation.
In the security reference implementation, the IT Security Manager job role hierarchy includes the Enterprise Role Management Duty role, which is entitled to manage job and abstract roles (the entitlement is Manage Enterprise Role). This entitlement provides the access necessary to perform the Manage Job Roles task in OIM.
A person with a job role must be able to perform certain duties. In the Oracle Fusion Applications security reference implementation, enterprise roles inherit duties through a role hierarchy. Each duty corresponds to a duty role. Duty roles specify the duties performed within applications and define the function and data access granted to the enterprise roles that inherit the duty roles.
Managing duties includes assigning duties to job and abstract roles in a role hierarchy using Authorization Policy Manager (APM). If your enterprise needs users to perform some actions in applications coexistent with Oracle Fusion applications, you may wish to remove the duty roles that enable those actions. For details about which duty roles are specific to the products in an offering, see the Oracle Fusion Applications Security Reference Manual for each offering.
OIM stores the role hierarchy and the spanning of roles across multiple pillars or logical partitions of applications.
In cases where your enterprise needs to provide access to custom functions, it may be necessary to create or modify the duty roles of the reference implementation.
Tip
As a security guideline, use only the predefined duty roles, unless you have added new applications functions. The predefined duty roles fully represent the functions and data that must be accessed by application users and contain all appropriate entitlement. The predefined duty roles are inherently without segregation of duty violations of the constraints used by the Application Access Controls Governor.
In the security reference implementation, the IT Security Manager job role hierarchy includes the Application Role Management Duty role, which is entitled to manage duty roles (the entitlement is Manage Application Role). This entitlement provides the access necessary to perform the Manage Duties task in APM.
Note
Product family administrators are not entitled to create role hierarchies or manage duty roles and must work with the IT security manager to make changes such as localizing a duty role to change a role hierarchy. Setup for localizations is documented in HCM documentation.
Prevent or limit the business activities that a single person may initiate or validate by managing segregation of duties policies in the Application Access Controls Governor (AACG) .
Note
In AACG, segregation of duties policies are called access controls or segregation of duties controls.
In the security reference implementation, the IT Security Manager job role hierarchy includes the Segregation of Duties Policy Management Duty role, which is entitled to manage segregation of duties policies (the entitlement is Manage Segregation of Duties Policy). This entitlement provides the access necessary to perform the Manage Application Access Controls task in AACG.
You can import workers from legacy applications to Oracle Fusion Applications using the Import Worker Users task. By enabling you to bulk-load existing data, this task is an efficient way of creating and enabling users of Oracle Fusion Applications.
Importing worker users is a two-stage process:
On the Initiate Data Load page, you generate and complete the Create Worker spreadsheet. You must map your data to the spreadsheet columns and provide all required attributes. Once the spreadsheet is complete, you import the data to the HCM Data Loader stage tables.
HCM Data Loader is a generic utility for loading data to Oracle Fusion Human Capital Management from external sources.
In the Data Exchange work area, you run the Load Batch Data process to load data from the HCM Data Loader stage tables to the Oracle Fusion application tables.
Oracle Fusion user accounts are created automatically for imported workers in Oracle Identity Management (OIM), unless automatic account creation is disabled.
By default, user account names and passwords are sent automatically to users when their accounts are created. This default action may have been changed at enterprise level, as follows:
User account names and passwords may be sent to an enterprise-wide e-mail rather than to users themselves.
Automatic sending of user account names and passwords may be disabled for the enterprise; in this case, you can notify users at an appropriate time.
Once user accounts exist, roles are provisioned to users automatically in accordance with current role-provisioning rules. For example, current rules could provision the employee abstract role to every worker. Role provisioning occurs automatically unless it has been disabled for the enterprise.
This example shows how to import worker users from legacy applications to Oracle Fusion Applications.
The following table summarizes key decisions for this task.
|
Decisions to Consider |
In This Example |
|---|---|
|
What are my spreadsheet names? You can define your own naming convention; in this example, the names are selected to make identifying the spreadsheet contents easy. |
For example, Workers042713Batch01.xlsx. |
|
What is my batch name? |
Workers042713Batchnn |
|
Where will I fix Load Batch Data errors? |
In the spreadsheet Workers042713BatchnnErrorsnn.xlsx |
Import worker users by:
Selecting the Import Worker Users task
Creating the spreadsheet
Entering workers in the spreadsheet
Importing the spreadsheet data to the HCM Data Loader stage tables
Loading workers to the application tables from the HCM Data Loader stage tables
Reviewing the results of the Load Batch Data process and correcting errors
Before you can complete this task, you must have:
|
Field |
Name |
|---|---|
|
Search |
Task |
|
Name |
Import Worker Users |
The task navigates to the Initiate Data Load page.
Alternatively, you can select the Import Worker Users task from an implementation project.
Create Worker appears after other business objects such as departments, locations, and jobs, because those business objects (regardless of how you create them) must be created before worker users.
Ensure that you provide any required values and follow instructions in the spreadsheet for creating additional rows.
Use the default values except where indicated.
As each row of data is uploaded to the HCM Data Loader stage tables, its status is updated.
Use the default values except where indicated.
An errors spreadsheet with a standard name is created automatically.
Leave the batch name in the errors spreadsheet as Workers042713Batch01.
If further errors occur, increment the errors-spreadsheet suffix by 1; for example, Workers042713Batch01Errors02, Workers042713Batch01Errors03, and so on.
To load a new batch of workers on the same date, increment the batch number in the spreadsheet and batch names; for example, Workers042713Batch02.
You can create users by entering basic person and employment data. A user account is created automatically for a person when you create the user record. You can assign the users Oracle Fusion Human Capital Management (HCM) and non-HCM data roles, each providing access to specific functions and data. This example demonstrates how to create a user and assign roles to the user.
Note
This user management functionality is available for HCM Foundation and Oracle Fusion Workforce Directory Management (WDM) users only.
|
Decisions to Consider |
In this Example |
|---|---|
|
For whom are you creating the user record? |
Gail Williams |
|
What is the user account name? |
Same as the e-mail ID, gail.williams@vision.com |
|
Where is Gail employed? |
Gail is an employee of Vision Corporation, and works in the Human Resources (HR) department in the Canada office. |
|
What roles must be provisioned to Gail? |
Autoprovision the employee role. Gail is responsible for processing workers' expense claims so provision the role Expense Claims Administrator manually to Gail. |
|
Attribute |
Value |
|---|---|
|
System Person Type |
Employee |
|
Assignment Status |
Active |
In the role mapping you include the:
Employee role, and select the Autoprovision option
Expense Claims Administrator role, and select the Self-requestable option
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Last Name |
Williams |
|
First Name |
Gail |
|
|
gail.williams@vision.com |
|
Hire Date |
4/12/11 |
|
Field |
Value |
|---|---|
|
Legal Employer |
Vision Corporation |
|
Business Unit |
Vision Canada |
|
Department |
Human Resources |
The Oracle BI Publisher User Details System Extract Report includes details of some or all Oracle Fusion Applications user accounts.
To run this report, you must have an HCM data role that provides view-all access to person records for the Human Capital Management Application Administrator job role.
To run the report:
Navigate to Tools - Reports and Analytics.
In the Contents pane of the Reports and Analytics work area, navigate to Shared Folders - Human Capital Management - Workforce Management - Human Resources Dashboard.
Select the User Details System Extract report.
In the report window, click More.
On the Oracle Business Intelligence page for the report, select Open to run the report immediately or Schedule to schedule the report.
Parameters
User Population
Enter one of the following values to identify the group of user accounts to include in the report.
|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
HCM |
User accounts with an associated HCM person record. |
|
TCA |
User accounts with an associated TCA party account. |
|
OIM |
Accounts for users in the PER_USERS table who do not have an associated person number or party ID. OIM users are also referred to as implementation users. |
|
ALL |
HCM, TCA, and OIM users accounts. |
From Date
Accounts for HCM and OIM users created on or after this date are included in the report. If you specify no From Date value, then accounts with any creation date are included, subject only to any To Date value that you specify.
From and to dates do not apply to the TCA user population; the report includes all TCA users if you include them in the report's user population.
To Date
Accounts for HCM and OIM users created on or before this date are included in the report. If you specify no To Date value, then accounts with any creation date are included, subject only to any From Date value that you specify.
From and to dates do not apply to the TCA user population; the report includes all TCA users if you include them in the report's user population.
User Active Status
Enter one of the following values to identify the user-account status.
|
Value |
Description |
|---|---|
|
A |
Include active accounts, which belong to users with current roles. |
|
I |
Include inactive accounts, which belong to users with no current roles. |
|
All |
Include both active and inactive user accounts. |
The output is an XML-formatted file where user accounts are grouped by type, as follows:
Group 1 (G_1) includes HCM user accounts.
Group 2 (G_2) includes TCA party user accounts.
Group 3 (G_3) includes OIM user accounts.
The information provided in the extract varies with the account type.
HCM User Accounts
The business unit from the primary work relationship.
The date when any one of a number of values, including assignment managers, location, job, and person type, was last updated.
The department from the primary assignment.
The worker type from the user's primary work relationship.
The user's name suffix (for example, Jr., Sr., or III).
The enterprise hire date.
A list of roles currently provisioned to workers whose work relationships are all terminated. This value appears for active user accounts only.
The job title from the user's primary assignment.
TCA User Accounts
A resource group.
A list of job, abstract, and data roles provisioned to the user.
The manager of a resource group.
OIM User Accounts
The date from when the account existed.
The user name of the user who created the account.
An e-mail containing the user name and password is sent to the user's primary work e-mail address. If the user has no primary work-email address, then the user name and password are sent to the primary work e-mail address of the user's line manager, if available; otherwise, no notification is sent.
You can select Send user name and password only if these details have not already been sent for this user: the user name and password can be sent once only for any user. If this option is available for selection but you do not select it, then you can run the process Send User Name and Password E-Mail Notifications later to notify users of their user names and passwords.
Yes. The Oracle BI Publisher User Details System Extract report includes details of all user accounts or a specified subset. For example, you can produce a report showing inactive user accounts, accounts created between specified dates, or accounts associated with TCA parties only.
To run the report, you must have an HCM data role that provides view-all access to person records for the Human Capital Management Application Administrator job role.