1 Oracle Financial Operations Control Integration Pack Overview
This chapter provides an overview of the Oracle Financial Operations Control Integration Pack for Oracle Retail Merchandise Operations Management and PeopleSoft Enterprise Financials. It also discusses key benefits and participating applications, and describes the retail sales financial, retail inventory financial, and retail procure to pay business process flows. Also included are solution assumptions and constraints.
This chapter includes the following sections:
1.1 Understanding the Oracle Financial Operations Control Integration Pack
The Oracle Financial Operations Control Integration Pack for Oracle Retail Merchandise Operations Management and PeopleSoft Enterprise Financials provides integration to a robust enterprise financial system that complements the Oracle Retail Merchandising system in a retail customer environment.
This process integration includes these four processes:
-
Life Cycle Data Management
This process enables users of Oracle Retail Merchandise Suite to perform functions with data that is shared with the PeopleSoft applications throughout the life cycle of the data that is created and updated. This process provides data synchronization for the initial load before implementation, and incremental data creation and maintenance after implementation. PeopleSoft Payables is the source of suppliers, payment terms, currency, and freight terms. This process synchronizes suppliers, payment terms, and currency exchange rates from PeopleSoft applications to the Oracle Retail Merchandising System (Oracle RMS). Freight terms are static in nature and their volume is very low; therefore, they must be manually synchronized between the two systems.
-
Inventory Valuation (Retail stock ledger)
This process enables users to post accounting entries generated from transactions that change the value of sellable products at retailers' inventory locations (stores and warehouses) from the Oracle Retail Merchandising stock ledger to PeopleSoft General Ledger (GL). Valuation of sellable inventory in stores and warehouses is based on the processing of transactions for movement, pricing, costing, and sale of the inventory. This valuation is captured and processed in the Oracle Retail stock ledger. These transactions include sales, shipments from warehouse to store, store receipts, store transfers, returns to vendors, price changes, stock counts, and shrinkage due to theft or damage.
-
Retail Revenue Recognition
This process enables users to post accounting entries generated from sales and returns transactions from retailer's stores for revenue and cash reconciliation to the appropriate ledgers. In this process, data flows from Oracle Retail Sales Audit (Oracle ReSA) to PeopleSoft GL. This process records the financial effect of sale and return, cash reconciliation, and void transactions from stores.
Note:
Sales and returns can also come from the Oracle RMS stock ledger.
The Revenue Recognition process begins when Oracle ReSA processes store transactions (sales and returns). For each store transaction, Oracle ReSA generates the appropriate accounting entries to be posted to PeopleSoft GL. Each accounting entry has a valid account code segment combination based on the transaction type, business unit, and location (store or warehouse).
-
Retail Merchandising Procure to Pay
This process begins with the Oracle Retail Invoice Matching (Oracle ReIM) application. Invoices from suppliers for retail merchandise are matched to the original purchase order (PO) for the merchandise and the receipt of the merchandise by the retailer. A proper match of invoice, PO, and receipt triggers the payment authorization of the supplier's invoice. Invoices may be authorized for payment before receipt of goods for which prepayment is required. When the authorization for payment is generated, the appropriate accounting distribution is also generated to support the payment authorization. The Retail Merchandise Procure to Pay integration automates the processing of invoice payments, adjustments, and write-offs from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft Payables and GL. Other accounting transactions are generated from Oracle ReIM to write off aged receipts that were never invoiced and to post accounting distribution for manually paid or prepaid invoices after receipt.
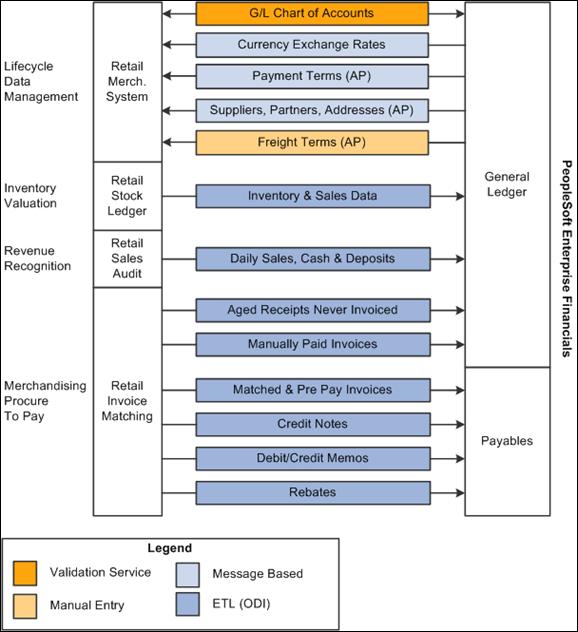
Figure 1-1 illustrates the Oracle Retail to PeopleSoft Financials process flow.
This PIP does not synchronize charts of accounts from PeopleSoft GL to Oracle Retail. Charts of accounts are combinations of account code segments. Because transaction types are defined and assigned combinations of code segments for proper handling of the financial effects in Oracle Retail, PeopleSoft GL provides a service that validates the code combinations. This service ensures that the accounting entries generated by the transactions are valid when they are posted to PeopleSoft GL.
The PIP also provides the drill back drill forward feature. This feature enables the PeopleSoft GL and Oracle Retail users to access information about the financial transactions from the integrated systems in a seamless and intuitive manner. It provides users an end-to-end traceability between PeopleSoft Payables and General Ledger back to Oracle RMS, Oracle ReSA, and Oracle ReIM. From PeopleSoft Enterprise Financials, users can drill back to query data from Oracle Retail applications. The drill back is initiated from the user interfaces (UI) of PeopleSoft Financials. Oracle Retail application users can drill forward to query integrated data from PeopleSoft Enterprise Financials. The drill back and drill forward feature provides traceability from retail transactions to journal entries, and back, and from invoices to vouchers, and back, between Oracle Retail and PeopleSoft Financials. This capability enables processes to support supplier servicing and financial auditing.
1.2 Key Benefits
Here are the key benefits of this PIP:
-
This integration is not a point-to-point integration between the PeopleSoft Financials and Oracle Retail applications.
This PIP implementation is independent of the version of integrated applications. An Oracle AIA layer serves as an intermediate thin layer of application between PeopleSoft Financials and Oracle Retail. This integration remains synchronized with the new releases of the edge applications.
-
The system exports the sales audit data to the PeopleSoft Financial applications days before the traditional audit process permits.
The Financials applications can use this timely data proactively, which results in increased productivity and operational efficiencies.
-
This PIP reduces the total cost of ownership for Oracle and its customers.
-
Drill back and drill forward actions between the PeopleSoft Financials and Oracle Retail applications are seamless.
The Oracle Retail and PeopleSoft Financials users do not require any training or must inquire about specific data in either application.
-
This PIP supports cost or retail accounting methods.
1.3 Participating Applications
This section discusses these topics:
1.3.1 Oracle RMS Overview
Oracle RMS is an integrated solution for global retailing. This solution enables retailers to better manage, control, and perform crucial day-to-day merchandising activities. From new product introduction to inventory management, Oracle RMS provides retailers with a complete end-to-end solution and is the most comprehensive and integrated solution for global retailing.
For more information about Oracle RMS, see the OracleRetail Merchandising System User Guide.
1.3.2 Oracle ReSA Overview
Oracle ReSA provides retailers with a flexible tool that evaluates and ensures accuracy and completeness of point of sale (POS) data. Realtime access to this audited sales data ensures integrity of information throughout the retail enterprise. With a highly configurable sales audit application, the retailer can maintain existing business practices while providing for future options as the operations grow and change.
ReSA enables retailers to receive POS transaction data, cleanse it, and export the data to the Oracle Merchandising system and the Oracle Retail Data Warehouse. By providing corporate control and visibility to sales audit information, Oracle ReSA enables retailers to make better decisions to improve merchandise operations and transform the economics of their business.
For more information about Oracle ReSA, see the Oracle Retail Sales Audit User Guide.
1.3.3 Oracle ReIM Overview
Oracle ReIM is a market-leading solution for retailers who require an automated application to better manage reconciliation and payment of invoices. This advanced solution enables account payables teams to resolve discrepancies on invoices quickly before payments are made. A highly automated, multidimensional matching engine minimizes time spent on manual reviews. Automated routing provides an effective method to ensure that accurate information is delivered to the correct internal teams for resolution and compliance controls.
For more information about Oracle ReIM, see the Oracle Retail Invoice Matching User Guide.
1.3.4 PeopleSoft Payables Overview
PeopleSoft Payables provides automated invoice and payment processing to ensure timely and accurate payment for goods and services. Best-practice business processes match purchase orders, receipts, and invoices and provide online approvals to identify exceptions and increase control over disbursements.
PeopleSoft Payables delivers built-in controls to help an enterprise meet regulatory requirements, enforce compliance, reduce risk, and implement due-diligence best practices, thereby reducing cycle times and errors. Other features include a flexible, user-defined system setup; extensive vendor maintenance; digital signatures and financials sanction validation; and powerful inquiry and analytical capabilities.
For more information about PeopleSoft Payables, see the PeopleSoft Enterprise Payables PeopleBook.
1.3.5 PeopleSoft GL Overview
PeopleSoft GL offers a fully automated close and consolidation solution for legal and management reporting, including support for Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Transactions are automatically processed and validated according to the best-practice business processes and control settings. In addition, an enterprise can proactively control expenditures by automatically checking spending requests against budget. With realtime reporting and information access, an enterprise can achieve complete visibility into financial results.
For more information about PeopleSoft GL, see the PeopleSoft Enterprise General Ledger PeopleBook.
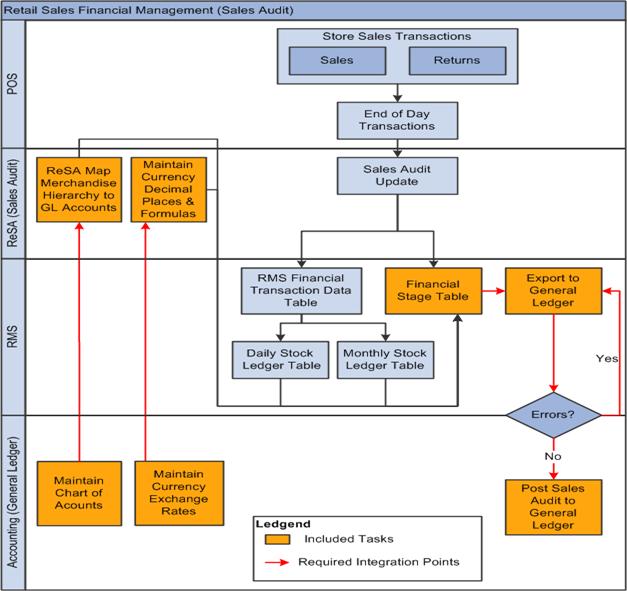
1.4 Retail Sales Financial Business Process Flow
The Retail Sales Financial business process consists of the Post Channel Sales, Cash, and Deposits from Oracle ReSA to PeopleSoft GL integration flow.
Figure 1-2 illustrates the Retail Sales Financial business process flow.
Oracle ReSA sends summarized sales audit information to PeopleSoft GL for the Sales Journal. The sales audit information includes channel sales, cash, and deposits. The Oracle ReSA Export processes select and format corrected and previously audited data from the Oracle ReSA database so that it can be sent to PeopleSoft Financials.
Oracle ReSA includes programs to automatically extract the required totals data and to format it to generic data files from a financial staging table for import into PeopleSoft GL. Sales audit data from Oracle ReSA is also posted directly to the Oracle RMS stock ledger and can be integrated into PeopleSoft GL through the stock ledger to the financial staging table and the accounting entry table. Before data is imported into PeopleSoft GL, a batch process writes balanced records to the financial staging table using the appropriate General Ledger account combinations (maintained in Cross Reference tables in Oracle ReSA and the Currency Exchange Rates.
The PeopleSoft Journal Generator loads the accounting entries from Oracle Retail to PeopleSoft GL journal entries. The accounting tables are referenced on the accounting entry definition defined for each type of accounting entry transaction. The Journal Generator uses the new accounting entry definitions to create PeopleSoft journal entries. After the journal entries are created by the PeopleSoft Journal Generator, they are edited and posted similarly to PeopleSoft subsystem journals.
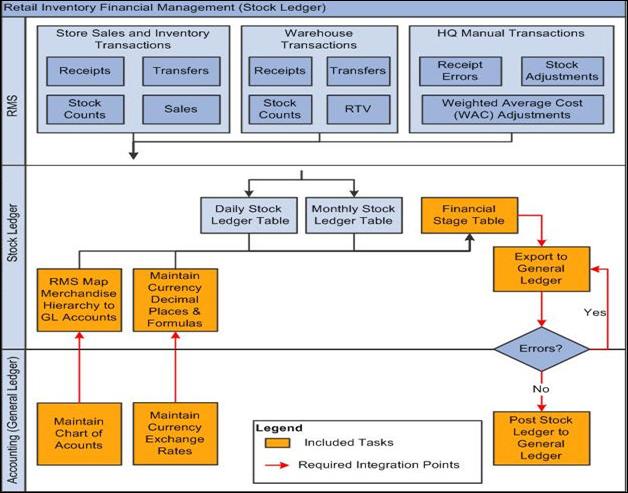
1.5 Retail Inventory Financial Business Process Flow
The Retail Inventory Financial business process consists of the posting stock ledger from Oracle RMS to PeopleSoft GL. integration flow
Figure 1-3 illustrates the Retail Inventory Financial business process flow.
Note:
This diagram is for illustration only. Stores, warehouses, and corporate write other inventory related transactions to the Oracle RMS stock ledger.
The stock ledger in Oracle RMS records the financial results of the merchandising processes that occur in the Retail system, such as buying, selling, price changing, transferring, and so on. All of these transactions are recorded in the Oracle RMS stock ledger and rolled up to the subclass/location-level for days, weeks, and months. Daily and period-based financial information is scheduled to be loaded into PeopleSoft.
Oracle RMS sends three levels of stock ledger information to PeopleSoft GL:
-
Monthly - no access to detailed reference information.
-
Daily by subclass, class, or department - no access to detailed reference information.
-
Daily by transaction.
The stock ledger transactions to be loaded into PeopleSoft are placed on the financial staging table with table triggers or batch, by the appropriate General Ledger account combinations (maintained in the Oracle RMS cross-reference table in Oracle Retail) and the currency exchange rates.
The PeopleSoft Journal Generator loads the accounting entries from Oracle Retail and creates PeopleSoft GL journal entries. The accounting tables are referenced on the accounting entry definition defined for each type of accounting entry transaction. The Journal Generator uses new accounting entry definitions to create PeopleSoft journal entries. After the journal entries are created by the Journal Generator, they are edited and posted similarly to PeopleSoft subsystem journals.
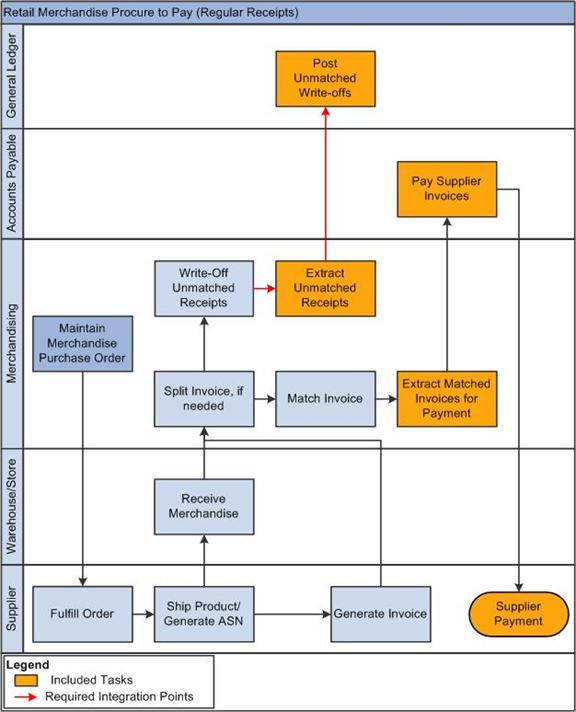
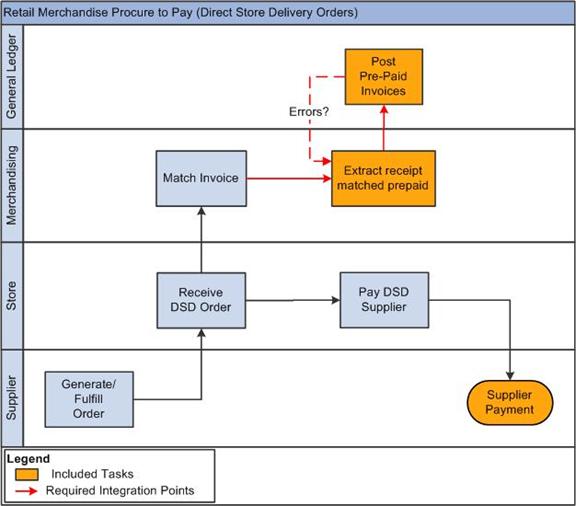
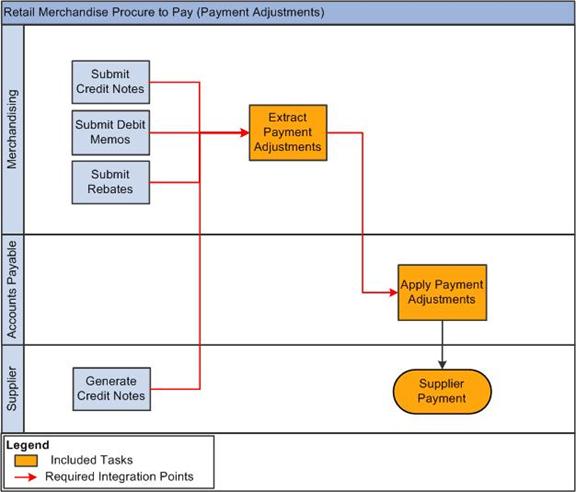
1.6 Retail Merchandise Procure to Pay Business Process Flow
The Retail Merchandise Procure to Pay business process consists of these integration flows:
-
Post matched prepaid invoices from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft GL.
-
Post manually matched paid invoices from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft GL.
-
Post receipt write-offs from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft GL.
-
Post matched invoices for payment from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft Payables.
-
Post credit notes (matched or unmatched) for payment adjustment from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft Payables.
-
Post debit or credit memos for payment adjustment from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft Payables.
-
Post rebates for payment adjustment from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft Payables.
-
Post unmatched invoices for prepayment from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft Payables.
Figure 1-4, Figure 1-5, and Figure 1-6 illustrate the Retail Merchandise Procure to Pay business process flow:
The Retail Merchandise Procure to Pay business process flow enables posting of matched invoices, matched credit notes, debit and credit memos, rebates, and unmatched invoices for prepayment from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft Payables. It also facilitates drill back from PeopleSoft Payables to Oracle ReIM and drill forward from Oracle ReIM to PeopleSoft Payables.
1.7 Solution Assumptions and Constraints
These are the assumptions and constraints for this PIP:
PeopleSoft GL
-
You must implement the PeopleSoft applications before you implement this PIP.
-
The set of books in Oracle Retail is equivalent to the PeopleSoft GL business unit, ledger group, assuming the default ledger group and setID.
You are not required to map the ledger group and setID on the Oracle Retail side. PeopleSoft publishes the associated business units for each transaction that is setID-driven. You are not required to persist with the structure in the middle layer. Each transaction message accounts for the setID business unit association.
-
Oracle Retail manually creates and stores valid segment (ChartField) combinations in the appropriate GL cross-reference tables (Oracle ReSA, Oracle RMS, and Oracle ReIM).
-
For PeopleSoft, 16 ChartFields are available and 4 additional inactive ChartFields can be activated by customers. Oracle Retail supports 20 segments structure.
Therefore, the PeopleSoft Chart of Accounts can be made of up to 20 ChartFields (segments) only.
-
PeopleSoft ChartFields are 30 characters in length.
The Oracle Retail Integration Bus (RIB) subscription format supports only 25 characters for segments (ChartFields). Therefore, the segment length for Oracle Retail customers is 25 characters.
Currency Exchange Rate
-
The Oracle Retail stock ledger supports multiple currencies.
All transaction-level information is stored in the local currency of the store or warehouse where the transaction occurred. In Oracle ReIM, the invoice currency on the invoice is often the currency of the supplier, which can be different than the local currency.
-
The currency amounts precision is limited to 3 digits.
Calendar
-
The PeopleSoft applications use multiple calendars.
In this PIP, both PeopleSoft Financials and Oracle Retail use a single calendar.
-
After a calendar is established, this integration does not support switching the calendar.
Sales Audit/Stock Ledger Transactions
-
Oracle Retail sends the accounting date and the transaction date with its transactions.
These dates must not be changed or manipulated in PeopleSoft.
-
Users handle accounting entry errors manually on both the Oracle Retail and the PeopleSoft Financials side.
-
The system passes use or sales tax accounting information as part of the accounting entries between Oracle Retail and PeopleSoft Financials.
-
Oracle Retail calculates value-added tax (VAT).
PeopleSoft Journal Generator does not recalculate VAT. The system passes the VAT calculation as part of the accounting entry.
-
Oracle Retail stock ledger determines the valuation of inventory for merchandise being directly procured.
It passes this information to PeopleSoft as the accounting entries.
-
Oracle RMS, through the Oracle Retail stock ledger, provides PeopleSoft Financials with the value of ending inventory at cost using the method that the retailer indicates (cost method or retail method of accounting) by an adjusting entry.
This information is provided through monthly feed.
-
You cannot load accounting entries twice into PeopleSoft Financials.
When journals are created, a status field called Distribution Status changes to D; therefore, you cannot create new journal vouchers for the same set of accounting entries.
Other
-
Both PeopleSoft and Oracle Retail support multiple organizations in one application instance.
-
If you rename, change the name but not the value, or create new ChartFields (segments), you have customized the middle layer.
-
Oracle RIB is required for all message-based integration to Oracle Retail.
Constraints
-
Oracle Retail and PeopleSoft applications do not support modifying date by time zones.
-
PeopleSoft Financials can handle only three decimal places in amount fields.
For this integration, no currency in Oracle Retail must contain more than three decimal places. Otherwise, the amounts are rounded from four decimals to three decimals that may cause out-of-balance issues.
-
Customers switching from one financials application to another must re-implement the integration pack.
-
Oracle AIA uses the location ID as a key and, when it changes, Oracle AIA cannot associate it with the former ID from the create operation.
Therefore, PeopleSoft users experience an issue when they change the location ID of an existing supplier location in an update operation.
Note:
Additional assumptions and constraints exist for each of the process integration flows; they are documented in their respective chapters.