14 Configuring a Disaster Recovery Solution
The Oracle Fusion Middleware Disaster Recovery solution for enterprise deployments makes use of storage replication technology using Oracle Data Guard. This technology supports components from various Oracle product suites, including Oracle Entitlements Server installed as a stand-alone distribution. This chapter describes how to set up for Oracle Entitlements Server to use Oracle Data Guard to synchronize data for disaster recovery in a multi-site deployment.
This chapter includes the following sections:
Note:
Review the information about the Oracle Fusion Middleware Disaster Recovery solution in Oracle Fusion Middleware Disaster Recovery Guide before setting up a disaster recovery solution for Oracle Entitlements Server in a multi-site deployment.
14.1 Overview of a Multi-Site Deployment
Disaster protection for Oracle databases is provided through Oracle Data Guard. In a multi-site deployment, you install and configure a database for both a primary site and a standby site. In this release, Oracle Entitlements Server supports Oracle Data Guard as the high availability solution for the database service. Oracle Data Guard provides the capability to create and maintain one or more synchronized replicas (standby databases) of a production database (primary database). An Oracle Data Guard standby database is open read-only while and Oracle Data Guard primary database is both readable and writable.
In a multi-site deployment, the Oracle Entitlements Server Administration Server will configure the Oracle Data Guard primary database in its policy store to support MAPI operations. The Oracle Entitlements Server Security Modules will configure either the primary database or one of the standby databases in their policy store for policy distribution.
Oracle Entitlements Server admin servers are deployed on a read-only Oracle Data Guard standby database in order to provide policy query services. In the case of an Oracle Data Guard database role transition (where a standby database becomes the new primary database), the Oracle Entitlements Server admin server can provide management services on the new primary database without restarting WebLogic Server.
An Oracle Entitlements Server multi-site deployment includes:
-
Oracle Entitlements Server Administration Console: A single master for policy management across data centers.
-
Security Modules: The SMs connect to the
-
Local site database (Master or Slave) for reading data.
-
Master site database (Master) for writing data.
-
-
Policy Data Replication: The mode of data replication.
14.2 Multi-Site Deployment Topology
In this release, the following configuration is required:
-
One site is acting as Master at any time. All the write operations are against the policy store configured for the current Master site.
-
All the Security Modules are configured in controlled-pull mode. Non-controlled and controlled push modes are not supported.
-
A policy store configured in mixed mode is not supported.
-
The Oracle Entitlements Server Administration Console in the IDM domain cannot leverage multi-site functionality
-
Oracle Entitlements Server is installed as a stand-alone distribution.
Figure 14-1 illustrates the relationship between the Oracle Entitlements Server components when configured in a multi-site deployment:
Figure 14-1 Multi-Site Deployment Topology
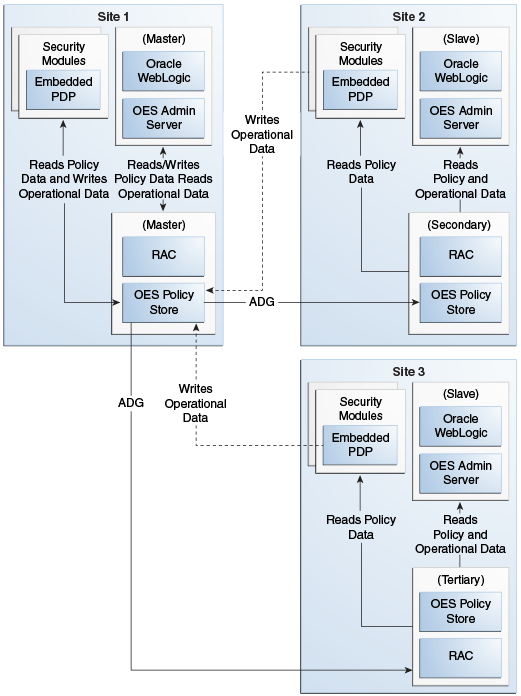
Description of "Figure 14-1 Multi-Site Deployment Topology"
As seen in the figure, when in a multi-site deployment the following relationships exist:
-
Policy Distribution: Security Modules are configured in controlled-pull mode on all the sites. The snapshot is generated by the admin server at the Master site and replicated to the secondary and tertiary sites using Oracle Data Guard. The PDP on the secondary and tertiary sites retrieve the snapshot from the local policy store.
-
Configuration: PDP are configured with multiple JDBC URL's. The primary JDBC URL is configured to the local policy store. In an event of failure to connect to the local Policy Store, a connection attempt to the secondary JDBC URL is made. This ensures that the policy store is accessible in an event of a failure.
-
SM ConfigUI: Can be used to configure the JDBC URLs that are required to support failover functionality.
14.3 Task Roadmap
Table 14-1 lists the high-level tasks for configuring Oracle Entitlements Server to use Oracle Data Guard to synchronize data for disaster recovery in a multi-site deployment.
Table 14-1 Configuration Flow for Disaster Recovery Solution
| No. | Task | Information |
|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Review the information about the Oracle Fusion Middleware Disaster Recovery solution |
|
|
2 |
Ensure you have complied with the prerequisites. |
|
|
Configuring Oracle Data Guard |
||
|
3 |
Configure the Primary Server site |
|
|
4 |
Configure the Standby Server site |
|
|
5 |
Force a switchover from Primary Server to Standby Server to test log file transfer |
|
|
6 |
Configure Oracle Data Guard Broker |
|
|
7 |
Test manual and switchover failover between Primary Server and Standby Server |
|
|
8 |
If necessary, install Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a Standalone Server |
|
|
9 |
Configure a virtual device for Oracle ASM |
Section 14.5.7, "Configuring a Virtual Device for Oracle ASM" |
|
10 |
Configure Oracle Restart |
|
|
Configuring Oracle Entitlements Server |
||
|
11 |
Create an OPSS database schema using RCU for Oracle Entitlements Server |
|
|
12 |
Install Oracle Entitlements Server Administration Console on the Primary Server |
|
|
13 |
Install Oracle Entitlements Server Administration Console on the Standby Server |
|
|
14 |
Configure the Security Module for multi-site deployment |
|
14.4 Prerequisites
-
Two servers with Oracle database installed. 11gR2 (11.1.2) is the minimum version required in order to provide Oracle Data Guard support.
In the following examples, the Primary Site server name is
primary_host. The Standby Site server name isstandby_host. -
The Primary Site server (
primary_host) has a running instance. In the examples, the database name and unique name are bothdb11g. -
The Standby Site server (
standby_host) has a software only installation. In the examples, the database name isdb11gand the database unique name isdb11g_stby.The
DB_NAMEof the standby database is the same as that of the primary, but it must have a differentDB_UNIQUE_NAMEvalue. -
The
primary_hostandstandby_hostboth have the sameORACLE_HOMEdirectory and structure.This is not a limitation but is recommended to simplify installation.
-
11gR2 (11.1.2) Oracle Grid Infrastructure for standalone server is installed on both
primary_hostandstandby_host.Both Oracle Restart and Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) are required and will be configured. They are both included when Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a standalone server is installed.
14.5 Configuring Disaster Recovery for Oracle Entitlements Server
This section contains the following topics:
-
Section 14.5.6, "Installing Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a Standalone Server"
-
Section 14.5.7, "Configuring a Virtual Device for Oracle ASM"
-
Section 14.5.10, "Installing the Primary Administration Console"
-
Section 14.5.11, "Installing the Secondary Administration Console"
14.5.1 Setting Up the Primary Server
To install the database that will serve as the Primary Server:
-
Configure
forced logging. Check the primary database is inarchivelogmode. If it is innoarchivelogmode, switch toarchivelogmode and enableforced logging. For example:sqlplus sys/welcome1 as sysdba select log_mode from v$database; shutdown immediate; startup mount; alter database archivelog; alter database open; alter database force logging;
-
Check the setting for the
DB_NAMEandDB_UNIQUE_NAMEparameters. In this example, they are both set todb11gon the primary database. TheDB_NAMEof the standby database is the same as that of the primary, but it must have a differentDB_UNIQUE_NAMEvalue. Set the initialization parameters to redo log apply. For example:show parameter db_name; show parameter db_unique_name; ALTER SYSTEM SET LOG_ARCHIVE_CONFIG='DG_CONFIG=(db11g,db11g_stby)'; ALTER SYSTEM SET LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_2='SERVICE=db11g_stby NOAFFIRM ASYNC VALID_FOR=(ONLINE_LOGFILES,PRIMARY_ROLE) DB_UNIQUE_NAME=db11g_stby'; ALTER SYSTEM SET LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_STATE_2=ENABLE; ALTER SYSTEM SET LOG_ARCHIVE_FORMAT='%t_%s_%r.arc' SCOPE=SPFILE; ALTER SYSTEM SET LOG_ARCHIVE_MAX_PROCESSES=5; ALTER SYSTEM SET REMOTE_LOGIN_PASSWORDFILE=EXCLUSIVE SCOPE=SPFILE; ALTER SYSTEM SET FAL_SERVER=db11g_stby; ALTER SYSTEM SET STANDBY_FILE_MANAGEMENT=AUTO;
-
Provide values for the primary and standby databases in the
$ORACLE_HOME/network/admin/tnsnames.orafiles on both servers. For example:db11g = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = primary_host)(PORT = 1521)) ) (CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = db11g.example.com) ) ) db11g_stby = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = standby_host)(PORT = 1521)) ) (CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = db11g.example.com) ) )
-
Set the following values for
listener.oraon the primary server:SID_LIST_LISTENER = (SID_LIST = (SID_DESC = (GLOBAL_DBNAME = db11g_DGMGRL.example.com) (ORACLE_HOME = /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1) (SID_NAME = db11g) ) (SID_DESC = (GLOBAL_DBNAME = db11g_DGB.example.com) (ORACLE_HOME = /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1) (SID_NAME = db11g) ) ) LISTENER = (DESCRIPTION_LIST = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = primary.example.com)(PORT = 1521)) ) (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC1521)) ) ) ADR_BASE_LISTENER = /scratch/example_user/app/example_user ENABLE_GLOBAL_DYNAMIC_ENDPOINT_LISTENER=ON # line added by Agent -
Create a control file and a parameter file for the standby database. Amend the PFILE to make the entries relevant for the standby database. For example:
ALTER DATABASE CREATE STANDBY CONTROLFILE AS '/tmp/db11g_stby.ctl'; CREATE PFILE='/tmp/initdb11g_stby.ora' FROM SPFILE; *.db_unique_name='db11g_stby' *.fal_server='db11g' *.log_archive_dest_2='SERVICE=db11g ASYNC VALID_FOR=(ONLINE_LOGFILES,PRIMARY_ROLE) DB_UNIQUE_NAME=db11g'
14.5.2 Setting Up the Standby Server (Duplicate)
Next you must install and configure the Standby Server that is the duplicate. This server has a software only installation.
To install the database that will serve as the Standby Server (duplicate):
-
Create the necessary directories on the Standby Server and copy the files from the Primary Server (
primary_host) to the Standby Server (standby_host). In this example, the database name isdb11gand database unique name isdb11g_stby:tnsnames.ora $ mkdir -p /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/oradata/db11g $ mkdir -p /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/fast_recovery_area/db11g $ mkdir -p /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/admin/db11g/adump $ # Standby controlfile to all locations. $ scp example_user@primary_host:/tmp/db11g_stby.ctl /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/oradata/db11g/control01.ctl $ cp /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/oradata/db11g/control01.ctl /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/flash_recovery_area/db11g/control02.ctl $ # Parameter file. $ scp example_user@primary_host:/tmp/initdb11g_stby.ora /tmp/initdb11g_stby.ora $ # Remote login password file. $ scp example_user@primary_host:$ORACLE_HOME/dbs/orapwdb11g $ORACLE_HOME/dbs
-
Edit the listener configuration file
listen.orato have the following entries:SID_LIST_LISTENER = (SID_LIST = (SID_DESC = (GLOBAL_DBNAME = db11g.example.com) (ORACLE_HOME = /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1) (SID_NAME = db11g) ) (SID_DESC = (GLOBAL_DBNAME = db11g_stby_DGMGRL.example.com) (ORACLE_HOME = /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1) (SID_NAME = db11g) ) (SID_DESC = (GLOBAL_DBNAME = db11g_stby_DGB.example.com) (ORACLE_HOME = /scratch/example_user/app/example_user/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1) (SID_NAME = db11g) ) ) LISTENER = (DESCRIPTION_LIST = (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = standby_host.example.com)(PORT = 1521)) ) (DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = IPC)(KEY = EXTPROC1521)) ) ) ADR_BASE_LISTENER = /scratch/example_user/app/example_user ENABLE_GLOBAL_DYNAMIC_ENDPOINT_LISTENER=ON # line added by Agent -
Verify the listener is started on the Standby Server.
$ lsnrctl start
-
Create standby Redo logs on primary server using the
DUPLICATEcommand. standby redo logs are created on the primary server to ensure the primary database is configured for switchover. For example:ALTER DATABASE ADD STANDBY LOGFILE ('/scratch/example_user/app/example_user/oradata/db11g/standby_redo01.log') SIZE 50M; ALTER DATABASE ADD STANDBY LOGFILE ('/scratch/example_user/app/example_user/oradata/db11g/standby_redo02.log') SIZE 50M; ALTER DATABASE ADD STANDBY LOGFILE ('/scratch/example_user/app/example_user/oradata/db11g/standby_redo03.log') SIZE 50M; ALTER DATABASE ADD STANDBY LOGFILE ('/scratch/example_user/app/example_user/oradata/db11g/standby_redo04.log') SIZE 50M; -
Create standby using
DUPLICATEcommand:-
Start the auxiliary instance on the standby server, using the temporary
init.orafile. For example:$ export ORACLE_SID=db11g $ sqlplus / as sysdba SQL> STARTUP NOMOUNT PFILE='/tmp/initdb11g_stby.ora';
-
Connect to
RMAN, specifying a full connect string for both theTARGETandAUXILLARYinstances. Do not use OS authentication.$ rman TARGET sys/password@db11g AUXILIARY sys/password@db11g_stby
-
Execute the following
DUPLICATEcommand.DUPLICATE TARGET DATABASE FOR STANDBY FROM ACTIVE DATABASE DORECOVER SPFILE SET db_unique_name='db11g_stby' COMMENT 'Is standby' SET LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_2='SERVICE=db11g ASYNC VALID_FOR=(ONLINE_LOGFILES,PRIMARY_ROLE) DB_UNIQUE_NAME=db11g' SET FAL_SERVER='db11g' COMMENT 'Is primary' NOFILENAMECHECK;
-
-
Restart.
SHUTDOWN IMMEDIATE; STARTUP MOUNT; ALTER DATABASE OPEN READ ONLY; ALTER DATABASE RECOVER MANAGED STANDBY DATABASE DISCONNECT FROM SESSION; select status,instance_name,database_role,open_mode from v$database,v$instance;
14.5.3 Test Log Transfer
Force a switchover from the Primary Server to the Standby Server in order to verify the log file transfer between the two site.
To verify the log files transfer on the two servers:
-
On Primary Server, check the latest archived redo log and force a log switch. For example:
ALTER SESSION SET nls_date_format='DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS'; SELECT sequence#, first_time, next_time FROM v$archived_log ORDER BY sequence#; ALTER SYSTEM SWITCH LOGFILE;
-
On the Standby Server, verify the new archived redo log has arrived and has been applied. For example:
ALTER SESSION SET nls_date_format='DD-MON-YYYY HH24:MI:SS'; SELECT sequence#, first_time, next_time, applied FROM v$archived_log ORDER BY sequence#;
14.5.4 Configuring the Oracle Data Guard Broker
To configure the Oracle Data Guard broker:
-
Start
DMONbackground process on primary and standby database.connect sys/welcome1@db11g as sysdba alter system set dg_broker_start=true; connect sys/welcome1@db11g_stby as sysdba alter system set dg_broker_start=true;
-
Call Oracle Data Guard Manager Linemode and configure. For example:
dgmgrl Help connect sys/welcome1@db11g create configuration myconfig as primary database is db11g connect identifier is db11g; add database db11g_stby as connect identifier is db11g_stby maintained as physical; enable configuration; show configuration;
-
Change to MA protection mode.
edit database db11g set property LogXptMode=SYNC; edit database db11g_stby set property LogXptMode=SYNC; edit configuration set protection mode as maxavailability;
Fast-start failover allows the broker to automatically fail over to a previously chosen standby database in the event of loss of the primary database. Fast-start failover quickly and reliably fails over the target standby database to the primary database role, without requiring you to perform any manual steps to invoke the failover. Fast-start failover can be used only in a broker configuration and can be configured only through DGMGRL or Enterprise Manager.
To enable Fast Start Failover:
-
Run the following command to enable Fast Start Failover.
EDIT DATABASE db11g SET PROPERTY FastStartFailoverTarget = db11g_stby; EDIT DATABASE db11g_stby SET PROPERTY FastStartFailoverTarget = db11g; EDIT CONFIGURATION SET PROPERTY FastStartFailoverThreshold = 30; Turn on flashback by sqlplus SQL> select flashback_on from v$database; SQL> alter database flashback on; ENABLE FAST_START FAILOVER;
-
Start the Observer on another host.
DGMGRL> connect sys/welcome1@db11g_stby DGMGRL> START OBSERVER;
14.5.5 Testing Failover and Switchover
To test the manual switchover and failover:
-
Test switchover and failover as follows.
-
To test switchover:
dgmgrl>connect sys/welcome1@db11g dgmgrl>switchover to db11g_stby;
-
To test failover:
dgmgrl>connect sys/oracle@db11g_stby dgmgrl>failover to db11g_stby;
-
-
Test Fast Start Failover by simulating a failure. For example:
-
Shutdown the current primary database to simulate a failure.
SQL> connect sys/welcome1@db11g as sysdba SQL> shutdown abort
-
Wait 20 seconds and verify the observer has initiated a failover.
After 20 seconds has lapsed, The observer has initiated a failover. 00:37:13.65 Thursday, May 30, 2013 Initiating Fast-Start Failover to database "db11g_stby"... Performing failover NOW, please wait... Failover succeeded, new primary is "db11g_stby" 00:37:20.67 Thursday, May 30, 2013
-
Confirm that the new Primary Server is
db11g_stbyDGMGRL> show configuration
-
14.5.6 Installing Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a Standalone Server
Both Oracle Restart and Oracle Automatic Storage Management (Oracle ASM) are required and must be configured. They are both included with an Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a standalone server installation.
If you do not already have Oracle Grid Infrastructure for a standalone server installed on both primary_host and standby_host, follow instructions in Oracle Database Installation Guide.
14.5.7 Configuring a Virtual Device for Oracle ASM
A virtual device is required for Oracle ASM. Use the losetup command to create virtual devices in place of real disk device.
Login as root to create a virtual device for Oracle ASM, for example:
mkdir /scratch/example_user/asmdisks chown example_user:dba /asmdisks dd if=/dev/zero of=/scratch/example_user/asmdisks/_file_disk1 bs=1k count=100000 dd if=/dev/zero of=/scratch/example_user/asmdisks/_file_disk2 bs=1k count=100000 dd if=/dev/zero of=/scratch/example_user/asmdisks/_file_disk3 bs=1k count=100000 dd if=/dev/zero of=/scratch/example_user/asmdisks/_file_disk4 bs=1k count=100000 "/sbin/losetup /dev/loop1 /scratch/example_user/asmdisks/_file_disk1" "/sbin/losetup /dev/loop2 /scratch/example_user/asmdisks/_file_disk2" "/sbin/losetup /dev/loop3 /scratch/example_user/asmdisks/_file_disk3" "/sbin/losetup /dev/loop4 /scratch/example_user/asmdisks/_file_disk4" "/bin/raw /dev/raw/raw1 /dev/loop1" "/bin/raw /dev/raw/raw2 /dev/loop2" "/bin/raw /dev/raw/raw3 /dev/loop3" "/bin/raw /dev/raw/raw4 /dev/loop4" "chown jianxliu:dba /dev/raw/raw1" "chown jianxliu:dba /dev/raw/raw2" "chown jianxliu:dba /dev/raw/raw3" "chown jianxliu:dba /dev/raw/raw4" "chmod 660 /dev/raw/raw1" "chmod 660 /dev/raw/raw2" "chmod 660 /dev/raw/raw3" "chmod 660 /dev/raw/raw4"
14.5.8 Configuring Oracle Restart
If Oracle Restart is installed after Oracle database, the database components need to be registered to Oracle Restart using srvctl command.
Note:
The following applies to restarting a service:
-
The
distribution.example.comservice must be explicitly started withSRVCTL START SERVICEand stopped withSRVCTL STOP SERVICEon primary database to ensure its information is propagated usingredoto physical standby. For example:srvctl start service -d db11g_stby -s distribution.example.com -
Whenever a role change occurs after an Oracle Data Guard automatic or manual failover, always make sure that both the manage and distribution services are started and running on both the primary and standby servers. If they are not running, start the service.
To register the database components if Oracle Restart is installed after the database, perform the following steps on both the primary and standby servers:
-
Add the database, ensure
ORACLE_HOMEis set to the database home. For example:srvctl add database -d db11g -o $ORACLE_HOME -r PRIMARY srvctl add database -d db11g_stby -o $ORACLE_HOME -r PHYSICAL_STANDBY -s MOUNT
-
If the listener is started from the database home, add the listener by ensuring the
ORACLE_HOMEis set to database home.srvctl add listener -o $ORACLE_HOME
-
Add the Oracle notification service (ONS/eONS) for Oracle Broker, ensure
ORACLE_HOMEis set to Oracle Grid Infrastructure home. For example:srvctl add ons srvctl enable ons srvctl start ons srvctl status ons srvctl add eons srvctl enable eons srvctl start eons srvctl status eons
By default ONS listening port for local client connections is 6100 and for connections from remote hosts is 6200
-
Add database service, ensure ORACLE_HOME is set to database home. For example:
-
On the primary database:
srvctl add service -d db11g -s manage.example.com -l PRIMARY -y AUTOMATIC -q FALSE -e NONE -m NONE -w 0 -z 0 srvctl add service -d db11g -s distribution.example.com -l PHYSICAL_STANDBY,PRIMARY -y AUTOMATIC -q FALSE -e NONE -m NONE -w 0 -z 0
-
On the standby database:
srvctl add service -d db11g_stby -s manage.example.com -l PRIMARY -y AUTOMATIC -q FALSE -e NONE -m NONE -w 0 -z 0 srvctl add service -d db11g_stby -s distribution.example.com -l PHYSICAL_STANDBY,PRIMARY -y AUTOMATIC -q FALSE -e NONE -m NONE -w 0 -z 0
-
14.5.9 Installing OPSS Schema
Run Oracle Fusion Middleware Repository Creation Utility (RCU) against the primary database. After it is finished, the OPSS schema can be propagated to the standby database. For more information about using RCU, see "Database Requirements" section in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity and Access Management.
14.5.10 Installing the Primary Administration Console
Install the primary Oracle Entitlements Server Administration Console. For information about installing Oracle Entitlements Server Administration Console, see "Installing and Configuring Oracle Entitlements Server" chapter in Oracle Fusion Middleware Installation Guide for Oracle Identity and Access Management.
Note the following when installing:
-
When running the
config.shscript to install a Weblogic domain, chooseGridLinkto create data source. -
When inputting listeners for GridLink data source, add primary database as the first listener.
-
When running the
configureSecurityStore.pyscript ensure-m createoption is added to parameters. For example:MW_HOME/oracle_common/common/bin/wlst.sh MW_HOME/Oracle_IDM1/common/tools/configureSecurityStore.py -d /scratch/example_user/Oracle/Middleware/user_projects/domains/domainname/ -t DB_ORACLE -j cn=jpsroot -m create -p welcome1
-
Edit the JPS configuration files to support HA failover mode operation as follows:
$MW_HOME/user_projects/domains/domainname/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml
The Gridlink JDBC URL configured for the datasource property in
opss-jdbc.xmlis used by WebLogic Server for switching. Edit thejps-config.xmlfile to comment out the following property entries underprops.db.1:jdbc.url jdbc.driver bootstrap.security.principal.map bootstrap.security.principal.key
Edit
$MW_HOME/user_projects/domains/domainname/config/fmwconfig/jps-config-jse.xml:<property name="jdbc.url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION_LIST = (LOAD _BALANCE = off) (FAILOVER = on)(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = primary.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = manage.example.com)))(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = standby.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = manage.example.com))))"/>
Edit
$MW_HOME/user_projects/domains/domainname/config/jdbc/opss-jdbc.xml:<url>jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION_LIST = (LOAD_BALANCE = off) (FAILOVER = on)(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = primary.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = manage.example.com)))(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = standby.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = manage.example.com))))</url>
14.5.11 Installing the Secondary Administration Console
Install the secondary Oracle Entitlements Server Administration Console. Note the following when installing:
-
Create a GridLink data source by following the steps in Section 14.5.10, "Installing the Primary Administration Console" with the following changes: use
distribution.example.cominstead ofmanage.example.com, and the first host is a standby database. -
Export
EncryptionKeyfrom primary domain. For example:exportEncryptionKey(jpsConfigFile="/scratch/example_user/Oracle/Middleware/ user_projects/domains/domainname/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml",keyFilePath="/net/ standby_host/scratch/example_user/keydir",keyFilePassword="welcome1")
-
When running the
configureSecurityStore.pyscript ensure-m joinoption is added, and the farm name is set to the one used when installing the Primary Administration Console. For example:MW_HOME/oracle_common/common/bin/wlst.sh MW_HOME/Oracle_IDM1/common/tools/configureSecurityStore.py -d /scratch/example_user/Oracle/Middleware/ user_projects/domains/domainname/ -t DB_ORACLE -j cn=jpsroot -m join -f domainname -p welcome1 -k /net/standby_host/scratch/example_user/keydir -w welcome1 --create_diagnostic_data
-
Edit the JPS configuration file to support HA failover mode operation. For example:
$MW_HOME/user_projects/domains/domainname/config/fmwconfig/jps-config.xml
The Gridlink JDBC URL configured for the datasource property in
opss-jdbc.xmlis used by WebLogic Server for switching. Edit thejps-config.xmlfile to comment out the following property entries underprops.db.1:dbc.url jdbc.driver bootstrap.security.principal.map bootstrap.security.principal.key
Edit
$MW_HOME/user_projects/domains/domainname/config/fmwconfig/jps-config-jse.xml:property name="jdbc.url" value="jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION_LIST = (LOAD _BALANCE = off) (FAILOVER = on)(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = standby.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = distribution.example.com)))(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = primary.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = distribution.example.com))))"/>
Edit
$MW_HOME/user_projects/domains/domainname/config/jdbc/opss-jdbc.xml:<url>jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION_LIST = (LOAD_BALANCE = off) (FAILOVER = on)(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = standby.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = distribution.example.com)))(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = primary.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = distribution.example.com))))</url>
-
After installation, launch WebLogic Server Console to change the GridLink data source JDBC connection's first host to be the local
standby_host.
14.5.12 Configuring the Security Module
When operating in a multi-site environment, Security Modules must be configured to be in controlled-pull mode.
To configure a Security Module:
-
Configure the domain (pull mode) using
config.shcommand with-multisiteparameter to enable the multi-site configuration.-
For a WebLogic Server domain:
config.sh -smType wls -smConfigId wlsPullDomain -serverLocation <MiddlewareHome>/wlsserver10.3 -multisite
-
For a Tomcat domain:
config.sh -smType tomcat -smConfigId tomcatSmPull -serverLocation /scratch/oesuser/tomcat7/ -multisite
-
-
When prompted for
primary JdbcURL, provide information similar to the following example:jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION_LIST = (LOAD_BALANCE = off) (FAILOVER = on)(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = primary-host.example.com)(PORT = 1522)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = manage.example.com)))(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = standby-host.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE _NAME = manage.example.com))))
-
When prompted for
Onsserver, provide information similar to the following example:nodes=primary-host.example.com:6200,standby-host.example.com:6200
-
Edit the
smconfig.prpfile on the standby site to include entries similar to the following example:# Policy distribution mode. oracle.security.jps.runtime.pd.client.policyDistributionMode=controlled-pull # Policy Store URL for DB policy store jdbc.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION_LIST = (LOAD_BALANCE = off) (FAILOVER = on)(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = standby-host.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE _NAME = distribution.example.com)))(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = primary-host.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = distribution.example.com)))) # Primary Policy Store URL for Mutli-site Deployment oracle.security.jps.runtime.pd.client.multisite.primaryJdbcUrl=jdbc:oracle:th in:@(DESCRIPTION_LIST = (LOAD_BALANCE = off) (FAILOVER = on)(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = primary-host.example.com)(PORT = 1522)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = manage.example.com)))(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = standby-host.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE _NAME = manage.example.com)))) # Oracle Notification Servers for Mutli-site Deployment oracle.security.jps.runtime.pd.client.multisite.onsserver=nodes=primary-host. example.com:6200,standby-host.example.com:6200 -
Edit the
smconfig.prpfile for the primary site to include entries similar to the following example. Note these differences from thesmconfig.prpfile for the standby site:-
The
jdbc.urlproperty references theSERVICE_NAMEasmanage.example.com. -
The first host in the URL is the primary host, then followed by the standby host.
jdbc.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@(DESCRIPTION_LIST = (LOAD_BALANCE = off) (FAILOVER = on)(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = primary-host.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE _NAME = manage.example.com)))(DESCRIPTION = (ADDRESS_LIST = (ADDRESS = (PROTOCOL = TCP)(HOST = standby-host.example.com)(PORT = 1521)))(CONNECT_DATA = (SERVICE_NAME = manage.example.com))))
-