4 Using the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility
This chapter describes how to use the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility. It contains the following sections:
Note:
The network administrator must check the network configuration, using the output files from the configuration utility, before the installation of Oracle Big Data Appliance. Otherwise, network errors may cause extensive delays. See "Preparing the Network for Oracle Big Data Appliance."4.1 Overview of the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility
The Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility is used to generate the installation and deployment files.
The utility is implemented as a spreadsheet containing these worksheets:
-
Welcome
-
Network Configuration
-
Server Group Configuration (1 to 3 worksheets)
-
Preview
An Oracle representative typically completes the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility from information provided by the customer in the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Worksheets. The customer and the Oracle representative work together to ensure that Oracle Big Data Appliance is configured correctly. For the sequence of steps involved in the configuration, see the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Worksheets.
4.2 Using the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility
This section explains how to use the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility. It contains these topics:
4.2.1 Using OpenOffice Spreadsheet
You must use Apache OpenOffice Spreadsheet 3.4 or Oracle Open Office Calc 3.3 to configure the spreadsheet. Do not use other spreadsheet programs like Microsoft Office Excel, which can modify the spreadsheet but not generate the files.
To obtain the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility, refer to My Oracle Support Information Center ID 1445745.2.
To open the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility:
-
Download OpenOffice from this website and follow the instructions for installing it:
-
Open Apache OpenOffice Spreadsheet.
-
From OpenOffice Spreadsheet, open the bda_configurator.ods file. If the current settings do not allow macros, you see a message.
-
To change the macro setting:
-
From the Tools menu, choose Options.
-
In the navigation tree, expand the OpenOffice.org folder and select Security.
-
In the right pane, click Macro Security.
-
Either lower the security level or enter a trusted source.
-
-
To turn off AutoCorrect:
-
From the Tools menu, choose AutoCorrect Options.
-
Select the Options tab.
-
Clear all check boxes, and then click OK.
AutoCorrect settings can make it difficult for you to enter passwords.
-
-
Save your changes and reload the spreadsheet.
-
If you see a security warning, select Enable Macros.
4.2.2 Generating the Configuration Files
This procedure describes how to use the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility to customize the default configuration settings for your installation. The other sections in this chapter provide detailed information about each field in the spreadsheet.
To generate the configuration files:
-
Open the spreadsheet with OpenOffice as described in the previous procedure.
-
On the Welcome page, choose the type of installation, then the layout of the servers from the drop-down menus. The layout choices vary depending on your choice of an installation. type
-
Click Next to edit the Network Configuration sheet.
-
Enter the network configuration settings as specified in the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Worksheets. If the server IP addresses are nonsequential, then you can enter them on the Preview page.
-
Click Next. If your changes are invalid, then you see an error message. You must correct the errors before continuing to the Server Group 1 sheet.
To discard your changes, click Reset.
-
Enter the software configuration settings as specified in the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Worksheets. If the group of servers is being added to an existing cluster, then all settings disappear from view.
-
Depending on your choices on the Welcome sheet, you must complete 1 to 3 Server Group sheets. Click Next to see the next Server Group sheet.
-
Click Preview to view the configuration settings defined by your entries. To make any changes, either click Previous, click the tab for a particular sheet, or enter the changes manually on the Preview page. You must click Preview on the Software Configuration sheet for any generated changes to appear on the Preview sheet.
-
When you are satisfied with the configuration, click Save Configuration on the Preview sheet to generate the configuration files.
This step does not save the worksheet. To save your changes, click the Save icon.
-
Choose a location for the configuration files in the Select Path dialog box. The files are created in a directory named bda-customer_name/rack_name in that location, such as bda-Example Inc/bda1.
-
If you are configuring a single rack, or multiple racks as a single CDH cluster, then you are done. Otherwise, generate separate configuration files for every set of racks that will be configured as a single CDH cluster.
-
Send the Installation Template to the network administrator to verify that the configuration is correct.
-
Send the final Installation Template, the hosts file, and the preinstall-checkip.sh script to the network administrator to prepare the network for the installation of Oracle Big Data Appliance.
4.2.3 About the Configuration Files
The Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility generates the following files to use when you configure the system. They are stored in a directory named cluster_name-customer_name/rack_name, such as bda-Example Inc/bda1.
- BdaDeploy.json
-
Contains the network configuration for a full rack, a starter rack, or a starter rack with one expansion kit. It contains information about all the servers, switches, and PDUs. Transfer this file to a USB drive for copying to Oracle Big Data Appliance. See "Configuring the Network".
- BdaExpansion.json
-
Contains the network configuration for one or two expansion kits. It contains information about all the servers, but no information about the switches and PDUs. Transfer this file to a USB drive for copying to Oracle Big Data Appliance. See "Configuring the Network".
- mammoth-rack_name.params
-
Contains all information for a server group provided in the spreadsheet, including the network configuration, port numbers, default user names, and passwords. The spreadsheet creates a separate parameter file for each cluster. If several clusters are being configured, then each parameter file is located in a separate subdirectory named config/cluster_name. Transfer the files to a USB drive for copying to Oracle Big Data Appliance. See "Installing the Software on a New Rack".
If an expansion kit is being configured as an addition to an existing cluster, then the spreadsheet does not generate a parameter file. The Mammoth utility generates it.
- rack_name-bda-install-template.pdf
-
Reproduces the Installation Preview page of the spreadsheet in a printable format. The network administrator and others can use this Installation Template to verify the settings and make any last minute corrections.
- rack_name-hosts
-
Lists the IP addresses and domains for all hosts on all networks:
-
Servers on the public (client) network
-
Servers on the administrative network
-
Servers on the private (InfiniBand) network
-
Oracle ILOMs on the administrative network
-
Switches and PDUs on the administrative network
-
- rack_name-preinstall-checkip.sh
-
Runs a series of tests to ensure the specified names and IP addresses for Oracle Big Data Appliance were added correctly to the name server, and they do not conflict with the existing network configuration. See "Preparing the Network for Oracle Big Data Appliance" for instructions on running this script.
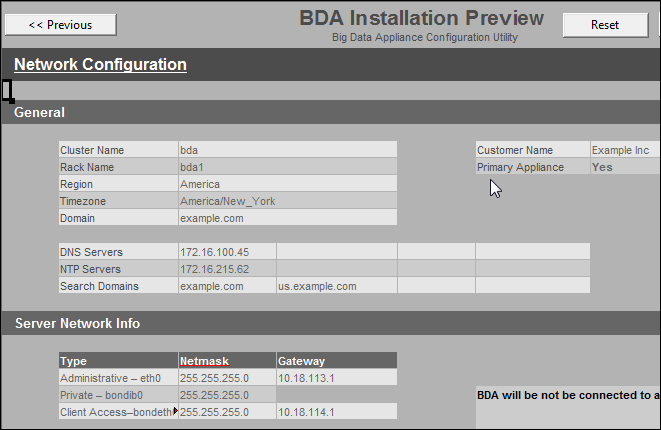
Figure 4-1 shows part of the first page of the Installation Template.
4.3 Welcome Page
You must identify the type of equipment being delivered to the customer site and the planned configuration. Table 4-1 describes these options.
Table 4-1 General Properties for the Installation
| Spreadsheet Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Type of Install |
Lists various configurations, including a full rack, a starter rack, and one or two expansion kits. Your selection in this field restricts the list in Layout of Servers to applicable choices only. |
|
Layout of Servers |
Lists the available options for configuring groups of servers into CDH clusters. The number of groups controls the number of Server Group pages in the spreadsheet: one, two, or three. |
4.4 Network Configuration
Table 4-2 to Table 4-6 briefly describe the fields in the Network Configuration sheet of the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility. See the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Worksheets for complete details.
Table 4-2 describes the general rack properties.
Table 4-2 General Properties for the Rack
Table 4-3 describes the network properties for the entire rack. If the site has isolated client and administrative networks with different DNS servers, NTP servers, or search domains, then complete this section for the client network and Table 4-7 for the administrative network.
Table 4-3 Network Properties for the Rack
Table 4-4 describes the network properties for individual servers in the rack. You specify the IP addresses assigned to node01. Sequential numbers are assigned automatically to the other servers. Ensure that an adequate range of addresses is free for each type of access. If sequential IP addresses are not available for the servers, then you can edit the Preview page.
Table 4-4 Network Properties for Servers
| Spreadsheet Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Administrative - eth0 |
First IP address of 18 from the administrative network |
|
Private - bondib0 |
First IP address of 18 |
|
Client Access - bondeth0 |
First IP address of 18 from the client access network |
|
ILOM |
First IP address of 18 from the administrative network |
Table 4-5 describes the network properties for all switches. You configure the switches manually, as described in Chapter 7. If three sequential IP addresses are not available for the InfiniBand switches, then you can edit the Preview page.
Table 4-5 Network Properties for Switches
| Spreadsheet Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
KVM Switch IP |
IP address of the KVM switch. Not applicable to Oracle Big Data Appliance X3-2, which does not have a KVM switch. |
|
Cisco Switch IP |
IP address of the Cisco switch |
|
First InfiniBand Switch IP |
First IP address of three for the InfiniBand switches |
Table 4-6 describes the network properties for the power distribution units (PDUs). You configure the PDUs manually, as described in Chapter 7.
Table 4-6 Network Properties for Power Distribution Units
| Spreadsheet Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
PDU A |
IP address of the first power distribution unit |
|
PDU B |
IP address of the second power distribution unit |
Table 4-7 describes the network properties for the administrative network if they are different from the client network. Typically, these properties are the same for both networks, and you can leave these fields blank. They default to the values you entered for the general network properties. See Table 4-3.
Table 4-7 Advanced Network Configuration Properties
| Spreadsheet Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Admin Domain |
The administrative domain name, if it is different from the domain you identified in the general rack properties. |
|
Are administrative host name entries in the DNS? |
Choose Yes or No. |
|
Admin DNS Servers |
Up to four IP addresses for the administrative Domain Name System server, if the addresses are different from those you provided for the general network properties. |
|
Admin NTP Servers |
Up to four IP addresses for the administrative Network Time Protocol server, if the addresses are different from those you provided for the general network properties. |
|
Admin Search Domains |
Up to four domain names in which Oracle Big Data Appliance administrative network operates, if the domains are different from those you provided for the general network properties. |
4.5 Software Configuration
Table 4-8 to Table 4-12 briefly describe the fields in the Software Configuration sheet of the Oracle Big Data Appliance Configuration Utility.
Table 4-8 describes the optional software available for Oracle Big Data Appliance. If you have a license for Oracle Big Data Connectors, then you can install the software For more information about these components, see the Oracle Big Data Appliance Software User's Guide.
Table 4-8 Installed Components
Table 4-9 describes the options for Auto Service Request (ASR). This service monitors the health of Oracle Big Data Appliance hardware. ASR Manager automatically submits a service request to Oracle Support Services when it detects a fault. See Chapter 5 for more information about ASR.
Table 4-9 Oracle Auto Service Request
| Spreadsheet Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable Auto Service Request? |
Although you can opt out of this service, Oracle strongly recommends that you enable ASR by choosing Yes. |
|
ASR Manager Host |
The fully qualified name of a Linux server on the network, where ASR will be installed |
|
The port number for ASR Manager. The default port is 162. |
|
|
ASR Server Root Password |
Password for |
Table 4-10 identifies the users, groups, and passwords that can be set during the software installation. If you leave the passwords blank, then the installation prompts for them. The Oracle IDs must match those of a connected Oracle Exadata Database Machine to support the network file system (NFS) protocol.
Table 4-10 Users, Groups, and Passwords
Table 4-11 describes the configuration settings for the email server that Cloudera Manager uses to send alerts from the CDH cluster.
Table 4-11 Cloudera Manager Email Alerts
| Spreadsheet Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
The fully qualified name of the existing SMTP server that the company uses on its internal network |
|
|
Email Server (SMTP) Port |
The port number used by the email server |
|
Email Server uses authentication? |
Choose Yes or No. |
|
Email Server (SMTP) User Name |
User name for Cloudera Manager to use for authentication on the SMTP server. This field is hidden when authentication is set to No. |
|
Email Server (SMTP) Password |
Password for the user name. This field is hidden when authentication is set to No. |
|
Email Server uses SSL? |
Choose Yes or No. |
|
Email Alert Recipients |
Up to four email addresses. These users receive the alerts from Cloudera Manager. |
Table 4-12 describes the configuration settings for the Oracle Enterprise Manager system monitoring plugin for Oracle Big Data Appliance.
Table 4-12 Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control
| Spreadsheet Field | Description |
|---|---|
|
Enable Enterprise Manager? |
To use the Oracle Enterprise Manager system monitoring plugin, choose Yes. |
|
Cloud Control host |
The fully qualified name of the server where Oracle Enterprise Manager is installed with the plugin for Oracle Big Data Appliance. |
|
OMS port |
The port number for the Oracle Enterprise Manager Cloud Control web interface. |
|
Cloud Control user name |
A Cloud Control user with super-administrative privileges to perform administrative |
|
Cloud Control password |
Password for the Cloud Control user name. |
|
Cloud Control registration password |
The Enterprise Manager agent registration password for validating the Oracle Management agents on Oracle Big Data Appliance. |