10 Administering Web Services
This chapter describes how to use the Configuration Service to administer web services within an ADF Mobile application.
This chapter includes the following sections:
10.1 Introduction to Administering Web Services
Web services are administered through the use of the ADF Mobile Configuration Service—a tool that enables applications already deployed to mobile devices to have their endpoints updated.
10.2 Using the Configuration Service
Using the Configuration Service provided by ADF Mobile, administrators can update web service connection endpoints for different ADF Mobile applications from a server, resulting in users obtaining a new connection. This is done by hosting and updating one or more connections.xml files for the application. The Configuration Service can be initiated every time the application starts by setting a parameter in the adf-config.xml file or by using the container utilities API to check for a new connection (see Section B.2.3, "checkforNewConfiguration").
Administrators should designate connections.xml files as resources protected by basic authentication (see Chapter 18, "ADF Mobile Application Security").
A client application can use the Configuration Service to check for updates.
The Configuration Service dialog allows you to do the following:
-
Update the Configuration Service URL and save the update for this application.
You can seed the Configuration Service URL with a URL value that assists in completing the Configuration Service dialog (see Example 10-1).
The following files must be present at the Configuration Service URL:
-
connections.xml -
adf-config.xml -
adfmf-config.xml
The files are retrieved from the Configuration Service in that order. These files should be accessed through the Configuration Service as opposed to directly through the application bundle. For more information, see Section 10.2.2, "What You May Need to Know About the URL Construction."
-
-
Enter the user name and password, which are saved in the keystore.
Administrators can use a setting in the adf-config.xml file for the application to define whether or not to call the Configuration Service at the application startup time (see Example 10-1). If the application starts for the first time, the dialog is displayed and the credentials are cached in the keystore. On subsequent starts (not including resume), you need to instruct your application to check for modifications against the server and to trigger the display of the Configuration Service dialog. ADF Mobile provides an API whereby you can specify a place in the application where the check for updates should be performed and against which the client API should be called to invoke the Configuration Service dialog. After the update, the application should run correctly (and be restarted if necessary).
Example 10-1 shows the use of the use-configuration-service-at-startup property, whose default value is false. Two additional properties can be defined in the adf-config.xml file to control behavior related to the Configuration Service: the adfmf-configuration-service-seed-url property can be specified to provide a static URL address with which to seed the URL presented in the Configuration Service dialog. Alternatively, the adfmf-configuration-service-seed-url-preference property can be specified to reference an application Preference (defined in the adfmf-application.xml file), in which case the Configuration Service dialog will use the value of the specified Preference as the seed value (see Section 13.5, "Creating a Preference for the Configuration Service URL").
Example 10-1 Configuration Service Settings in adf-config.xml File
<adf:adf-properties-child xmlns="http://xmlns.oracle.com/adf/config/properties">
<adf-property name="use-configuration-service-at-startup" value="true" />
<adf-property name="adfmf-configuration-service-seed-url"
value="http://myhost.us.example.com:7777/
ConfigServerWebDavFolder/" />
</adf:adf-properties-child>
The Configuration Service performs the following steps when the application starts:
-
It starts at the application startup time.
-
It checks the
Documentsdirectory for a copy of the managed files. If they are found, the Configuration Service finishes its process.If the Configuration Service does not locate configuration files in the
Documentsdirectory, the following takes place:-
If the
adf-config.xmlfile indicates that the Configuration Service is not in use, then the Configuration Service copies the managed files from the application bundle to theDocumentsdirectory managed folder, and then the Configuration Service finishes its process. -
If the
adf-config.xmlfile indicates that the Configuration Service is in use, then the Configuration Service tries to download the managed files in the order they are listed.
-
-
It checks for stored credentials from the secure store. If the credentials are found and they provide access to the Configuration Server, then the
connections.xmlfile is downloaded and placed in theDocumentsdirectory managed folder, and at this point the Configuration Service finishes its process.If the credentials are not found or the stored credentials fail to provide access to the Configuration Server, the user is prompted for the connection information (user name, password, and endpoint URL).
-
The Configuration Service reattempts the prompt or download five times before failing and dropping out of the application.
-
After a successful connection has been made to the Configuration Server, the
connections.xmlfile is downloaded and the connection information is stored for later use.
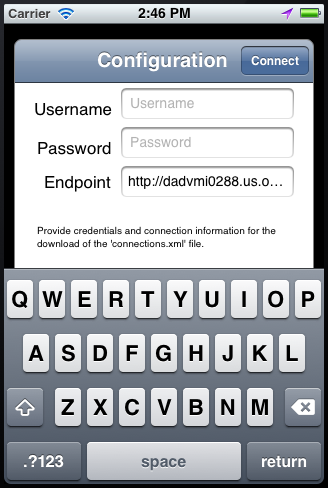
Figure 10-1 shows the Configuration Service prompt dialog on an iPhone.
10.2.1 How to Set Up the Configuration Service on the Server
The Configuration Service can be implemented as a Web Distributed Authoring and Versioning service (WebDAV) or as a service that accepts HTTP GET request and returns the connections.xml file.
The URL used by the Configuration Service client is of the following format:
url configured in adf-config.xml/application bundle id/connections.xml
The Configuration Service endpoint may be secured using basic authentication (BASIC_AUTH) over HTTP and HTTPS.
10.2.2 What You May Need to Know About the URL Construction
The URL to each of the Configuration Service-managed resources is constructed. It contains the application ID and the file name as follows:
If the user provides the URL of http://my.server.com:port/SomeLocation and the application ID of com.mycompany.appname, the following three URLs will be used to download the configuration files:
http://my.server.com:port/SomeLocation/com.mycompany.appname/connections.xml http://my.server.com:port/SomeLocation/com.mycompany.appname/adf-config.xml http://my.server.com:port/SomeLocation/com.mycompany.appname/adfmf-config.xml