1 Getting Started
This chapter provides information about the Oracle Communications MetaSolv Solution Network Grooming tool.
About Network Grooming
Network grooming is the process of reassigning connections or ports from one or more facilities to new or alternative facilities. You use the Network Grooming tool to make these changes.
The Network Grooming tool lets you do the following:
-
Reassign connections or ports from underused facilities to free up ports for other services
-
Replace equipment assignments
-
Conduct traffic-flow type changes
The Network Grooming tool provides an easy, efficient way to manage high-volume equipment and connection moves within the MetaSolv Solution application.
The Network Grooming tool facilitates management of connection moves in support of a new switch, installation, and other related business functions. It supports single-facility and multiple-facility moves, equipment moves, and connection renaming and runs a mass facility reconciliation for all child connections affected.
All the child connections that are part of a grooming project are reconciled when modifications are made to the port address assignment or connection position assignment of the parent facility.
During a facility groom, when a parent facility is assigned or moved to a new port address, the child connections are reconciled to display the updated equipment information on the assignment block on the child connection's Design Layout Report (DLR).
If child connections have Enabled Port Address assignments and the parent facility is unassigned or moved, the child connections are reconciled to display the target equipment information on the assignment block of the child connection's DLR.
The Network Grooming tool supports the following types of circuits:
-
Facility
-
Special
-
Trunk
-
Telephone Number:
-
Working Telephone Number (WTN)
-
Number Ported Out (NPOUT)
-
Number Ported In (NPIN)
-
-
Next-Generation Network (NGN) Connection
-
Bandwidth
-
Virtual
The Network Grooming tool supports all template-based connections, including virtuals, enabling you to manage allocations to and from parent bandwidth connections. Unlike physical connections, any changes to virtual connections made within the grooming workspace will be reflected within the schematic design view of Connection Design when the grooming order has been processed.
Because virtual connections do not occupy a specific channel on a parent connection, the Network Grooming tool provides the ability to manage the individual allocation parameters (stored as custom attributes) for each parent to child relationship, when applicable.
To use this capability, use the Specify Virtual Channel right-click option within the Maintenance and Connection Hierarchy views of the Network Groom Maintenance window. Allocation parameters are also auto-generated during the Groom To step if the template is set up to provide this capability.
When making design changes for template-based connections within the grooming workspace, you are prevented from making assignments that would break the rules defined for the connection specification of the connection being modified.
In addition to managing virtual connection allocations to parent bandwidth connections, you can use the Network Grooming tool to allocate physical circuits to bandwidth connections using circuit emulation, which are represented by bandwidth blocks on the DLR within Connection Design.
Network Grooming Rules
For the network grooming process to be successful, do the following:
-
Begin with the highest-level connection, such as a T3 circuit, then a T1 circuit, and so on.
-
Replace facility assignments.
-
Replace equipment assignments.
-
Add any new facility or equipment assignments.
-
Delete the assignments that will not be used. If you leave these assignments in the workspace without a reassign, these assignment will be removed when the groom is processed.
-
Verify that the application has correctly determined the new connection ID. If not, you must rename the connection ID manually.
-
Remove unchanged assignments from the groom workspace.
-
Remove any lower-level connections from the groom workspace that must not be groomed.
Groom Types
There are two basic types of grooms:
Channel/Bandwidth Modification Groom (Facility Groom)
There are four types of Channel/Bandwidth Modification Groom (Facility Groom):
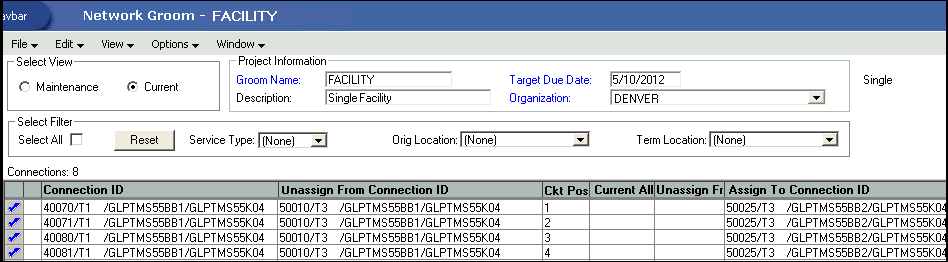
Single-Facility Groom
A single-facility groom is characterized by the following:
-
Lets you groom a facility that has only one parent.
-
A connection is represented by a single row.
-
The Connection ID column displays the connection identification of the connection being maintained.
-
The Unassign From Connection ID column represents the child circuit that will be removed after the groom has been processed, and the Ckt Pos (circuit position) column beside it represents the circuit position on the parent facility from which the groom originates.
-
The Assign To Connection ID column represents the new parent facility, and the Ckt Pos column beside it represents the circuit position.
-
The Service Type Code column represents the service-type code of the circuit.
Figure 1-1 shows the columns that are displayed in the Network Groom Current View for a single-facility groom.
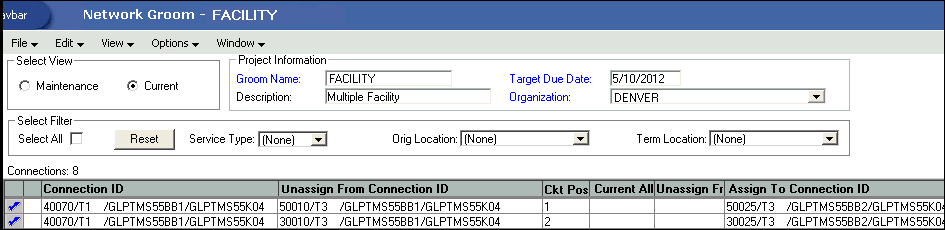
Multiple-Facility Groom
A multiple-facility groom is characterized by the following:
-
Lets you groom a facility that has multiple parents.
-
A connection rides more than one parent facility.
-
A row in the groom workspace represents each assignment. Both rows have the same connection ID as shown in the Connection ID column, but each has its own distinct unassign ID and connection position as shown in the Unassign From Connection ID and Ckt Pos columns, which represent the circuit position and the connection ID of the parent facilities, respectively.
-
Each row may be assigned to a different circuit position and facility.
Figure 1-2 shows the columns that are displayed in the Network Groom Current View for a multiple-facility groom.
Near-End Facility Groom
In a near-end facility groom:
-
You can groom just one leg of the path.
-
A connection's equipment assignment is selected.
-
All facility assignments for both the parent and the child connection are included in the groom workspace.
Far-End Facility Groom
In a far-end facility groom:
-
You can groom an entire path from one terminating point to the other.
-
A connection is selected and all the facility assignments for the parent connection are included in the groom workspace.
-
Only the selected assignment for the child connection comes into the groom workspace.
Equipment Groom
Equipment grooms are performed when a circuit is moved from one equipment port to another (for example, a T3 from one DACS to another DACS). All equipment grooms are near-end grooms and therefore only populate the workspace with the circuits terminating at the mounting positions/port addresses that you selected in the Network Groom Maintenance window. No child circuits are included into the workspace.
Note:
Far-end equipment grooms do not exist.Network Grooming Preferences
There are preferences in the MetaSolv Solution application that govern the Network Grooming tool.
The following preferences are located under Preferences - Equipment - Groom:
Note:
An asterisk (*) beside the preference denotes that it is a system preference.-
Convert EPAs to Facility Assignments: When set to N (the default), any connections with enabled port addresses are not accepted for assignment when equipment is reassigned. When set to Y, any connections with enabled port addresses are overwritten and made available for facility assignments when equipment is reassigned.
-
Default groom selection: This preference applies only to facility grooms.
This preference has the following options:
-
Near End: If you select this option, the Near End option is automatically selected in the New Groom Facility window. This makes near-end grooming the default option each time a new groom facility is started. For near-end grooms, the parent facility selected for grooming is the only facility included in the groom.
-
Far End: If you select this option, the Far End option is automatically selected in the New Groom Facility window. This makes far-end grooming the default option each time a new groom facility is started. For far-end grooms, additional facility assignments from downstream segments will be impacted by the groom and therefore must be included in the groom project.
-
-
Groom query defaults: If you select the Created (the default) check box, only the created groom projects are included for searching in the Network Groom Search window. Select any of the following check boxes to include other search criteria by default when searching for a groom project:
-
Completed
-
Completed w/ errors
-
On Order
-
Processed
-
Processed w/ errors
-
Processing
-
-
* Maximum number of ports added to workspace: Enter a numeric value that represents the maximum number of ports that can be added to a workspace.
-
Maximum Number to Process in Foreground: Enables you to specify the maximum number of facilities and connections to be processed in the foreground during a groom. If this number is exceeded, processing occurs in the background. The default is 100.
-
Remove or disconnect blocks?: When set to Remove, the previous assignments that are disconnected as a result of the groom are deleted from the design lines. When set to Disconnect, the previous assignments remain on the design lines and are indicated by a D on each row representing a disconnected assignment.
-
Reserve connection positions when target facility is selected: When set to Yes, the "groom to" positions are automatically reserved as the grooming project is created. When set to No, the terminating positions are not reserved until the ISR is generated.
-
* Update ckr when processing groom: When set to N (the default), the application does not update the ckr field in the From Order Confirmation table of an ASR. When set to Y, the application updates the ckr field in the From Order Confirmation table of an ASR.
The following preferences are located under Preferences - Equipment - Groom - CLF Facility Designation:
-
* Starting facility designation range for DS0 circuits = 1: If the Auto-Populate CLF Designation preference is not set, this range is used for DS0 circuits when grooming.
-
* Starting facility designation range for DS1 circuits = 101: If the Auto-Populate CLF Designation preference is not set, this range is used for DS1 circuits when grooming.
-
* Starting facility designation range for DS3 circuits = 101: If the Auto-Populate CLF Designation preference is not set, this range is used for DS3 circuits when grooming.
-
* Starting facility designation range for other circuits = 101: If the Auto-Populate CLF Designation preference is not set, this range is used for circuits other than DS0, DS1, and DS3 when grooming.
Note:
The Auto-Populate CLF Designation preference is located under Preferences - Service Request - Connection. When this preference is set to N (the default), any CLF facility designation can be entered. When this preference is set to Y, the facility designation is auto-populated, but you can change it if the connection is reopened.