Setting Up Financial Calculation Rules
This section discusses how to:
Describe financial calculation rules.
Establish general processing information.
Assign behavioral models.
Assign pricing rules to behavioral models.
Assign stratification rules.
Specify portfolio forecast definitions.
Assign funds transfer pricing (FTP) rules.
Assign break funding rules.
Assign risk-weighted capital (RWC) rulesets.
Assign repricing gap and liquidity rules.
Set up balance segmentation rules.
Note: Rules for ledger and treasury position accounts are assigned on the Balance Sheet Rules and Income Statement Rules pages.
Pages Used to Set Up Financial Calculation Rules
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Financial Calculation Rules - Definition |
FI_FCALC_DEFN |
|
Describe the financial calculation rule. |
|
Financial Calculation Rules - Financial Calculation |
FI_FCALC_FC_SEQ |
|
Indicate the financial measures that are calculated for the product. |
|
Financial Calculation Rules - Behavioral Models |
FI_FCALC_PP_SEQ |
|
Assign the rule to a behavioral model. |
|
Financial Calculation Rules - Pricing |
FI_FCALC_PR_SEQ |
|
Assign pricing rules to the behavioral model. |
|
Financial Calculation Rules - Stratification |
FI_FCALC_SE_SEQ |
|
Assign stratification rules to products and exceptions to stratification rules for product subsets. |
|
Financial Calculation Rules - Portfolio Forecast |
FI_FCALC_FA_SEQ |
|
Specify a portfolio forecast definition for each product. You need to define a forecast definition with prior to using this page. Also define the forecast FTP settings for the calculation of FTP rates based on spreads or indices. |
|
Financial Calculation Rules - FTP Rules |
FI_FCALC_FT_SEQ |
|
Assign FTP rules to a product through Financial Calculation Rules. |
|
Financial Calculation Rules - FTP BF Rules |
FI_FCALC_BF_SEQ |
|
Assign break funding rules to a product through financial calculation rules. |
|
Financial Calculation Rules - RWC Rules |
FI_FCALC_RW_SEQ |
|
Assign RWC rulesets to a product through Financial Calculation Rules. |
|
Financial Calculation Rules - Reprice & Liquidity |
FI_FCALC_AL_SEQ |
|
Assign reprice gap and liquidity rules to a product through financial calculation rules. |
|
Balance Segmentation |
BALANCE_SEGMENTS |
|
Allocate balances for various accounts according to your specifications. |
|
Balance Segmentation-Notes |
BAL_SEG_NOTES_PNL |
|
Enter any notes about setup. |
Financial Calculation Rules - Financial Calculation Page
Use the Financial Calculation Rules - Financial Calculation page (FI_FCALC_FC_SEQ) to indicate the financial measures that are calculated for the product.
Image: Financial Calculation Rules - Financial Calculation page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Financial Calculation Rules - Financial Calculation page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
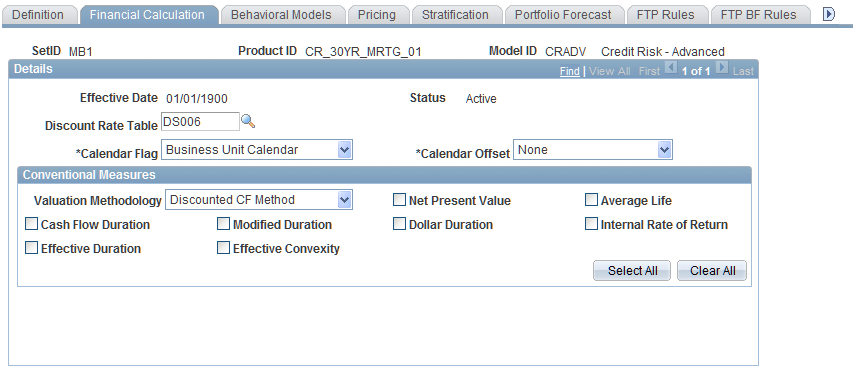
To further specify how the system processes financial products:
Specify the discount rate yield curve with the Discount Rate Table field to discount cash flows that are used to calculate the conventional measures.
Determine which calendar the system uses with the Calendar Flag field.
Select either theBusiness Unit Calendar or theCurrency Calendar.Use the currency calendar for cash flow calculations; it differs from the domestic operations calendar. For example, use it for financial products whose rate and maturity dates are derived from indices or markets in another country.
Select the calendar offset to indicate the number of business days between interest dates (adjusted for weekends and holidays) that are used to calculate interest payments. Options are:
Establish the conventional measures that this rule uses:
Set up the valuation methodology.
Use Discounted CF for conventional cash flows,Indeterminate Deposit for nonmaturing deposit products (such as demand deposits and money market accounts).
Select one or more of the following financial measures: Cash Flow Duration, Effective Duration, Modified Duration, Effective Convexity, Net Present Value, Dollar Duration, Optional Adjusted Spread, Average Life, Internal Rate of Return, andOption Cost.
Click theSelect All button to select all of them, or click theClear All button to clear all selections.
If you select Optional Adjusted Spread orOption Cost, define the benchmark instrument information.
Select if the product pool is a market-issued financial product (select the Benchmark Instrument field) and define the market issue code. If the product pool is not a market-issued financial product, selectCalculated NPV to calculate the NPV for this product by using the discount rate table. This is the likely choice when you calculate values for products that do not have a corresponding market trading.
Financial Calculation Rules - Behavioral Models Page
Use the Financial Calculation Rules - Behavioral Models page (FI_FCALC_PP_SEQ) to assign the rule to a behavioral model.
Image: Financial Calculation Rules - Behavioral Models page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Financial Calculation Rules - Behavioral Models page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
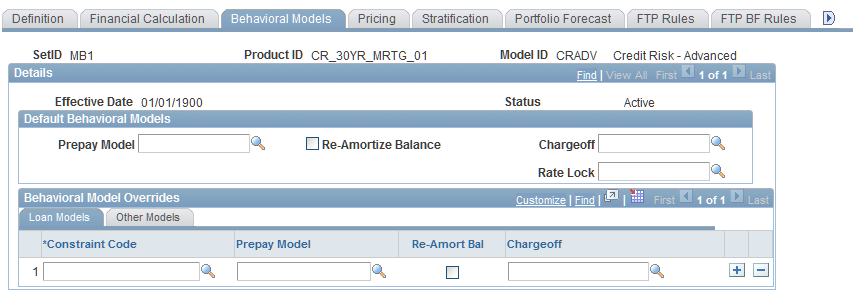
Options for default behavioral models are limited to those that are relevant to the product type that you define. For example, the Prepay Model field is active if this a loan, but not active if this is a deposit account.
To assign a financial calculation rule to a behavioral model:
Specify a particular model in the active field.
If the prepay model applies, then you can specify that the Cash Flow Generator reamortizes the loan balances after every payment period.
If the deposit growth model applies, the Cash Flow Generator can recalculate the instrument count of a pool after every payment period.
Specify behavioral model overrides for Constraint Code, the particular model, and whether to reamortize the loan balances or recalculate the instrument count of a pool after every payment period.
Financial Calculation Rules - Pricing Page
Use the Financial Calculation Rules - Pricing page (FI_FCALC_PR_SEQ) to assign pricing rules to the behavioral model.
Image: Financial Calculation Rules - Pricing page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Financial Calculation Rules - Pricing page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
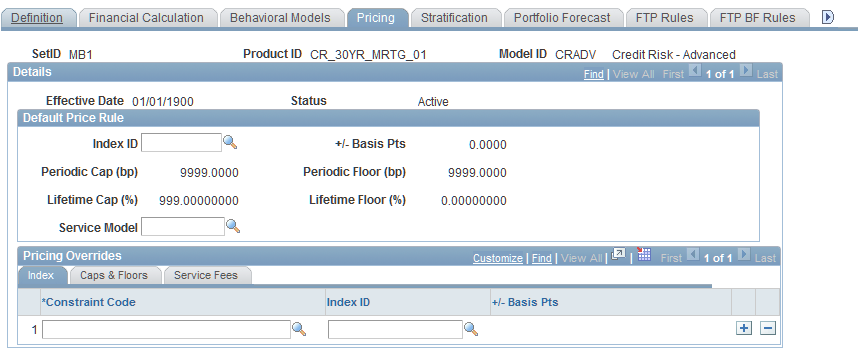
Use this page to set the pricing index that is used to construct benchmark interest rates for behavioral models. The Cash Flow application engine uses the data that you enter on this page to determine whether behavior models must be invoked. The selection applies to both historic and forecast scenarios.
To assign pricing rules to the behavioral model:
Set up the default price rule.
In the Index ID field, select the pricing index to use in the construction of the interest rate. Then, enter in the+/- Basis Pts field a spread for pricing index in basis points) to further refine the interest rate that is constructed from the pricing index. The spread can be a positive or negative value depending on the relationship of the product to the pricing index.
If it applies, enter a Periodic Cap value and aPeriod Floor value in basis points.
These values constrain the basis point shift that is assigned in the previous field. The periodic rate change can never be higher than the periodic cap, and, conversely, it can never be lower than the periodic floor.
If it applies, enter a percentage value in the Lifetime Cap field.
This value serves as the absolute ceiling limit for the pricing structure of the product class. For example, ARMS have lifetime caps that must be assigned to those products according to the original pricing period agreement. The same logic applies to lifetime floor, but in this case, the value serves as the absolute floor limit for the pricing structure.
You may assign a predefined Service Model ID. For example, some products may have a one-time origination fee or recurring service fees that are associated with them. Recurring fees are applied by the Cash Flow Generator in accordance with the product's payment frequency.
Specify pricing overrides by using the Index, Cap & Floors, and Service Fees tabs.
This enables you to specify subsets of instruments by using the Constraint Code, for which you can assign different pricing models. The fields that are displayed in this group box correspond to the constraint code. As with pricing indices, you can use constraints to override service fees.
Financial Calculation Rules - Stratification Page
Use the Financial Calculation Rules - Stratification page (FI_FCALC_SE_SEQ) to assign stratification rules to products and exceptions to stratification rules for product subsets.
Image: Financial Calculation Rules - Stratification page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Financial Calculation Rules - Stratification page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
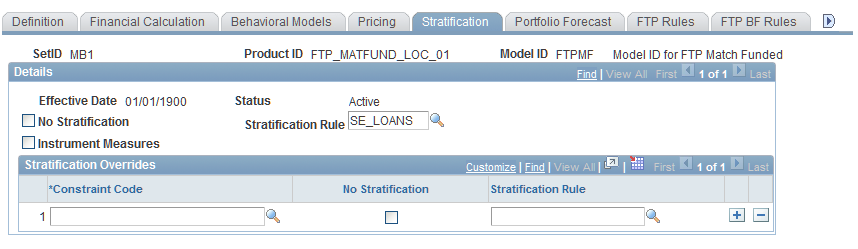
To assign stratification rules to products and exceptions to stratification rules for product subsets:
Set up general stratification information.
Select the No Stratification check box if you do not want the stratification rule to be applied to the product ID (in that case every instrument is processed separately by the Cash Flow Generator.
Depending on the number of instruments that a bank has, this can be a very time-consuming process). If you apply the rule, then specify the stratification rule in the Stratification Rule field.
To populate the Instrument Financial Calculations table (FI_ICALC_R00), select the Instrument Measures check box (in this case, the pooled calculations, such as NPV and durations, are recalculated at an individual instrument level).
Clear the check box to store the measures at the pool level only (for example, stored in the FI_POOLCALC_R00). The advantage of storing the measures at the pool level is that it can result in significantly less data being populated in the warehouse and faster processing times. The disadvantage of not storing the measures at the instrument level is that if you want to query or report on measures at the instrument level, it requires a minimum of a three-table join.
A financial product might have a subset that would not be stratified by a desired stratification rule that is defined for the product class. The exception could be assigned in the Stratification Overrides group box. For example, financial institutions use vanilla swaps frequently to limit their interest rate risk exposure. There may be a custom swap on the books that the institution wants to track closely. Rather than having the custom swap agreement lumped into the vanilla swap pool by the default stratification rule, you can establish an exception to this rule for the desired swap product according to the unique attributes of the product.
In the Stratification Overrides group box you may specify subsets of instruments (by using the constraint code) for which you may assign different stratification models.
The fields that appear in this group box correspond to the fields that are active in the Default Stratification Rule group box. Select from the drop-down list box the overriding stratification rule that you want to assign to the specified constraint code defined in the EPM Warehouse.
Financial Calculation Rules - Portfolio Forecast Page
Use the Financial Calculation Rules - Portfolio Forecast page (FI_FCALC_FA_SEQ) to specify a portfolio forecast definition for each product.
You need to define a forecast definition with prior to using this page. Also define the forecast FTP settings for the calculation of FTP rates based on spreads or indices.
Image: Financial Calculation Rules - Portfolio Forecast page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Financial Calculation Rules - Portfolio Forecast page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
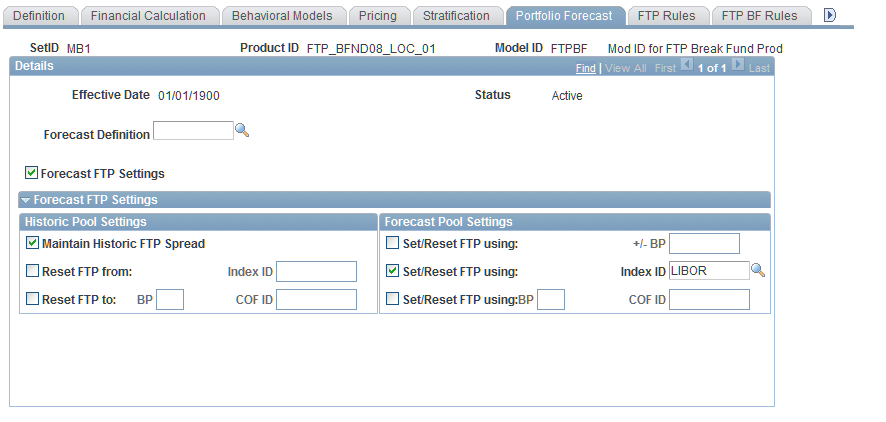
To specify a portfolio forecast definition for each product:
Select a predefined forecast definition to apply to this product and the resulting instrument pool if you want to generate cash flows for this product based on forecasted product origination amounts.
Select the Forecast FTP check box if you want to also forecast FTP rates when you run the Portfolio Forecast application engine (FI_FCSTFTP).
The system displays the Forecast FTP Settings group box, providing you with multiple ways to set FTP rates on the historic or current book and on new forecast balances. Historic pool settings and forecast pool settings function independently from one another. When you run the Portfolio Forecast application engine, it sets the FTP rate based on the rate calculation settings that you specify. To forecast FTP rates based on the more detailed historic FTP setup information, clear this check box and run the FTP_FRATE engine separately after you run the Portfolio Forecast engine.
In the Historic FTP Settings group box, select from the following FTP rate calculation settings:
Select the Maintain Historic FTP Spread check box to have the Portfolio Forecast application engine compare the FTP rate for historic pools and the current interest rate, calculate the spread, and set the forecasted FTP rate based upon maintaining that spread over the currency cost of funds index for future periods.
Select the Reset FTP From check box to have the Portfolio Forecast application engine reset the FTP rate for all historic pools based on the currency cost of funds index that you specify in the correspondingIndex field.
Select the Reset FTP To check box to specify additional basis points in the correspondingBP field, and enter the index rate that you want the Portfolio Forecast engine to use in calculating the FTP rate in the correspondingto Index field.
In the Forecast Pool Settings group box, select from the following FTP rate calculation settings:
Select the Set/Reset FTP Using check box to specify the basis point spread by which you want to set or reset the FTP rate, and enter the basis point spread in the correspondingBP Spread field.
The engine sets the FTP rate equal to the forecasted interest rate plus the spread.
Select the Set/Reset Rate Using check box to have the Portfolio Forecast application engine set or reset the FTP rate for all forecast pools based on the currency cost of funds index that you specify in the corresponding Index field.
Select the Set/Reset FTP Using check box to specify additional basis points in the correspondingBP field, and enter the exact index rate that you want the Portfolio Forecast application engine to use in calculating the FTP rate in the correspondingto Index field.
Financial Calculation Rules - FTP Rules Page
Use the Financial Calculation Rules - FTP Rules page (FI_FCALC_FT_SEQ) to assign FTP rules to a product through Financial Calculation Rules.
Image: Financial Calculation Rules - FTP Rules page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Financial Calculation Rules - FTP Rules page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
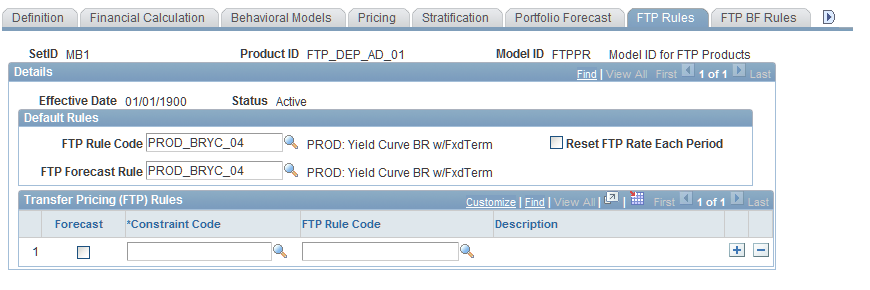
To assign FTP rules to a product through a financial calculation rule:
Set up default rules to assign the default funds transfer pricing rules for historical and forecasted balances of this product.
The FTP Rule Code establishes an FTP rule for this product ID andFTP Forecast Rule specifies the product's forecasted balance.
If you have a product that reprices or has variable interest rates, you may want to select Reset FTP Rate each Period check box to recalculate the FTP rate each period.
Specify subset or overriding values in the Transfer Pricing (FTP) Rules group box.
You can assign FTP rules that differ from the default rules for products that fall within specified constraint codes. Select Forecast if you are setting alternate rules for a forecast balance. Assign a constraint code to specify subsets of balances under this product ID. Then assign a rule code that applies to balances under this constraint code.
Financial Calculation Rules - FTP BF Rules Page
Use the Financial Calculation Rules - FTP BF Rules page (FI_FCALC_BF_SEQ) to assign break funding rules to a product through financial calculation rules.
To assign break funding rules to a product through a financial calculation rule:
Select a Break Funding Rule to apply to this product.
Specify subsets of this rule by assigning a constraint code and additional break funding rules to this product ID.
Financial Calculation Rules - RWC Rules Page
Use the Financial Calculation Rules - RWC Rules page (FI_FCALC_RW_SEQ) to assign RWC rulesets to a product through Financial Calculation Rules.
Image: Financial Calculation Rules - RWC Rules page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Financial Calculation Rules - RWC Rules page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
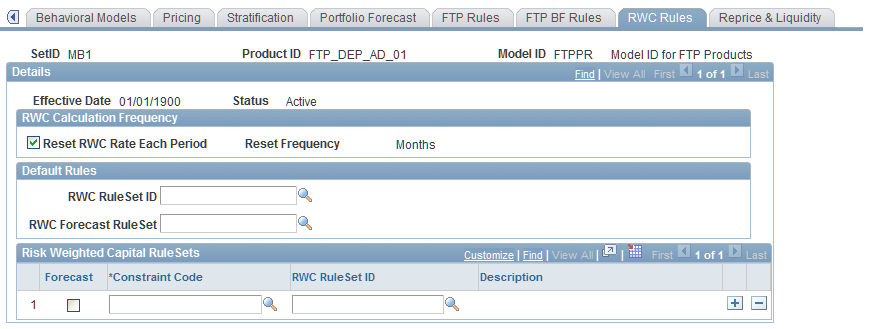
To assign RWC rulesets to a product through a financial calculation rule:
Select Reset RWC Rate Each Period to recalculate the RWC and normalized loss rates for each processing period for all instruments for this product.
Enter the Reset Frequency to recalculate risk weights and normalized loss weights for any instruments that exceed the recalculation frequency period.
Define the default RWC rulesets for this product.
Select an RWC ruleset ID and an RWC forecasted ruleset for this product ID.
Add exceptions to the default rules in the Risk-Weighted Capital RuleSets grid.
Assign RWC rules that compliment the default rules established above for products that occur within specified constraint codes. Select the Forecast option to set alternate RWC rules for a forecasted pool balance. Specify a constraint code and an RWC ruleset ID to apply to balances for the constraint code.
Financial Calculation Rules - Reprice & Liquidity Page
Use the Financial Calculation Rules - Reprice & Liquidity page (FI_FCALC_AL_SEQ) to assign reprice gap and liquidity rules to a product through financial calculation rules.
Image: Financial Calculation Rules - Reprice & Liquidity page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Financial Calculation Rules - Reprice & Liquidity page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
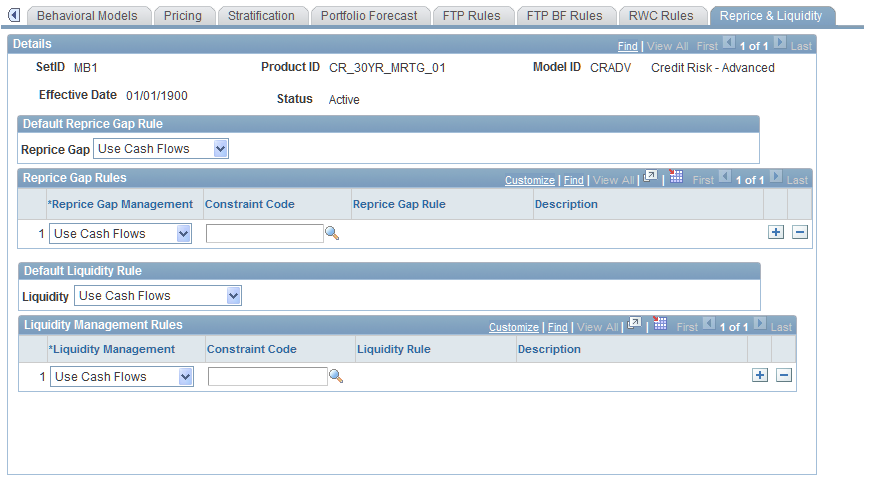
To assign reprice gap and liquidity rules to a product through a financial calculation rule:
For both reprice gap rules and liquidity rules, you need to determine if the system manages the cash flows for this product by using the defined contractual cash flow (field values: Use Cash Flows), or if you want the system to manage the cash flow for this product differently than the stated product contractual cash flow (field values:Override Cash Flows).
For example, you might want to classify six-month time deposits with balances of 5,000 USD or less as a product subject to early withdrawal.
Specify one of these management options for the default reprice gap rule, and then do the same for the Default Liquidity Rule.
Specify subsets of instruments for the reprice gap and liquidity default rules.
Select how the system manages the cash flows, apply a constraint code, and apply a Reprice Gap Rule or Liquidity Rule, if necessary (these fields appear if you select Override Cash Flows).
Balance Segmentation Page
Use the Balance Segmentation page (BALANCE_SEGMENTS) to allocate balances for various accounts according to your specifications.
Your organization may have a policy regarding the allocation of balances according to a schedule. This schedule might allocate 60 percent of total balance of demand deposit accounts (DDAs) in the one month reprice bucket, followed by 20 percent in the eighteen month bucket and finally 20 percent in the thirty-six month bucket. The Balance Segmentation page enables you to specify both percent of balance and dollar amounts for accounts that have widely varying balances. You may find it more effective to assign a recurring balance amount in an assigned reprice bucket rather than a percentage of balance.
Another useful feature of balance segmentation is the reprice assignment of off-balance sheet (OBS) products. Often, the product definitions of OBS products suffice for an aggregation rule, but there may be instances where you must assign reprice information that contradicts the contracts for hedge accounting treatment. For example, the contracts may be June 2003 contracts identified to assets repricing or maturing in September 2003. You can override the June flow to September to adhere to the hedge identification. Similarly, you can attach PF Ledger accounts to balance segmentation rules as well.
Once you set up the balance segmentation rules, you can assign them to the Financial Calculator and Balance Sheet Rules pages.
Image: Balance Segmentation page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Balance Segmentation page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
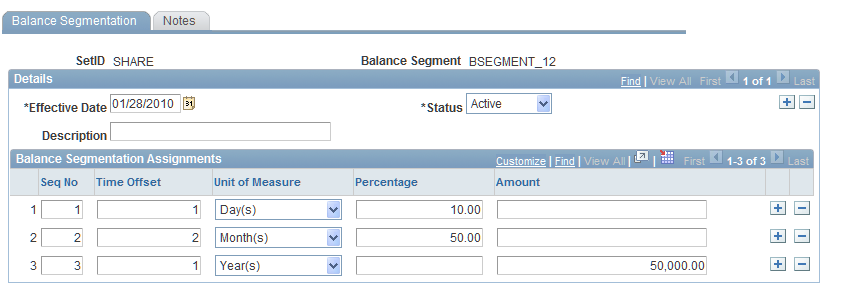
Establish a balance segmentation rule for cash flows. Create an assignment that specifies when the balance segmentation is to be effective. The Time Offset andUnit of Measure fields determine the length of time for this balance segmentation rule. ThePercentage andCurrency fields enable you to choose how you want the balance of the product to be pooled. If you choose percentage, enter a percentage of the product's pool balance. If you choose currency, enter a fixed amount.