Establishing Book Code Functionality
Book code functionality is an optional feature that is implemented at the Global Consolidations system level. This section discusses:
Understanding book codes.
Enabling book code functionality.
Enabling row-level security by book code.
Understanding Book Codes
In Global Consolidations, you use the book code dimension to identify source data and specific types of adjustments, for example harmonization adjustments. You combine book codes into book code groups and use the book code groups to segregate source ledger amounts from harmonization and other types of adjustments in reports and inquiries.
Harmonization adjustments are journal entries and allocations that adjust the consolidation balances for consolidation reporting under the requirements of International Accounting Standards (IAS), United States-Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (US-GAAP), or other statutory requirements. Using book codes and book code groups enables you to maintain multiple accounting methods for separate local and consolidation reporting books within a single scenario.
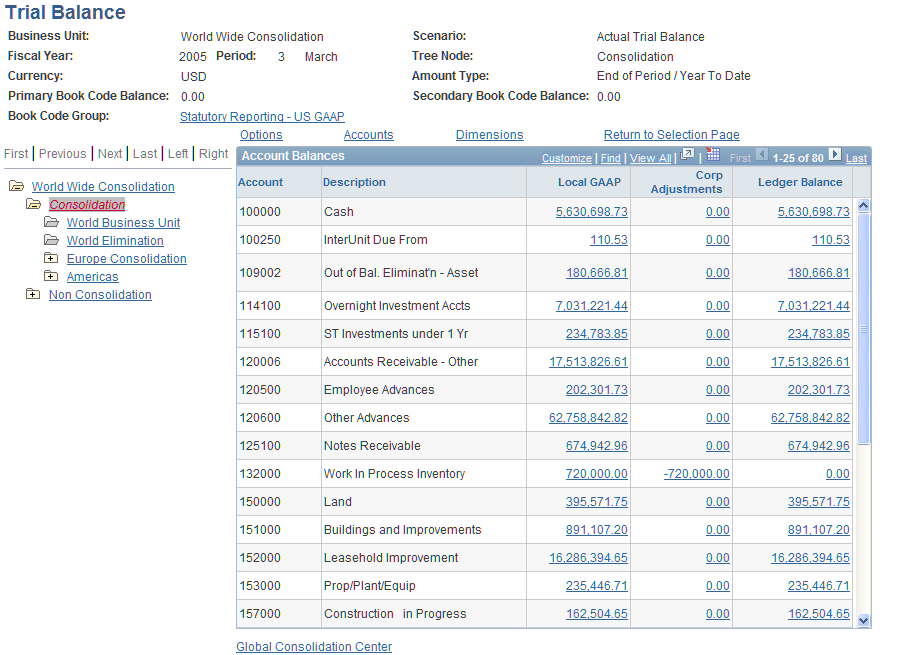
If you enable book code functionality, the trial balance and other inquiry selection pages display a book code group option so that you can use a book code group as one of your inquiry criterion. When book code functionality is enabled, the trial balance inquiry contains columns for both the primary and secondary book codes within the book code group.
For example, after enabling book codes, you could establish these three book codes:
COMN (common) used for source data.
COAJ used for US GAAP adjustments.
CORP used for US GAAP reporting.
You would then identify source data, journals, and allocations with the book codes COAJ (corporate adjustments) or CORP (for corporate reporting). You also combine these three book codes into a book code group, CORP, which you use when you want inquiries and reports to display the local GAAP plus adjustments that are identified by these book codes.
Note: You can group as many book codes together as needed to define a book code group. For example, you might define one book code group for US-GAAP reporting, another for IAS reporting, and another for local statutory reporting.
Image: Example of a book code group.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Example of a book code group.. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
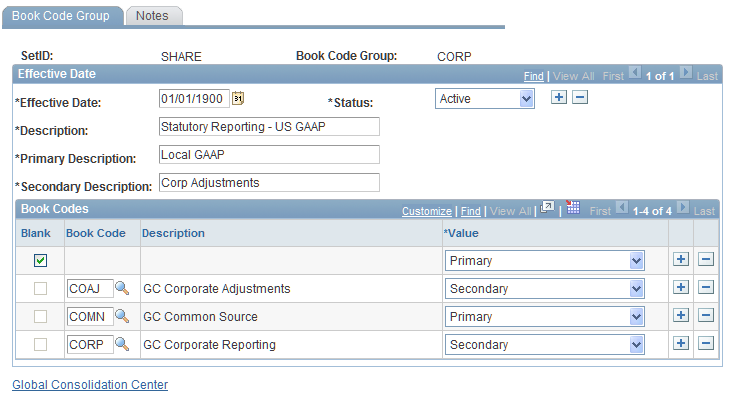
When you run a trial balance inquiry, you can specify the book code group to use and group the amounts in the first (primary) and second (secondary) columns.
Image: Example of the Trial Balance Inquiry page showing amounts segregated by primary and secondary book codes.
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Example of the Trial Balance Inquiry page showing amounts segregated by primary and secondary book codes.. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
See Access My Oracle Support to see the Global Consolidations Implementation Guide Red Paper.
Enabling Book Code Functionality
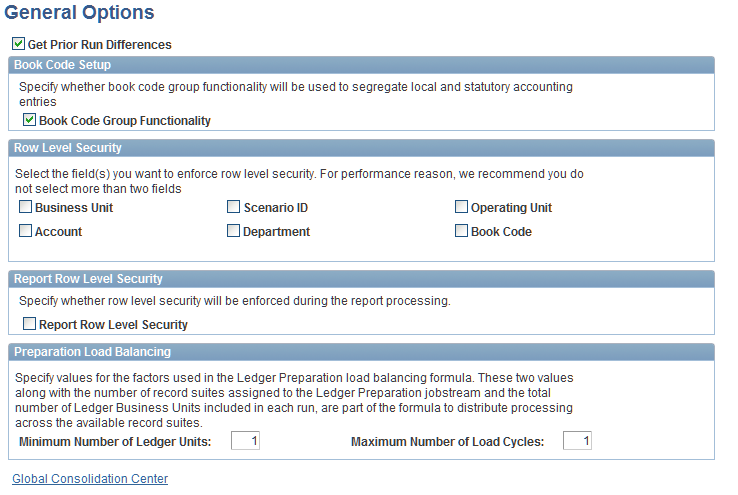
You enable book code functionality on the General Options page by selecting the Book Code Group Functionality check box.
Image: General Options page showing book code functionality enabled and row level security by book code
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the General Options page showing book code functionality enabled and row level security by book code. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
Enabling Row Level Security by Book Code
After setting up and assigning EPM security user and user roles, you can restrict access to book codes based on the row-level security setup options on the General Options page in the Global Consolidations application. You can assign users to security groups that you tie to book codes and restrict their ability to enter and make inquiries of data for these specific book codes. You enable row-level security by book code by selecting the Book Code check box in the Row Level Security section.
Pages Used to Establish Book Code Functionality
|
Page Name |
Definition Name |
Navigation |
Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
|
General Options |
GC_INSTALLATION |
|
Establish whether to implement book code functionality, along with other system options. |
|
Maintain Book Code |
BOOK_CODE_D00 |
|
Set up and maintain book code dimensions. Book codes are dimensions that are used to categorize and segregate source ledger amounts and adjustment amounts. |
|
Book Code Group |
GC_BKCD_GRP |
|
Assign individual book codes to a book code group. |
|
Book Code Group-Notes |
GC_BKCD_GRP_NOTES |
|
Enter notes about book group setup. |
Book Code Group Page
Use the Book Code Group page (GC_BKCD_GRP) to assign individual book codes to a book code group.
Image: Book Code Group page
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Book Code Group page. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
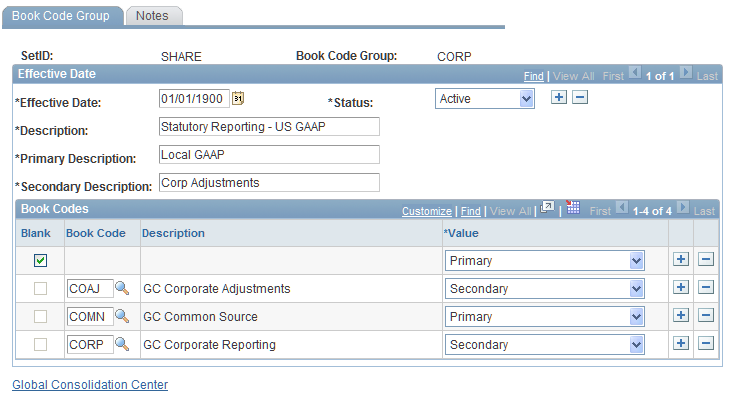
Book code groups enable you to limit what data appears in inquiry and reports, so that you can view different sets of adjustments to the source data. For example, one book code could contain all the GAAP adjustments, another could contain local statutory adjustments.
Book Codes
Enter a row for each book code that you want to include in the book code group.
Note: The underlying book code group table (GC_BKCD_GRP) contains the date/timestamp and user ID information for audit purposes.