Knowing how the Web Crawler processes URLs helps you understand where a new plugin fits in, because the URL processing is accomplished by a series of plugins.
Each URL is processed in the following way:
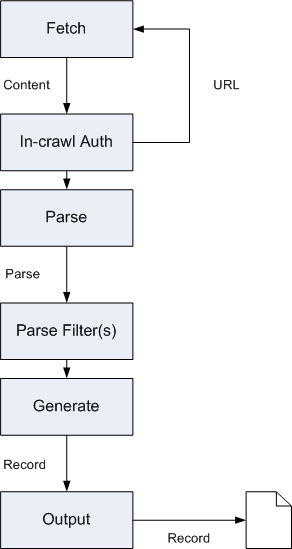
The processing flow is as follows:
- The scheduler determines which URL should be fetched (this step is not shown in the diagram).
- Fetch: A Protocol plugin (such as the protocol-httpclient plugin) fetches the bytes for a URL and places them in a Content object.
- In-crawl Auth: An Authenticator plugin can determine whether form-based authentication is required. If so, a specific login URL can be fetched, as shown in the diagram.
- Parse: A Parse plugin parses the content (the Content object ) and generates a Parse object. It also extracts outlinks. For example, the parse-html plugin uses the Neko library to extract the DOM representation of a HTML page.
- Filter: ParseFilter plugins do additional processing on raw and parsed content, because these plugins have access to both the Content and Parse objects from a particular page. For example, the endeca-xpath-filter plugin (if activated) uses XPath expressions to prune documents.
- Generate: A record is generated and written to the record output file. In addition, any outlinks are queued by the scheduler to be fetched.
