This topic describes implementation details of graphs to load the Property Description Records (PDRs) to create the standard attribute schema.
Use a CSV-based configuration graph to load the standard attribute schema. See CSV-based configuration graphs.
Input file
The PDR input file defines one or more Endeca standard attributes, with the specific settings of required and optional PDR properties. The input file resembles the following illustration:
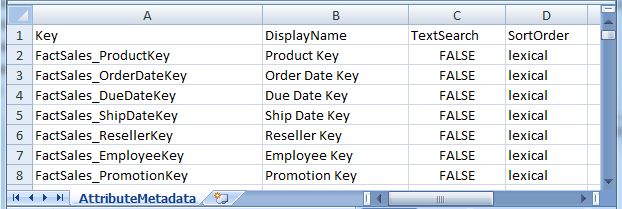
The first line of the sample file is the header row, which specifies the properties defined in the input file. You must specify the value for the mdex-property_Key. Other mdex-* and system navigation properties are optional. Attribute properties you do not specify either use defaults or are not defined. For information on the system default values for standard attributes, see Standard attribute default values.
Key,DisplayName,TextSearch,SortOrder
The names of these properties are arbitrary; you can use different names in your input file if you choose (for example, you can use AttrName instead of Key). The properties are delimited (for example, by the comma in a CSV file or the pipe character in a text file).
| Input Header Property | Maps to PDR Property |
|---|---|
| Key | mdex-property_Key |
| DisplayName | mdex-property_DisplayName |
| TextSearch | mdex-property_IsTextSearchable |
| SortOrder | system-navigation_Sorting |
The second and following rows in the input file contain the values for the configuration properties.
Standard attribute Transformer
In the configuration graph, use a Reformat component to build the XML to submit to the server to define your standard attribute schema. The XML consists of a set of PDRs (<mdex:record>), each of which comprises attribute properties (for example, <mdex-property_Key>, <mdex-property_DisplayName>).
integer n = 1;
integer aggrKey = 0;
// Transforms input record into output record.
function integer transform() {
string searchBool = "";
string saRecord = "<mdex:record xmlns=\"\">";
saRecord = saRecord + "<mdex-property_Key>" + $0.Key + "</mdex-property_Key>";
saRecord = saRecord + "<mdex-property_DisplayName>" + $0.DisplayName + "</mdex-property_DisplayName>";
// Lower case the boolean in the CSV file
searchBool = lowerCase($0.TextSearch);
saRecord = saRecord + "<mdex-property_IsTextSearchable>" + searchBool + "</mdex-property_IsTextSearchable>";
saRecord = saRecord + "<system-navigation_Sorting>" + $0.SortOrder + "</system-navigation_Sorting>";
$0.xmlString = saRecord + "</mdex:record>";
// Batch up the web service requests.
$0.singleAggregationKey = aggrKey;
n++;
if (n % 15 == 0) {
aggrKey++;
}
return ALL;
}
First, the code defines two integer variables, the first as a loop counter, the second as the aggregation key (aggKey).
Next, the transform() function builds the PDRs by creating the <mdex:record> container, and populating it with nodes corresponding to the properties defined in the input file (<mdex-property_Key>, <mdex-property_DisplayName>). The value of each node is derived from the corresponding value in the input file.
Note that in this example, the value of the Text Search field, which is specified in ALL CAPS, is converted to lower case before it is added to the XML.
Finally, the records are grouped into batches of 15 for submission to the server. Submitting in batches ensures a continuous stream of processing through all components in the graph, which improves performance of both Integrator ETL and the Endeca Server.
Web service request
Use the updateProperties operation of the Configuration Web Service to load the PDR configurations into the Endeca Server. This operation creates new standard attributes, and updates any affected existing standard attributes with new data. The following code illustrates a typical updateProperties operation to load PDRs:
<config-service:configTransaction
xmlns:config-service="http://www.endeca.com/MDEX/config/services/types/3/0">
<config-service:OuterTransactionId>${OUTER_TRANSACTION_ID}</config-service:OuterTransactionId>
<config-service:updateProperties
xmlns:mdex="http://www.endeca.com/MDEX/XQuery/2009/09">
$xmlString
</config-service:updateProperties>
</config-service:configTransaction>
This example includes two variables:
-
OUTER_TRANSACTION_ID
This variable specifies the outer transaction ID for the request. The variable and its value are stored in the workspace.prm file of the Integrator ETL project.
-
$xmlString
This variable contains the PDRs that have been constructed by the Reformat component in the graph.
This code is added to the Web Services Client component in the configuration graph.
