Data domain profiles define the hardware resources that the Endeca Server cluster makes available to the data domains it hosts. This topic explores the interaction between oversubscribing of data domains and hardware utilization.
Data domain profiles are defined by an administrator to control the resources allocated to data domains, and provide a mechanism to offer different levels of service for data domains hosted by the Endeca Server.
The following examples, along with their supporting diagrams, explore how data domain profiles relate to the utilization of CPU resources on the nodes of an Endeca Server cluster.
CPU utilization by data domains without oversubscribing
The following diagram illustrates several possible ways to configure a data domain profile that is configured so that it does not oversubscribe CPU resources.
The fact that a data domain profile does not allow oversubscribing means that the Endeca Server cluster will allocate hardware resources to such a profile based on what is specified in the profile, but only if the Endeca Server nodes have these resources.
- --oversubscribe false.
- --num-compute-threads <num_threads>.
In addition to options from endeca-cmd, you can use equivalent parameters from the putDataDomainProfile operation of the Cluster Web Service — allowOversubscribe and numComputeThreads.
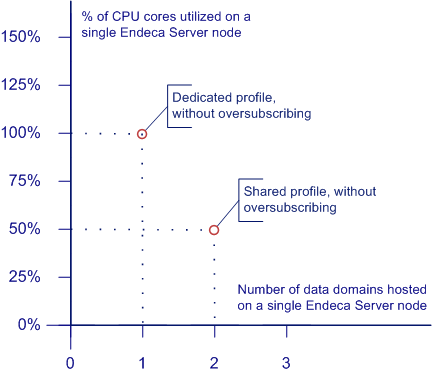
The diagram shows the CPU utilization of a single Endeca Server node as a function of the number of domains it hosts.
-
A dedicated profile, without oversubscribing. This profile may be applicable for data domains that will support production applications. In the diagram, this type of usage is illustrated by a single data domain hosted on a single Endeca Server node that allocates 100% of its CPU capacity to this data domain.
- A shared profile, without oversubscribing. This profile divides an Endeca Server machine's CPUs between data domains. In the diagram, this type of usage is illustrated by two data domains each utilizing 25% of CPU capacity on each Endeca Server node (in this case, the total CPU usage is 50%).
CPU utilization by data domains with oversubscribing
The following examples demonstrate profiles that allow Endeca Server to host domains on nodes that may be oversubscribed.
A profile that allows oversubscribing means that the Endeca Server will allocate the resources specified in the profile but may choose to host the domains on nodes where those resources are already allocated to other domains. In other words, an oversubscribed profile instructs the Endeca Server cluster to allow domains to be hosted on nodes where the resources allocated to domains exceed the actual available resources. For example, the Endeca Server may host ten 4-CPU Dgraphs on a 12 CPU machine.
When an Endeca Server node is oversubscribed, the domains it hosts will compete for the available resources. Managing the competing demands for resources is delegated to the underlying operating system.
- --oversubscribe true.
- --num-compute-threads <num_threads>.
The following diagram illustrates four examples of shared oversubscribed data domain profiles:
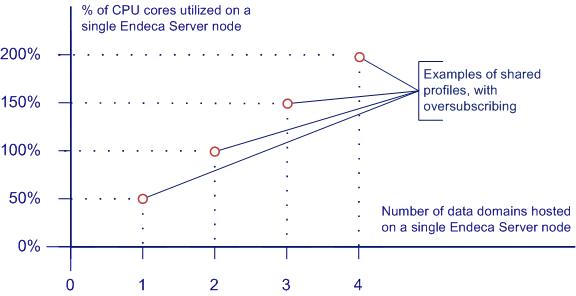
- The first scenario shows a single shared data domain, where a data domain hosted on the Endeca Server node takes 50% of its CPU. Even if the Endeca Server node may not have enough CPU, the data domain will be allocated the required CPU because its profile is configured to allow oversubscribing. In this example, since there is only a single domain hosted on the node, the node itself is not yet oversubscribed.
- The second scenario shows two shared data domains, where each Endeca Server node hosts two Dgraph nodes (each from a different data domain), configured so that they allow oversubscribing. In this example, the Endeca Server node is not oversubscribed but is fully subscribed, since the two domains together are using 100% of the CPU resources.
- The next scenario shows three shared data domains, where all data domains combined can take up to 150% of the CPU on the Endeca Server node. In this example, the node is oversubscribed, since 150% of its CPU resources are allocated to the three domains it hosts.
- The last scenario shows four shared data domains, where all data domains combined can take up to 200% of the CPU on the Endeca Server node. In this example, the Endeca Server node is also oversubscribed.
Oversubscribed profiles may be useful for domains where strict performance guarantees are not required, such as development or testing scenarios.
