6 About the OCECAS Architecture and Environment
This section explains the Oracle Communications Evolved Communications Application Server (OCECAS) architecture and how its components work together.
About the OCECAS Technical Architecture
OCECAS is an application server for VoLTE services. More specifically, it is an IMS application server responsible for call control. It provides VoLTE-centric single radio voice call continuity (SRVCC) telephony voice and video communications to packet-switched IMS networks. It comes pre configured to work with border controllers such as the Oracle Communications Session Border Controller.
OCECAS is based on and uses features from both the Oracle Communications Converged Application Server (Converged Application Server) and the Oracle Fusion Middleware WebLogic application server (WebLogic server). These products are included in OCECAS.
OCECAS includes the Session Design Center GUI tool that allows non-technical personnel to customize subscriber communication sessions. The Session Design Center tool uses a simple and efficient drag-and-drop interface to control sessions.
About the OCECAS Environment
OCECAS sits on the edge of your IMS telecom network and serves as a multimedia (VoLTE voice and video) application server. It enables you to serve VoLTE applications on hybrid 2G/3G/IMS networks.
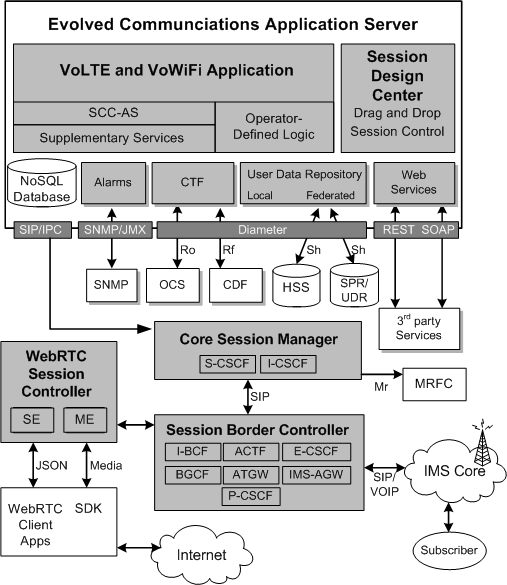
Figure 6-1 shows a detailed view of OCECAS components and how they relate and communicate. The top level shows the Evolved Communication Application Server and it's main components, the VoLTE and VoWifi application, Session Design Center, the NoSQL database, alarms, CTF, user data repository, and web services. OCECAS connects to these external elements: SNMP, an OCF, a CDF, an HSS, a UDR, WebRTC Session Controller, and Core Session Manager. OCECAS connects to your IMS network through Core Session Manager using Session Border Controller. Your WebRTC client applications connect through WebRTC Session Controller, and then through Session Border Controller.
Understanding the OCECAS Components
This section explains the main components that comprise OCECAS. Together, these technologies provide high-bandwidth packet-switched networks with a pure IMS solution for serving applications as an SCC-AS, which provides SRVCC voice and video communication.
By providing supplementary services, OCECAS offers video call support as defined in the GSMA IR.92 IMS Profile for Voice and SMS specification. ECAS also supports the User Entity (UE) registration of video as defined in the IR.92 IMS Profile for Video and SMS.
Understanding WebRTC Session Controller
Oracle Communications WebRTC Session Controller (WebRTC Session Controller) is a separate Oracle product that acts as a SIP endpoint. If your implementation requires it, you purchase this product separately. WebRTC Session Controller enables real-time communication between web browsers and SIP, and web browsers and public switched telephone network (PSTN) phones. WebRTC Session Controller uses WebRTC (Web Real Time Communication), an API being standardized by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). WebRTC enables web browsers to directly share video, audio, and data.
WebRTC Session Controller is a gateway server. You place it at the edge of the network to facilitate integration between WebRTC browser clients with the IP Multimedia Subsystem (IMS). It reuses the Oracle WebLogic Server infrastructure already provided by Converged Application Server, including WebLogic Server domains and servers.
Understanding Converged Application Server
Included as a component of OCECAS, Converged Application Server serves multimedia applications that use the SIP protocol. As the name implies, one of its strengths is serving ”converged” applications that rely on various different protocols and interfaces. Converged Application Server supports 3rd-party application development and hosting, and allows multiple applications to execute on the same incoming or outgoing request. The applications can each execute separately from the others, and uses its own set of rules. Each SIP servlet stores application date in a container-managed session object, so implementations persist and replicate this data to create a highly available implementation. Converged Application Server supports the JSR 359 SIP Servlet Specification, version 2.0:
Understanding WebLogic Server
Included as a component of OCECAS, WebLogic Server is a scalable, enterprise-ready Java Platform, Enterprise Edition (Java EE) application server. It is an ideal foundation for building applications based on service-oriented architecture (SOA).
The WebLogic Server implementation of the Java EE 6.0 specification provides a standard set of APIs for creating distributed Java applications. These applications can access a wide variety of services, such as databases, messaging services, and connections to external enterprise systems. WebLogic server also provides server support, such as diagnostic tools to tune performance, and the ability to capture business intelligence.
Understanding Session Border Controller
OCECAS requires a border controller and it comes pre-integrated to use Oracle Communications Session Border Controller (Session Border Controller) and Oracle Communications Core Session Manager (Core Session Manager) for this purpose. However, you can use any session border controller that your implementation requires.
Session Border Controller is a component required by OCECAS that you purchase separately. It enables service providers to deliver trusted, first-class real-time communications services across Internet Protocol (IP) network borders, including any services across IMS borders. The functions offered by Session Border Controller satisfy critical service provider requirements in five major areas: security, interoperability, reliability and quality, regulatory compliance, and revenue/cost optimization.
Understanding Core Session Manager
Core Session Manager is a product that you need to purchase separately. However most implementations require it. It is an agile session core for supporting Voice over LTE (VoLTE) services (VS-CSCF). It directs signaling flows through the network and between elements. Network Function Virtualization (NFV) allows service providers to share hardware resources efficiently across different services and customers. Core Session Manager is designed to support core session management capabilities in virtualized environments. It provides a complete set of session core functions including IP Multi-media Subsystem (IMS) Call/Session Control Functions (CSCF) and their associated 3GPP interfaces.
About Integrating OCECAS into Your Network
When you install OCECAS you automatically get Converged Application Server and WebLogic Server technologies included in the installation.
In addition, obtain and install these Oracle Communications products:
-
Core Session Manager
-
Session Border Controller
-
WebRTC Session Controller (Optional)
Note:
Instead of purchasing Core Session Manager and Session Border Controller separately, you could purchase a copy of Oracle Communications Unified Session Manager (Unified Session Manager). Unified Session Manager contains both Core Session Manager and Session Border Controller pre-configured to work on their own hardware system as a I/S-CSCF.Once installed, configure OCECAS to connect to them.
Understanding How OCECAS Communicates
OCECAS uses the REST and SOAP protocols to interact with the applications it serves, and provide voice and video communication between applications, subscribers, and 3rd-party services. It uses REST and SOAP to integrate with other IT and network systems Voice Over Long-Term Evolution (VoLTE). The internal OCECAS servers use the SIP protocol to build up and tear down calls. They also use the Diameter protocol to exchange and store subscriber information, charge for communications and otherwise communicate with your IMS core.
The charging control function (CTF) communicates with the online charging server (OCS) using the Diameter Ro online charging specification. The CTF communicates with the charging data function (CDF) using the Diameter Rf offline charging specification.
The user data repository uses the Diameter Sh specification to communicate with the home subscriber server (HSS) and external subscriber data repository (SPR/UDR).
The Core Session Manager communicates using the JSR 309 Media Control Server API Standard to communicate with media resource servers. The JSR 309 specification is available from the Java Community Process web site:
About Overload Protection
OCECAS uses the Converged Application server capabilities to provide failover protection. As shown in Figure 1-3, the OCECAS production environment uses the Converged Application Server Engine Tier and Data Tier (in this case the Services and Change Set). The Engine Tiers control the SIP sessions, but keep the session state and data inside the Data Tier. Data Tier is distributed and replicated which prevents failover. So calls are not lost.
OCECAS is self-throttling to prevent call degradation in overload situations. Any existing sessions continue, but the platform only lets new sessions form if there is enough bandwidth to run them efficiently.