18 Transactional Logging and Decision Analytics
This chapter describes the transactional logging and decision analytics feature. This feature provides analytics on the decisions and events that are processed by Oracle RTD, that is, it provides transactional reporting capabilities on Oracle RTD choice events and decisions. It enables business users to easily see a summary performance of choices by decision.
Transactional logging and decision analytics uses other business intelligence technologies such as Oracle Business Intelligence Enterprise Edition (OBIEE).
This chapter contains the following topics:
18.1 High Level Architecture
This section introduces the main architecture concepts underlying this feature, namely logging through APIs, a transformation stored procedure, and the reporting mechanism based on OBIEE.
This section contains the following topics:
18.1.1 Terminology
Decision Analytics - The transactional reports based on OBIEE.
18.1.2 Logging
Inline Services can use Java APIs to log decision and event information in transactional tables within SDDS.
18.1.3 Transformation
A stored procedure is provided to move the contents of the transactional tables in SDDS into a star schema. This star schema resides in a different database schema.
The stored procedure is typically run once a day.
18.1.4 Reporting
OBIEE is used to provide dashboards reporting on this star schema.
Sub-components include:
-
An OBIEE RPD which provides the physical and logical mappings
The RPD also provides some measures that are used by the reports. These measures are specific to the marketing use case.
-
A Web Catalog which provides dashboards for the marketing use case. One dashboard is generic and can be used with any kind of choices (static or dynamic).
The generic dashboard can be viewed within OBIEE Presentation Services.
Note:
Several other dashboards are specific to the Base Marketing Decision Manager application, and can be viewed within Decision Manager.
18.2 Specifications
Two tables, SDDecisionLog and SDChoiceEventLog, have been added to SDDS. This section describes these tables and the other components of the transactional logging and decision analytics feature.
This section contains the following topics:
18.2.1 SDDecisionLog
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
|
session_key |
Key of session (customer identification) |
|
app_name_id |
ID of the application (Inline Service) |
|
version_id |
Version of the application. This gets incremented every time the Inline Service is redeployed |
|
choice_parent_id |
ID of the choice group to which this choice belongs |
|
choice_parent_id_name |
Name of the choice group to which this choice belongs. |
|
choice_id |
ID of the choice. |
|
choice_id_name |
Name of the choice |
|
channel_id |
Channel in which this decision was made |
|
happened |
Timestamp of the decision based on application time (in seconds since January 1st 1970 UTC) |
|
day_of_month |
Day of the month of the decision in format day_n or day_nn |
|
decision_instance_id |
Unique id representing the decision |
|
ip_name |
Name of the integration point |
|
decision_name |
Name of the decision |
|
control_group |
Whether this is a control group decision or not ('Y' or 'N') |
|
is_random |
Whether this is a random decision or not ('Y' or 'N') |
|
segment_id |
ID of the decision segment |
|
segment_name |
Name of the decision segment |
|
perf_goal_1 |
Name of the first performance goal |
|
individual_score_1 |
Score for the first performance goal |
|
individual_weight_1 |
Weight for the first performance goal |
|
perf_goal_2 perf_goal_10 |
Names, scores, and weights for subsequent performance goals |
|
total_score |
Total score for all performance goals |
|
score_rank |
Rank of this choice among other choices in this decision |
|
hierarchy_id_1 |
ID of the first related choice or choice group in the hierarchy. |
|
hierarchy_id_2,..., hierarchy_id_10 |
IDs of subsequent related choices or choice groups in the hierarchy |
|
hierarchy_id_name_1 |
Name of the first related choice or choice group in the hierarchy. |
|
hierarchy_id_name_2,..., hierarchy_id_name_10 |
Names of subsequent related choices or choice groups in the hierarchy |
|
event_flex_float_1 |
First float flex field |
|
event_flex_float_2,..., event_flex_float_10 |
Subsequent float flex fields |
|
event_flex_int_1 |
First int flex field |
|
event_flex_int_2,..., event_flex_int_10 |
Subsequent int flex fields |
|
event_flex_string_1 |
First string flex field |
|
event_flex_string_2,..., event_flex_string_10 |
Subsequent string flex fields |
|
event_flex_date_1 |
First date flex field |
|
event_flex_date_2,..., event_flex_date_10 |
Subsequent date flex fields |
A row is inserted in this table for each choice returned as part of a decision and each key in the current session.
If the decision returns multiple choices, multiple rows will be inserted, with different choices (and scores) for each row.
If the session is identified by multiple keys, multiple rows will be inserted, with a different session key for each row.
Note: if the session has multiple keys, all the counts in the dashboards will be multiplied by the number of keys.
Oracle RTD logs only the choices that are returned as part of the decision, not the ones that are eligible but not returned.
More details about some of the SDDecisionLog fields:
is_random: The value is 'Y' in the following cases:
-
The decision was specified to select choices at random
-
Total score could not be calculated for any eligible choice in that decision (therefore it is truly a random decision as all the choices were randomly selected)
control_group: The value is 'Y' if session().isControlGroup() is true. This attribute is used to distinguish choices returned by a decision when control group is set to Y versus N. If control_group is 'Y' then the choices returned by the decision is random. If control_group is 'Y' then the is_random attribute is always 'Y'.
individual_score_n: This is the score for this performance goal, un-weighed, un-normalized, that is, not multiplied by the weight and not divided by the performance goal normalization factor. This is different from the Studio trace that shows the weighted, normalized score. The score is null if it cannot be computed.
individual_weight_n: This is the weight of this performance goal, as a number between 0 and 100.
total_score: This is the total score for this choice, computed as the sum of the weighted, normalized individual score. If a score cannot be determined for a required performance goal, the total score is null. If a score cannot be determined for a non-required performance goal, the total weight is normalized so that the other performance goals cover 100% of the weights.
score_rank: This is the rank of the choice after the selection function has been applied. Note that a choice for which a total score cannot be computed is assigned a random score and can therefore be ranked above another choice that has a real total score.
18.2.2 SDChoiceEventLog
| Column | Description |
|---|---|
|
session_key |
Key of session (customer identification) |
|
app_name_id |
ID of the application (Inline Service) |
|
version_id |
Version of the application. This gets incremented every time the Inline Service is redeployed |
|
choice_parent_id |
ID of the choice group to which this choice belongs |
|
choice_parent_id_name |
Name of the choice group to which this choice belongs. |
|
choice_id |
ID of the choice. |
|
choice_id_name |
Name of the choice |
|
channel_id |
Channel in which this event was made |
|
choice_event_id |
ID of the choice event |
|
happened |
Timestamp of the event based on application time (in seconds since January 1st 1970 UTC) |
|
day_of_month |
Day of the month of the event in format day_n or day_nn |
|
decision_instance_id |
Unique id representing the decision this event belongs to |
|
control_group |
Whether this event occurred in a control group decision or not ('Y' or 'N') |
|
segment_id |
ID of the decision segment this event occurred in |
|
segment_name |
Name of the decision segment this event occurred in |
|
hierarchy_id_1 |
ID of the first related choice or choice group in the hierarchy. |
|
hierarchy_id_2,..., hierarchy_id_10 |
IDs of subsequent related choices or choice groups in the hierarchy |
|
hierarchy_id_name_1 |
Name of the first related choice or choice group in the hierarchy. |
|
hierarchy_id_name_2,..., hierarchy_id_name_10 |
Names of subsequent related choices or choice groups in the hierarchy |
|
event_flex_float_1 |
First float flex field |
|
event_flex_float_2 ,..., event_flex_float_10 |
Subsequent float flex fields |
|
event_flex_int_1 |
First int flex field |
|
event_flex_int_2,..., event_flex_int_10 |
Subsequent int flex fields |
|
event_flex_string_1 |
First string flex field |
|
event_flex_string_2,..., event_flex_string_10 |
Subsequent string flex fields |
|
event_flex_date_1 |
First date flex field |
|
event_flex_date_2,..., event_flex_date_10 |
Subsequent date flex fields |
A row is inserted in this table for each event and each key in the current session. If the session is identified by multiple keys, multiple rows will be inserted, with a different session key for each row.
18.2.3 Partitioning
SDDS can be configured to use partitioning or not. If SDDS uses partitioning, the following partition tablespaces are created: SDLogging_TS0, SDLogging_TS1 and SDLogging_TS2.
If partitioning is enabled, the tables SDChoiceEventLog and SDDecisionLog are partitioned by the day_of_month column to have 10 (or 11) consecutive days in each partition tablespace.
18.2.4 Inline Service APIs
This section describes the APIs that implement the logging.
Note:
If you do not modify an existing Inline Service, no transaction logging will occur.
The logging occurs in three instances:
-
When a decision is made
-
When a base event occurs
-
When a positive event occurs ("closing the loop")
Typically (in web channels), the base event occurs during the advisor. But sometimes, the base event occurs in an informant (this is typical in call center channels where the base event occurs only when the sales or service agent tells the offer to the customer).
To tie base events and positive events to the decision, a unique decision_instance_id is generated for each decision. When logging the base or positive events, the decision_instance_id must be provided. Inline Service developers must modify their Inline Service logic and client code to be able to remember the decision_instance_id. This would typically be done by sending the decision_instance_id as choice attribute; to close the loop, the informant must pass the decision_instance_id as request attribute. The web site or call center client must remember this id between the advisor and informant calls.
The call to log the decision must be made in the decision post selection logic or the advisor asynchronous logic.
For the base event, if it occurs at the same time as the decision, the call to log the choice event must be made in the decision post selection logic or the advisor asynchronous logic. Note that if you log in decision post selection logic, the number of offers returned can be overridden later in the advisor.
For the base event, if it occurs in a subsequent informant, the call to log the choice event must be made in the informant logic or asynchronous logic.
For a positive event, the call to log the choice event must be made in the informant logic or asynchronous logic.
Note:
Oracle RTD provides distinct APIs to log decisions into SDDecisionLog and events into SDChoiceEventLog. The current choice performance dashboard and the Oracle RTD Base Marketing dashboards are based only on the data from SDChoiceEventLog, and work even if SDDecisionLog is turned off.
The data logged into SDDecisionLog is planned to be used in a future release, and is available if you want to build your own dashboards.
18.2.4.1 APIs
SDChoice (the parent class for all choices) has the following new methods:
-
public String getDecisionId();
-
public void setDecisionId(String decisionId);
-
public HashMap<String, Object> getChoiceEventLogValues();
-
public void setChoiceEventLogValue(String key, Object value);
-
public HashMap<String, Object> getDecisionLogValues();
-
public void setDecisionLogValue(String key, Object value);
In addition, the following methods are automatically generated for each choice class for each choice group:
-
public void recordDecisionLog(String eventName, String channel, String decisionId, HashMap<String, Object> decisionLogFields);
-
public void recordChoiceEventLog(String eventName, String channel, String decisionId, HashMap<String, Object> choiceeventLogFields, String decisionClassName);
In the APIs, decisionId is the name for the element described previously in this section as decision_instance_id. It is set on the choice when the decision is evaluated so you do not typically need to call the setter. But you call the getter to get the id so you can remember it when you close the loop.
The decisionLogFields hashmap contains the key value pairs for most of the columns logged as part of the decision.
The choiceEventLogFields hashmap contains the key value pairs for most of the columns logged as part of the choice event.
Decision log logging occurs when recordDecisionLog is called, where:
-
eventName is the name of the base event (required).
-
channel is the name of the channel (optional).
-
decisionLogFields is the decision log values hashmap (required).
Choice event log logging occurs when recordChoiceEventLog is called, where:
-
eventName is the name of the base or positive event (required).
-
channel is the name of the channel (optional).
-
choiceEventLogFields is the decision log values hashmap (required).
-
decisionClassName is the class name of the decision that was used for the base event of this choice, for instance "OfferDecision" or "RandomDecision"
The following table provides a detailed description of how each of the database columns are set for the decision log.
Note:
In the tables that follow, set values for the italicized names.
For example, for the API method for choice_parent_id, replace newValue with the value of your choice_parent_id.
| Column | Default Value | API Method |
|---|---|---|
|
session_key |
Set automatically |
None |
|
app_name_id |
Set automatically |
None |
|
version_id |
Set automatically |
None |
|
choice_parent_id |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("choice_parent_id", newValue) |
|
choice_parent_id_name |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("choice_parent_id_name", newValue) |
|
choice_id |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("choice_id", newValue) |
|
choice_id_name |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("choice_id_name", newValue) |
|
channel_id |
None |
choice.recordDecisionLog(event, channel, decision_instance_id, logValues) |
|
happened |
Set automatically |
Application.setTime(currentTimeMillis) [Note: happened stores the time as the number of seconds since January 1st 1970 UTC, but to override the current time, you must call Application.setTime with the number of milliseconds since January 1st 1970 UTC.] |
|
day_of_month |
Set automatically |
None |
|
decision_instance_id |
Generated automatically but you have to pass it as parameter to method |
choice.recordDecisionLog(event, channel, decision_instance_id, logValues) |
|
ip_name |
None |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("ip_name", newValue) |
|
decision_name |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("decision_name", newValue) |
|
control_group |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("control_group", newValue) |
|
is_random |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("is_random", newValue) |
|
segment_id |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("segment_id", newValue) |
|
segment_name |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("segment_name", newValue) |
|
perf_goal_1 |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("perf_goal_1", newValue) |
|
individual_score_1 |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("individual_score_1", newValue) |
|
individual_weight_1 |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("individual_weight_1", newValue) |
|
perf_goal_2 perf_goal_10 |
Set automatically |
<Similar to perf_goal_1, individual_score_1, individual_weight_1> |
|
total_score |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("total_score", newValue) |
|
score_rank |
Set automatically |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("score_rank", newValue) |
|
hierarchy_id_1 |
None |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("hierarchy_id_1", newValue) |
|
hierarchy_id_2,..., hierarchy_id_10 |
None |
<Similar to hierarchy_id_1> |
|
hierarchy_id_name_1 |
None |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("hierarchy_id_name_1", newValue) |
|
hierarchy_id_name_2,..., hierarchy_id_name_10 |
None |
<Similar to hierarchy_id_name_1> |
|
event_flex_float_1 |
None |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("event_flex_float_1", newValue) |
|
event_flex_float_2,..., event_flex_float_10 |
None |
<Similar to event_flex_float_1> |
|
event_flex_int_1 |
None |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("event_flex_int_1", newValue) |
|
event_flex_int_2,..., event_flex_int_10 |
None |
<Similar to event_flex_int_1> |
|
event_flex_string_1 |
None |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("event_flex_string_1", newValue) |
|
event_flex_string_2,..., event_flex_string_10 |
None |
<Similar to event_flex_string_1> |
|
event_flex_date_1 |
None |
choice.setDecisionLogValue("event_flex_date_1", newValue) |
|
event_flex_date_2,..., event_flex_date_10 |
None |
<Similar to event_flex_date_1> |
The following table provides a detailed description of how each of the database columns are set for the choice event log.
| Column | Default Value | API Method |
|---|---|---|
|
session_key |
Set automatically |
None |
|
app_name_id |
Set automatically |
None |
|
version_id |
Set automatically |
None |
|
choice_parent_id |
Set automatically |
None |
|
choice_parent_id_name |
Set automatically |
None |
|
choice_id |
Set automatically |
None |
|
choice_id_name |
Set automatically |
None |
|
channel_id |
None |
choice.recordChoiceEventLog(event, channel, decision_instance_id, logValues, decisionClassName) |
|
choice_event_id |
None |
choice.recordChoiceEventLog(event, channel, decision_instance_id, logValues, decisionClassName) |
|
happened |
Set automatically |
Application.setTime(currentTimeMillis) [Note: happened stores the time as the number of seconds since January 1st 1970 UTC, but to override the current time, you must call Application.setTime with the number of milliseconds since January 1st 1970 UTC.] |
|
day_of_month |
Set automatically |
None |
|
decision_instance_id |
None |
choice.recordChoiceEventLog(event, channel, decision_instance_id, logValues, decisionClassName) |
|
control_group |
Set automatically |
choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("control_group", newValue) |
|
segment_id |
Set automatically |
choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("segment_id", newValue) |
|
segment_name |
Set automatically |
choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("segment_name", newValue) |
|
hierarchy_id_1 |
None |
choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("hierarchy_id_1", newValue) |
|
hierarchy_id_2,..., hierarchy_id_10 |
None |
<Similar to hierarchy_id_1> |
|
hierarchy_id_name_1 |
None |
choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("hierarchy_id_name_1", newValue) |
|
hierarchy_id_name_2,..., hierarchy_id_name_10 |
None |
<Similar to hierarchy_id_name_1> |
|
event_flex_float_1 |
None |
choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("event_flex_float_1", newValue) |
|
event_flex_float_2,..., event_flex_float_10 |
None |
<Similar to event_flex_float_1> |
|
event_flex_int_1 |
None |
choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("event_flex_int_1", newValue) |
|
event_flex_int_2,..., event_flex_int_10 |
None |
<Similar to event_flex_int_1> |
|
event_flex_string_1 |
None |
choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("event_flex_string_1", newValue) |
|
event_flex_string_2,..., event_flex_string_10 |
None |
<Similar to event_flex_string_1> |
|
event_flex_date_1 |
None |
choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("event_flex_date_1", newValue) |
|
event_flex_date_2,..., event_flex_date_10 |
None |
<Similar to event_flex_date_1> |
Notes:
If you logged the decision for this decision_instance_id before logging the choice event, the control_group, segment_id, and segment_name will be the same as the decision's control_group, segment_id, and segment_name and cannot be overridden.
If you did not log the decision for this decision_instance_id before logging the choice event, the control_group value will be determined by the value of session().isControlGroup(), unless you override it by calling choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("control_group", newValue).
If you did not log the decision for this decision_instance_id before logging the choice event, the segment_id and segment_name value will be determined by evaluating the segments of the decision passed as decisionClassName when you called the recordChoiceEventLog method, unless you override it by calling both choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("segment_id", newValue) and choice.setChoiceEventLogValue("segment_name", newValue).
If you do override the segment_id and segment_name, make sure that you pass the right decisionClassName, which can be different in the control group.
18.2.4.2 Putting it All Together
Here is an example of decision logging, given an event named event, a channel named channel and an integration point name named integrationPointName, and setting a flex field:
creative.setDecisionLogValue("ip_name", integrationPointName);
creative.setDecisionLogValue("decision_flex_int_1", session().getCustomer().getCallsLast6Months());
creative.recordDecisionLog(event, channel, creative.getDecisionId(), creative.getDecisionLogValues());
Here is an example of choice event logging, given an event named event, a channel named channel and a decision instance id named decision_instance_id, and setting a flex field:
creative.setChoiceEventLogValue("event_flex_int_1", session().getCustomer().getCallsLast6Months());
creative.recordChoiceEventLog(event, channel, decision_instance_id, creative.getChoiceEventLogValues(), "CreativeDecision");
18.2.5 Report Schema
The following is a diagram of the report schema:
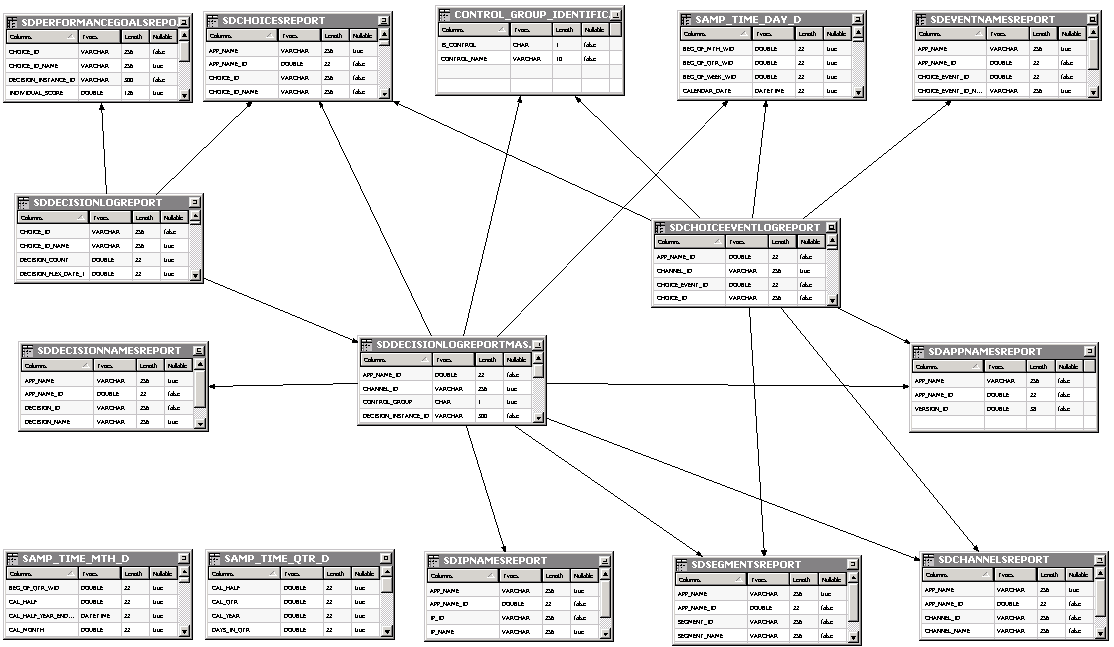
Description of the illustration image001.png
18.2.5.1 Description
The report schema is in a different schema than SDDS. It is a traditional star schema with three tables as facts: SDDECISIONLOGREPORTMASTER, SDDECISIONLOGREPORT and SDCHOICEEVENTLOGREPORT.
SDDECISIONLOGREPORTMASTER contains data that is different for each choice in a decision, for instance the performance goal weights and scores. SDDECISIONLOGREPORT contains data that is common for every choice returned as part of a decision.
The dimensions correspond to the main columns available in the fact tables. Additional dimensions can be created if, for instance, you want to slice and dice based on the flex fields.
The SAMP_TIME_DAY_D, SAMP_TIME_MTH_D and SAMP_TIME_QTR_D tables are standard BI tables for date representations (as in the SampleApp RPD).
18.2.5.2 Stored Procedures
The following stored procedures are created as part of the schema:
-
GEN_TIME: Generates additional data in the SAMP_TIME_DAY_D, SAMP_TIME_MTH_D and SAMP_TIME_QTR_D tables. If the time intervals covered by the initial data in these tables are not enough, call this stored procedure to specify a new time interval. Use I_START_DATE and I_END_DATE to specify the interval, for instance, Gen_Time (TO_DATE ('01-JAN-2013','DD-MON-YYYY'), TO_DATE ('31-DEC-2025','DD-MON-YYYY')).
-
SDDeleteAllData: Deletes all report data (facts and dimensions, but not the SAMP_TIME_DAY_D, SAMP_TIME_MTH_D and SAMP_TIME_QTR_D tables)
-
SDPopulateReportTables: Populates the report schema from the transactional log schema. Typically a customer would call this daily for the previous day, passing the day as argument day_of_month with a value such as 'day_1' or 'day31'. This stored procedure moves the data from one to the other: the rows in the transactional log schema that are moved will be deleted; for example:
SDPopulateReportTables('day_1');
Note:
By default, OBIEE caches information for performance reasons. In order to see the new data that was populated by SDPopulateReportTables in the OBIEE reports, you must clear the OBIEE RPD and presentation layer caches.
18.2.5.3 Functions
The following function is created as part of the schema:
-
NormalizedEventName: The RPD contains measures based on a marketing scenario where choices go through 3 stages: presented, interested and converted. This function allows for mapping Inline Service event names to these 3 pre-defined events. By default, "Presented" and "Delivered" are allowed as the base presented event, "Interested" and "Clicked" are allowed as the positive interested event and "Converted" and "Purchased" are allowed as the positive converted event. You can modify this function if your inline service uses different event names.
18.2.6 OBIEE Integration
You can do your own reporting on top of the report schema, or you can use the OBIEE integration provided with Oracle RTD.
The OBIEE integration consists of:
-
A RPD that contains physical/model/presentation layer for the report schema. This RPD also contains marketing specific measures such as acceptance rate and conversion rate,
-
A web catalog that contains one out of the box dashboard for marketing specific solutions. It also contains dashboards that provide out of the box integration with the Base Marketing Oracle RTD Apps reference application.
18.2.6.1 RPD
The RPD contains two entries in the physical layer, one containing the model snapshot physical schema and one containing the decision analytics report schema.
Two variables are used to define the connection to the report schema: RTD_REPORT_DSN and RTD_REPORT_USERNAME.
18.2.6.2 Web Catalog
The web catalog contains two folders, one for "Decision Analytics" (generic) and one for "Decision Analytics - Base Marketing".
18.2.6.3 Compute Functions
The Choice Performance Dashboard in OBIEE makes use of a number of compute functions, as defined in this section.
IFNULL(FILTER("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Event Count" USING "RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Events"."Normalized Event" = 'Presented'), 0)
IFNULL(FILTER("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Event Count" USING ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Events"."Normalized Event" ='Presented') AND ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Control Group" ='Y')), 0)
IFNULL(FILTER("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Event Count" USING ( ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Events"."Normalized Event" ='Presented') AND ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Control Group" ='N'))), 0)
IFNULL(FILTER("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Event Count" USING "RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Events"."Normalized Event" = 'Interested'), 0)
IFNULL(FILTER("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Event Count" USING ( ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Events"."Normalized Event" ='Interested') AND ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Control Group" ='Y'))), 0)
IFNULL(FILTER("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Event Count" USING ( ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Events"."Normalized Event" ='Interested') AND ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Control Group" ='N'))), 0)
IFNULL(FILTER("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Event Count" USING "RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Events"."Normalized Event" = 'Converted'), 0)
IFNULL(FILTER("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Event Count" USING ( ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Events"."Normalized Event" ='Converted') AND ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Control Group" ='Y'))), 0)
IFNULL(FILTER("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Event Count" USING ( ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Events"."Normalized Event" ='Converted') AND ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Control Group" ='N'))), 0)
IFNULL("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Interested Count for All" *100/"RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Presented Count for All", 0)
IFNULL("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Interested Count for Control" *100/"RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Presented Count for Control", 0)
IFNULL("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Interested Count for Test" k,*100/"RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Presented Count for Test", 0)
IFNULL("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Converted Count for All" *100.00/"RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Presented Count for All", 0)
IFNULL("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Converted Count for Control" *100.00/"RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Presented Count for Control", 0)
IFNULL("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Converted Count for Test" *100.00/"RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Presented Count for Test", 0)
Response lift is defined by the following function:
IFNULL((("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Response Rate for Test") - ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Response Rate for Control")) *100.00 /"RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Response Rate for Control", 0)
Conversion lift is defined by the following function:
IFNULL((("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Conversion Rate for Test") - ("RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Conversion Rate for Control")) *100.00 /"RTD DM Report Schema"."Choice Log"."Conversion Rate for Control", 0)
18.3 Installation
To enable transactional logging and decision analytics, you must perform a number of additional operations after you have installed Oracle RTD.
This section contains the following topics:
18.3.1 Post Oracle RTD-Installation Steps
After a regular Oracle RTD installation, you must perform the following operations:
Create the report schema, for instance, by running these commands as SYS to create a schema called rtd_rep:
-
CREATE USER rtd_rep IDENTIFIED BY welcome1 DEFAULT TABLESPACE users TEMPORARY TABLESPACE temp QUOTA UNLIMITED ON users;
-
GRANT CREATE VIEW, CONNECT, RESOURCE TO rtd_rep;
Additionally you must grant permissions between your SDDS and report schema. Assuming the names rtd for your SDDS schema and rtd_rep for your report schema, run the following commands as SYS:
-
GRANT SELECT ON rtd.SDStrings TO rtd_rep;
-
GRANT SELECT,DELETE ON rtd.SDChoiceEventLog TO rtd_rep;
-
GRANT SELECT,DELETE ON rtd.SDDecisionLog TO rtd_rep;
-
GRANT EXECUTE ON rtd.SDTruncateLogTablesPartition TO rtd_rep;
-
GRANT CREATE materialized view to rtd_rep;
Then you can initialize the report schema using the following command in <install_dir>\RTD\scripts\sql\Oracle:
InitReportDB sdroot host port db runtimeReportDBUser rtdUser [runtimeReportDBPassword]
For example:
InitReportDB C:\OracleBI\RTD localhost 1521 orcl rtd_rep rtd overture
(Oracle RTD supports this command on both Windows and Linux).
Review the contents of SAMP_TIME_DAY_D, SAMP_TIME_MTH_D and SAMP_TIME_QTR_D tables and call GEN_TIME if necessary.
The default population of these tables is from Jan-2013 to Dec-2025 (that is, Call Gen_Time (TO_DATE ('01-JAN-2013','DD-MON-YYYY'), TO_DATE ('31-DEC-2025','DD-MON-YYYY'))
You are now ready to deploy and use an Inline Service that uses this feature. The CrossSellLogging Inline Service in the examples directory is pre-configured for that.
The CrossSellLogging Inline Service is based on the CrossSell Inline Service with modifications for performing logging to the newly introduced Decision Analytics tables SDDecisionLog and SDChoiceEventLog, during the asynchronous logic of the advisor and in the logic of the loop closing informant.
18.3.2 OBIEE Steps
You must install OBIEE (during this operation, you do not need to install Oracle RTD and Essbase).
Note:
The procedures described in this section require that you edit these files:
-
DecisionAnalytics.rpd, which is located in the Oracle RTD Platform zip file, in the folder OracleBI\RTD\Analytics.
-
Decision Analytics.catalog, which is located in the Oracle RTD Platform zip file, in the folder OracleBI\RTD\Analytics.
-
Decision Analytics - Base Marketing.catalog, which available in the Oracle RTD Applications zip file, in the folder RTD_Apps_3xxx\software\Oracle Real-Time Decisions Base Application\Analytics.
18.3.2.1 Update Repository (RPD)
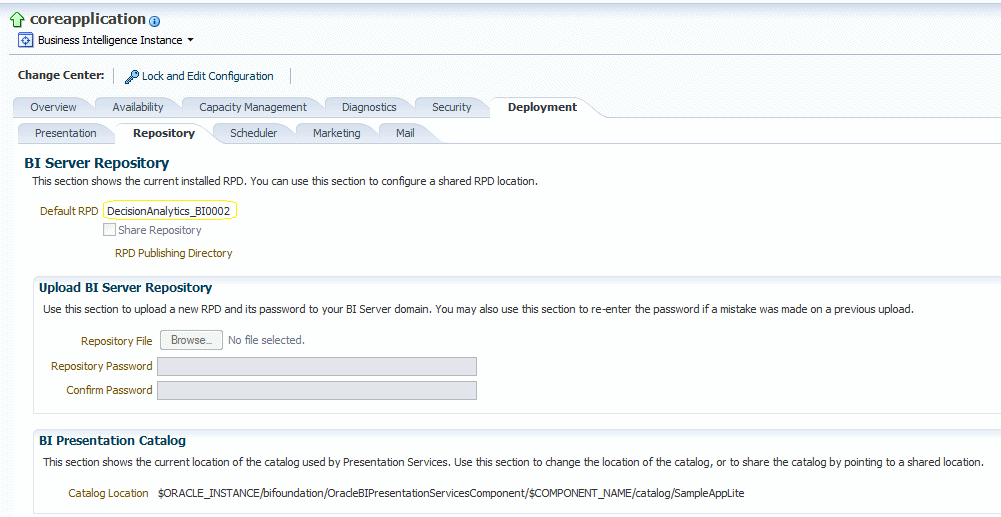
You need to update the repository to ensure that the custom measures and other components upon which the decision analytics dashboards depend are present. To achieve this, you must perform the following steps:
-
Login to the OBIEE WebLogic EM console.
-
In the left hand pane, select the coreapplication node under Root_Domain >Business Intelligence.
-
In the right hand pane, select the tabs Deployment > Repository.
-
Click Lock and Edit Configuration to make the changes.
-
Under the Upload BI Server Repository section, click Browse and provide the path to the RPD file to be used for Decision Analytics.
-
Provide the repository password (Admin123 for the shipped DecisionAnalytics.rpd, by default).
-
Click the Apply button.
The Default RPD name changes, for example, from DecisionAnalytics _001 to DecisionAnalytics_002.
-
Click Activate Changes to effect the change.
After the change is effected, a new link is available indicating Restart to apply recent changes. Click the link, and in the overview tab restart all the services by clicking the restart button.
Configure the Connection Pool for the RPD
To configure the connection pool for the RPD, perform the following steps:
-
In WebLogic Console, add a user Administrator and give that user access to the group BIAdministrators (refer to WebLogic manuals on provisioning a new user, such as Oracle Fusion Middleware Securing Resources Using Roles and Policies for Oracle WebLogic Server).
-
If the OBIEE has been installed on Linux/Unix, install the OBIEE Developer Client Tools 11.1.1.7 on a Windows platform and set up a DSN to the OBIEE server. This step is not required if OBIEE is installed on the Windows platform. Note that the BI Administration tool is available only on the Windows platform.
-
Start the BI Administration from the Start Menu > Program Files > Oracle Business Intelligence.
-
Select File > Open > Online and provide the Repository and Administrator password.
-
Under the Physical Layer, select the properties for Reporting DB under the node RTD DM Report Schema.
You can set the password for the Reporting DB here. Also you can see that the DATASOURCE and USERNAME is being picked up from the variables RTD_REPORT_DSN and RTD_REPORT_USERNAME respectively.
The variables RTD_REPORT_DSN and RTD_REPORT_USERNAME can be edited from under Manage-> Variables.
-
Check in all changes via File -> Check In Changes.
-
Save via File -> Save
It may be necessary to restart the BI Server if there were any changes made. Restart the services from EM or from the command line (opmnctl).
18.3.2.2 Update Web Catalog
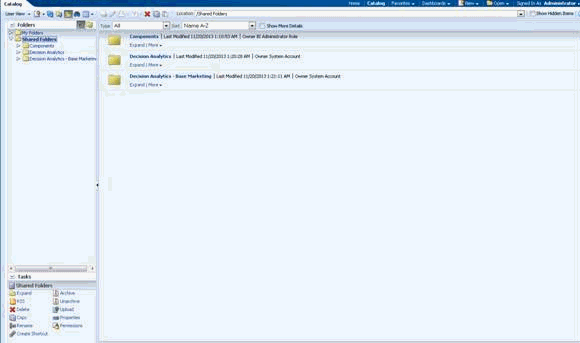
To update the catalog to include dashboards and other elements for Decision Analytics, perform the following steps:
-
Login to OBIEE.
-
Click catalog on the top right hand corner.
-
In the Folders pane on the left hand side, select the Shared Folders.
-
Under the tasks pane on the left hand side, select the unarchive option and select the archive for Decision Analytics folder (Decision Analytics.catalog) and Decision Analytics - Base Marketing folder (Decision Analytics - Base Marketing.catalog).
18.4 Customization
Oracle RTD logs data into both the SDDecisionLog and SDChoiceEventLog tables. Currently, the choice performance dashboard is based on the data from SDChoiceEventLog.
18.4.1 Adding Flex Fields to the Dashboard
You can customize the dashboard by adding and removing flex fields. There are 40 flex fields (10 each for flex field of data type int, float, string, and date) in each of the SDDecisionLog and SDChoiceEventLog tables where data can be logged to from within an Inline Service by programmatic APIs
For example:
choices.get(i).setChoiceEventLogValue("event_flex_string_1",session().getCustomer().getMaritalStatus());
This data can subsequently be used to slice and dice from within OBIEE.
The following example shows how to add a flex field.
Assume you have logged the Marital Status to column EVENT_FLEX_STRING_1 in SDChoiceEventLog.
You can add this flex field in the dashboard (in this case, Choice Performance Dashboard) by performing the following steps:
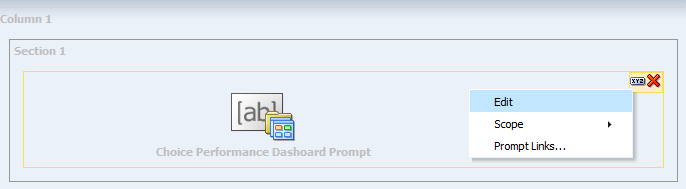
-
Click the Edit button of the Choice Performance Dashboard.
-
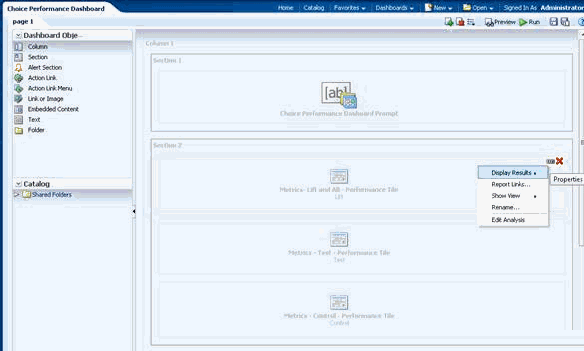
In Section 1 which defines the dashboard prompts, click the Properties button (XYZ in the following image) on the top right hand corner and select Edit.
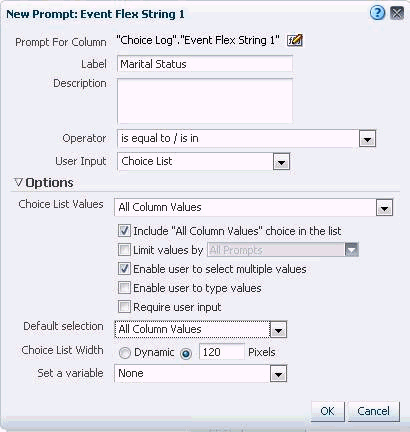
-
Click the button to select adding a column prompt.
-
Select the column to add, in this case Choice Log to Event Flex String 1.
-
Give a relevant label, for example, Marital Status, and select relevant options.
The best practice is to allow users to make multiple selections and to set the default value as All Column Values.
-
Click OK to finish adding the column prompt.
-
Return to Editing the Choice Performance Dashboard.
-
In Section 2 there are 3 views defined. For each view, click the Properties button on the top right hand corner and select Edit Analysis.
-
Go to criteria tab of the view and under filters pane, click the button, select more columns and select the column Choice Log -> Event Flex String 1.
-
In the New Filter dialog, select is prompted as the operator and click OK.
-
Repeat the process to add the flex string to the other two views in section 2.
Repeat the process to add the flex string in Section 3 and 4 as well.
Now, the dashboard responds to the column prompt Marital Status in all sections and views defined in within it.