Understanding External Search/Match
External Search/Match functionality looks and feels much like the standard Search/Match that resides in Campus Solutions (CS). However, External Search/Match integrates with any external system and enables your institution to perform searches within that external system and import records into Campus Community. The goal is to provide complete and meaningful lists of potential duplicate IDs in your entire environment, including IDs that reside outside of the CS database.
External Search/Match executes these searches with the help of two delivered web service operations. You can then use web services to import a matching constituent that does not exist inside the CS database. Web services send outbound search requests from the system of record to an external system and also receive inbound responses coming directly from the external system. As enterprise architectures grow more complex and CS may no longer be the sole source of person data entry and maintenance, searching against external systems ensures that no duplicates exist in your environment.
As with Search/Match, you can perform three types of searches with External Search/Match: applicant, person, and organization. However, the system performs applicant and organizational searches only using Search/Match at this time; you are able to search for only people when using External Search/Match as part of integration with an external system. External Search/Match allows you to search for people simultaneously against the CS database (using the current Search/Match), as well as directly inside an external system; the process displays the combined results inside CS search results pages. If your institution integrates External Search/Match with an external system that allows advanced searching capabilities (for example, External Search/Match is integrated with a data hub that has fuzzy matching capabilities), this extra search logic can be leveraged and the results returned to you contain a richer set of matching candidates.
External Search/Match reuses the same setup parameters and security configuration used for standard Search/Match functionality.
You can perform either an online or an automatic search using External Search/Match.
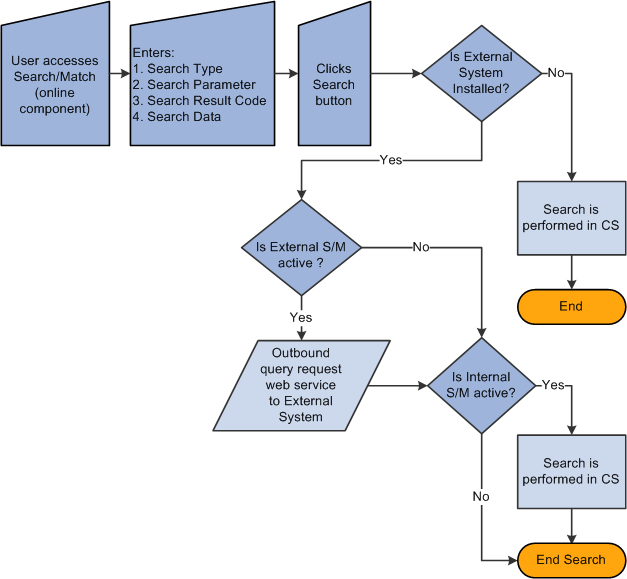
To perform an online search:
Access the Search/Match Integrated component.
Select a Search Type, Search Parameter, Search Result Code, and other search fields as appropriate; this step is the same as the existing Search/Match.
After populating some or all of these fields with search data, click the Search or Selective Search button.
The system validates the external system data settings and determines whether the institution is configured for Search/Match, External Search/Match, or both. This determination causes the system to then perform the search inside the CS database and/or outside to an external system.
If the system determines that an external search should occur, then it generates the outbound search request (Match Request). That search request contains all information known about the search. The XML message might contain the search parameters used, the search fields and their values, and so on.
If your institution integrates with external systems using the Higher Education Constituent Hub (HECH), before the external system can understand the search information contained in the message, search fields must be mapped to fields contained inside the external system. This occurs inside the transformation layer. The external system can then interpret the search data and perform its own search using its search engine, taking advantage of all its search capabilities. If your institution integrates with HCM as an external system, this mapping is not required.
Image: Online search business processdiagramsSearch/Match online search
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Online search business processdiagramsSearch/Match online search. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
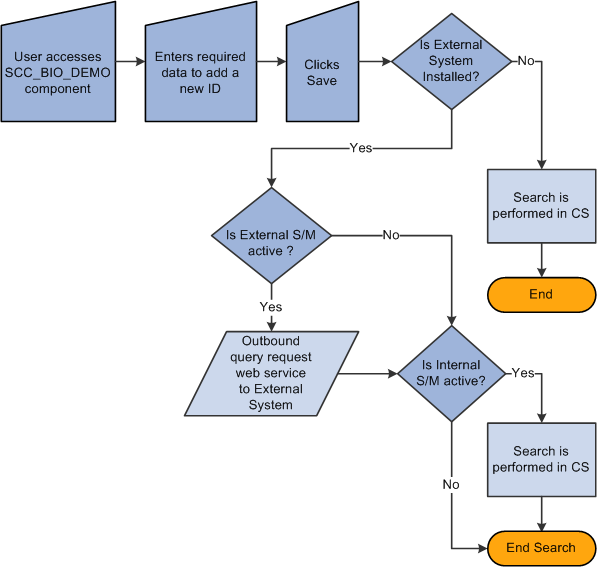
To perform an automatic search, all of the above information applies. When you enter data to create an EmplID on a CS page and then click the Save button, the system invokes additional logic to validate the external data integration settings and then triggers the Match Request.
Image: Automatic search business processdiagramsSearch/Match automatic search
This example illustrates the fields and controls on the Automatic search business processdiagramsSearch/Match automatic search. You can find definitions for the fields and controls later on this page.
After the external system search process completes its search for potential matches, the result data is sent to CS via the response message (Match Response). When you perform a search that triggers both the Internal Search/Match and External Search/Match processes, the system may not find results on the same search order number. The rule for External Search/Match functionality is to display all search results, beginning with the lowest search order number obtained (the most restrictive search rule where matching EmplIDs are found). The search order is determined by the Results Engine.
Before it can display your search results, the Results Engine receives the results from both the Internal Search/Match and External Search/Match processes. The engine evaluates the search order number from each system's matching candidates.
If Internal Search/Match found matching candidates with a lower search order number than the external system, then the Results Engine displays the results from Internal Search/Match; the lowest search order indicates that it was a more restrictive search.
If the opposite is true, then the Results Engine displays the results found from the external search.
If both searches retrieve results on the same search order number, the Results Engine combines the search results into a single display for the user.
Regardless of whether you invoke Internal Search/Match, External Search/Match, or both, the search results appear on the Integrated Search Results page. This page contains many of the same fields as the Search Results page. In addition, the Results tab contains optional columns such as the external system ID (referred to as the Universal ID), the EmplID (when it exists) and the Score% (or the weight) of each matching candidate found if the external system provides that information. The Results tab uses the same masking configuration that is in place for Search/Match.
When External Search/Match finds a matching candidate that does not exist inside the internal system (the matching candidate is not tied to an EmplID), you can still use the Detail link to view more information about the constituent. This case triggers an outbound web service request for more information (Fetch Request). The external system receives the information and returns detailed constituent information inside its response web service (Fetch Response). The system then displays (but does not store) the detailed information inside a Detail page that enables you to review the data.
If you determine that the matching candidate is the person you are looking for, you can import the person record from the Integrated Search Results page. When you click the Import button, the system generates a Fetch Request (the same web service used to retrieve more details about the constituent) and uses the information contained in the Fetch Response to create the new person record inside the CS database. After you generate the person's EmplID, you can then use it to perform subsequent transactions.
See the following documents on My Oracle Support:
PeopleSoft Campus Solutions Constituent Web Services Developer's Guide
Implementing External Search/Match between CS and HCM
Integrating Campus Solutions with Human Capital Management