Hive tables contain the data for the Data Processing workflows.
When processed, each Hive table results in the creation of a BDD data set, and that data set contains records from the Hive table. Note that a Hive table must contain at least one record in order for it to be processed. That is, Data Processing generates an error when an empty Hive table is found, and no data set is created for that empty table.
Starting workflows
- A user in Studio invokes an operation that creates a new Hive table. After the Hive table is created, Studio starts the Data Processing process on that table.
- The DP CLI (Command Line Interface) utility is run.
The DP CLI, when run either manually or from a cron job, invokes the BDD Hive Table Detector, which can find a Hive table that does not already exist in the DataSet Inventory. A Data Processing workflow is then run on the table. For details on running the DP CLI, see DP Command Line Interface Utility.
New Hive table workflow and diagram
Both Studio and the DP CLI can be configured to launch a Data Processing workflow that does not use the Data Enrichment modules. The following high-level diagram shows a workflow in which the Data Enrichment modules are run:
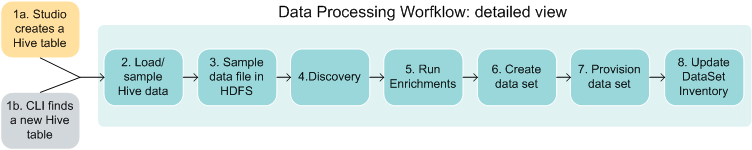
- The workflow is started for a single Hive table by Studio or by the DP CLI.
- An Oozie job is started, which in turn assigns the workflow to a Spark worker. Data is loaded from the Hive table's data files. The total number of rows in the table is counted, the data sampled, and a primary key is added. The number of processed (sampled) records is specified in the Studio or DP CLI configuration.
- The data from step 2 is written to an Avro file in HDFS. This file will remain in HDFS as long as the associated data set exists.
- The data set schema and metadata are discovered. This includes discovering the data type of each column, such as long, geocode, and so on. (The DataSet Inventory is also updated with the discovered metadata. If the DataSet Inventory did not exist, it is created at this point.)
- The Data Enrichment modules are run. A list of recommended enrichments is generated based on the results of the discovery process. The data is enriched using the recommended enrichments. If running enrichments is disabled in the configuration, then this step is skipped.
- The data set is created in the Dgraph, using settings from steps 4 and 5. The DataSet Inventory is also updated to include metadata for the new data set.
- The data set is provisioned (that is, HDFS files are written for ingest) and the Dgraph HDFS Agent is notified to pick up the HDFS files, which are sent to the Bulk Load Interface for ingesting into the Dgraph.
- After provisioning has finished, the Dgraph HDFS Agent updates the ingestStatus attribute of the DataSet Inventory with the final status of the provisioning (ingest) operation.
Handling of updated Hive tables
Existing BDD data sets are not updated if their Hive source tables are updated. For example, assume that a data set has been created from a specific Hive table. If that Hive table is updated with new data, the associated BDD data set is not changed. This means that now the BDD data set is not in synch with its Hive source table.
- From Studio, delete the data set. As part of the delete operation, the Data Processing workflow adds the skipAutoProvisioning property to the Hive table from which the data set was sourced. This property will prevent Data Processing from processing the table.
- From the Hive environment, remove the skipAutoProvisioning property from the Hive table.
- Run the CLI, which will launch a Data Processing workflow for the table.
Data Processing creates a new data set representing the newer version of the Hive table.
Handling of deleted Hive tables
BDD will never delete a Hive table, even if the associated BDD data set has been deleted from Studio. However, it is possible for a Hive administrator to delete a Hive table, even if a BDD data set has been created from that table. In this case, the BDD data set is not automatically deleted and will still be viewable in Studio. (A data set whose Hive source table was deleted is called an orphaned data set.)
The next time that the DP CLI runs, it detects the orphaned data set and runs a Data Processing job that deletes the data set.
Handling of empty Hive tables
Data Processing does not handle empty Hive tables. Instead, Data Processing throws an EmptyHiveTableException when running against an empty Hive table. This causes the DP Oozie job to fail.
Deletion of Studio projects
When a Studio user deletes a project, Data Processing is called and it will delete the transformed data sets in the project. However, it will not delete the data sets which have not been transformed.
