When the DSR receives a Request message from a downstream peer, it performs the following functions:
- Verifies that the DSR has not previously processed the message (message loop detection) by looking for one or more identities in the message's Route-Record AVPs of the message.
- Searches the Peer Routing Rules based on the contents of the received message to see where to route the message. A Peer Routing Rule can be associated with a Route List that contains a prioritized list of Peer Nodes used to route a Request message.
- Selects a Peer Node from the Route List that is available for routing the message based on Route Group priorities and Peer Node weights.
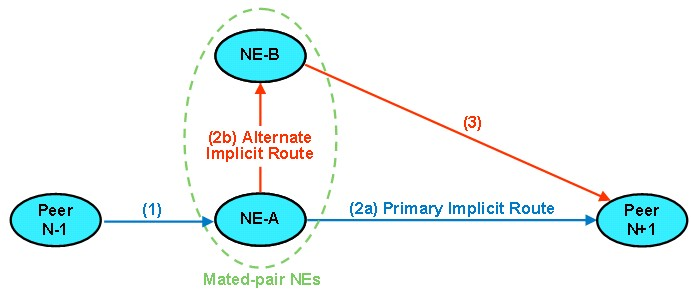
If a message does not match a Peer Routing Rule and contains a Destination-Host AVP that is associated with a Peer Node, then the DSR invokes Implicit Routing to the Peer Node if the Peer Node Operational Status is Available.
Diameter configuration for Implicit Routing:
- Configure each Peer Node.
- Configure Peer Route Tables.
- Configure Route Groups.
- Configure Route Lists.
- Edit Peer Route Tables and configure Peer Routing Rules in each Peer Route Table.
Peer Routing Rules are primarily intended for Realm-based routing and intra-network routing to non-Peer Nodes. For messages that are addressed to a Peer Node using the Destination-Host AVP, it is not necessary to put explicit Destination-Host entries in a Peer Routing Rule.
Figure 1 illustrates implicit routing in the DSR.
DSR Implicit Routing