Verify that the SAN host communicates with the Oracle FS System LUNs after installing the FSPM software.
Note: In this section, all references to GUI screens refer to the layout of the Oracle FS System Manager (GUI) version 6.1. Other GUI versions are organized differently, but all versions offer equivalent functionality. Refer to the Administrator’s Guide for details on how to access the features in older versions of the GUI.
To use the Oracle FS System Manager (GUI) to validate the LUN configuration, perform these steps:
- In the GUI, navigate to .
- Verify that the individual entries for the host ports are grouped under the host name.Examples of before and after FSPM installation are shown in the following illustrations.
Figure 1: Host ports before FSPM installation
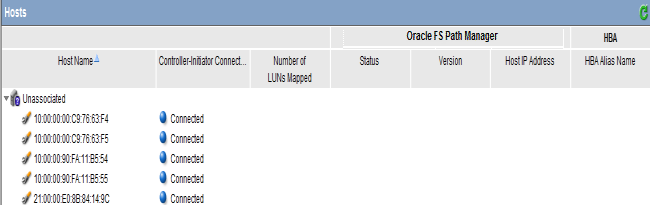
Figure 2: Host ports after FSPM installation
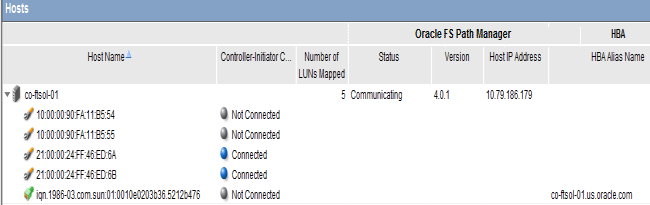
Note:The following Oracle FSPM Status and Controller-Initiator Connectivity messages can be displayed on the Hosts page:
- FSPM Status
- Communicating: The host control path is logged in to the Pilot. Note: Communicating status is required for the FSPM Control Path to report path status and use the Oracle FS System to collect FSPM diagnostic logs.
- Not Registered: A Control Path from an FSPM with this name has never logged in to the Pilot.
- Not Communicating: The FSPM host Control Path was logged in to the Pilot but is not now logged in to the Pilot.
- Controller-Initiator Connectivity
- Connected: The host SAN connection is logged in to a Controller on the Oracle FS System.
- Not connected: The host SAN connection is not logged in to a Controller on the Oracle FS System.
- Create new LUNs on the Oracle FS System for this host and set up mappings of LUNs to the new host entry.
-
Verify that all mapped LUNs are available as drives on the host.
If the LUNs do not appear automatically on the host within one or two minutes, run the following command:
devfsadm
.The LUNs are displayed as drives on the host. If the drives do not appear on the host after running the devfsadm command, restart the host. -
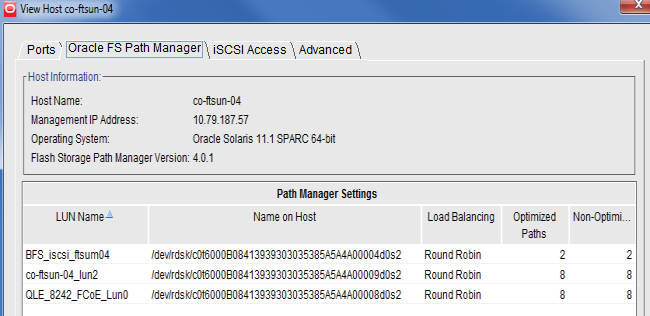
Select the name of the new host and then select to verify the installed FSPM version information. The operating system and FSPM versions shown in the illustration can differ from your configuration.
Figure 3: Detailed FSPM information
-
Review the LUN names on the Oracle FS System under the LUN Name column.
The column titled LUN Name on Host shows the name that Oracle Solaris I/O multipathing features has allocated to the LUN device on the host.Note: After you map a LUN to the host, it can take two or three minutes for FSPM to make the LUN accessible at the host and report the LUN name and other information to the GUI. You might need to refresh the GUI screen to see the information when it is reported, as there can be a delay between the time the configuration change was made and when the change is displayed on the GUI.
- Review the load balancing algorithm being used for each LUN to determine if you need to change the current load balancing setting.
- Review the numbers of optimized and non-optimized paths currently reported by FSPM under Optimized Paths and Non-Optimized Paths.
-
Navigate to and verify that the host and LUN connections are as expected.
The Host-LUN Mapping tab should display the LUNs that are mapped to the host and information about the LUN. Verify that the following information is displayed:
- Each LUN name as allocated by Oracle Solaris on the host.
- The LUN numbers used to make the LUN visible to the host..
- An indication whether each SAN port on the host has a connection to at least one port on the Controller.