| Oracle® Health Sciences Empirica Signal Installation Guide Release 8.0 E50114-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
| Oracle® Health Sciences Empirica Signal Installation Guide Release 8.0 E50114-02 |
|
 Previous |
 Next |
This chapter includes the following topics:
You must have access to the following types of accounts:
A user account that allows the user to start and stop the Oracle database.
This account should not have sudo privileges.
This document refers to this user account as the non-privileged user account.
A user account with sudo privileges. This user executes certain steps as root.
This document refers to this user account as the privileged user account.
You must have access to the following types of user accounts:
A user account that allows the user to start and stop the WebLogic server.
This account should not have sudo privileges.
This document refers to this user account as the non-privileged user account.
Unless otherwise specified in this document, the non-privileged user should perform all activities.
A user account that has sudo privileges. This user executes certain steps as root.
This document refers to this user account as the privileged user account.
This section discusses the requirements and assumptions for the Linux accounts.
This guide provides steps for setting several system-wide environment variables. This guide sets the following system-wide variables:
ORACLE_HOME
ORACLE_BASE
ORACLE_SID
PATH
|
Note: This guide assumes that the values of these variables are not overridden by user configuration files, such as.login, .profile, .bashrc, and .cshrc. |
Perform this step as the non-privileged user on the application server.
Edit the ~/.login file, and add the following command to the file:
umask 027
The command sets the default file creation umask, so that by default, files you create give read-only access to other users in your group and no permissions to users outside the group.
This section discusses the steps to unpack the Signal installation files.
Choose an installation directory that is on the application server and that is accessible to the WebLogic software, such as /u01/stage. The installation directory stores Empirica Signal components during the installation process.
Log in to the application server as the non-privileged user.
Using a tool such as the tar command, unpack the Signal_Install.tar.gz to the /u01/stage directory. For example, use the following command:
$ cd /u01/stage/
$ tar xvf /u01/stage/Signal_Install.tar.gz
The /u01/stage/Signal_Install directory is created.
|
Note: In this document,<INSTALL_DIR> refers to the folder created in this step, such as /u01/stage/Signal_Install. This document assumes that you are installing to this directory. |
Using a tool such as unzip, unpack the Signal-8_0_0_0_XXX.zip file into the <INSTALL_DIR>/Signal directory.
Execute the following command:
$ chmod u+x <INSTALL_DIR>/Signal/WEB-INF/classes/MGPS
Unpack the Database.zip file:
Create the following directory:
/u01/stage/Database
Using a tool such as unzip, unpack the contents of the Database.zip file into the directory.
This section includes the following topics:
Perform these steps using the non-privileged user account.
On the application server, open the tnsnames.ora file, located in the following directory:
<ORACLE_HOME>/network/admin/
If the file does not exist, create it.
Add an entry that points to the database, using the information found in the TNSNAMES.ORA file on the database server. For more information, see Information to collect before you begin.
In this procedure, you edit configuration scripts, which set environment variables for the command shells you use. You must log out and log in again for the changes you make in this section to take effect.
In this section, you configure environment variables for your application server using your privileged account and using sudo. This section requires you to edit files, using commands such as the following. The first command logs you in as root. If you are prompted for your password after typing this command, type your password, not the password of root.
$ sudo su - root# vi <file_name># exit
To set environment variables:
Edit the /etc/profile file as follows. This change sets environment variables for sh and bash command shells.
Add the following lines to the file.
For the values in the first two lines, use information about your Oracle client installation.
ORACLE_BASE=/u01/app/oracle
ORACLE_HOME=/u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0
ORACLE_SID=<server_sid>
NLS_LANG=AMERICAN_AMERICA.AL32UTF8
export ORACLE_BASE ORACLE_HOME ORACLE_SID NLS_LANG
Add the bin directory of your Oracle client installation to the PATH variable. For example, add the following line as the last line where the PATH variable is set:
export PATH=$ORACLE_HOME/bin:$PATH
Edit the /etc/csh.login file. This change sets environment variables for csh and tcsh command shells.
Add the following lines to the file.
For the values in the first two lines, use information about your Oracle client installation.
setenv ORACLE_BASE /u01/app/oraclesetenv ORACLE_HOME /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0setenv ORACLE_SID <server_sid>setenv NLS_LANG AMERICAN_AMERICA.AL32UTF8
Add the bin directory of your Oracle client installation to the PATH variable. For example, add the following line as the last line where the PATH variable is set:
setenv PATH ${ORACLE_HOME}/bin:${PATH}
Perform these steps as the non-privileged user on the application server.
In a command shell, use the following command to navigate to the /u01/stage/Database directory:
$ cd /u01/stage/Database
Review the 1_create_webvdme_tablespaces_linux.sql file:
Edit the 1_create_webvdme_tablespaces_linux.sql file. For example:
$ vi 1_create_webvdme_tablespaces_linux.sql
To create the data files in a location other than the default location of your database, specify the alternate location in the datafile_path variable. The path must end in a forward slash (/). For example:
DEFINE datafile_path = '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/<sid>/'
Save the file, and exit the vi editor.
Create the application tablespace:
Execute the 1_create_webvdme_tablespaces_linux.sql script from the Oracle system account.
For example, type:
$ sqlplus system@<TNS_Name> @1_create_webvdme_tablespaces_linux.sql
When prompted, type the Oracle system account password.
Create the application Oracle user and schema:
Type the following text:
$ sqlplus sys@<TNS_Name> as sysdba @2_create_webvdme_oracle_user.sql
When prompted, type the Oracle sys account password.
When prompted a second time, create a password for the Empirica Signal database account. Retype the password to verify it.
|
Note: Remember this password for later in this procedure. |
When prompted, create a password for the empirica_admin account.
Retype the password to verify it.
|
Note: Remember this password. |
Populate the application schema:
Execute the 3_create_all SQL script from the Empirica Signal database account (not the sys or system accounts). For example:
$ sqlplus webvdme@<TNS_name> @3_create_all.sql
When prompted, type the webvdme database account password that you created in the previous step.
In this optional procedure, you perform the following steps to prepare the Empirica Signal software for using the Topics feature:
Create the Oracle tablespace and account.
Supply the contents of the account.
To set up the Sample Topic Workflow Oracle account:
In a command shell, use the following command to navigate to the /u01/stage/Database directory:
$ cd /u01/stage/Database
Create the Topic Workflow account:
In a command shell, execute the create_topics_oracle_user.sql SQL script from the system account. For example:
$ sqlplus system@<TNS_name> @create_topics_oracle_user.sql
Type the Oracle system account password.
When prompted a second time, create a password for the Topic Workflow database account. Retype the password to verify it.
|
Note: Remember this password. |
Create sample topics tables:
In a command shell, execute the create_sample_topics_tables.sql SQL script from the TOPIC_WORKFLOW database account created in step 2. For example:
$ sqlplus topic_workflow@<TNS_name> @create_sample_topics_tables.sql
You are prompted to type a password.
Type the TOPIC_WORKFLOW database account password that you specified in step 2.
Create sample topics:
In a command shell, execute the populate_sample_topics_tables.sql SQL script from the TOPIC_WORKFLOW database account in step 2. For example:
$ sqlplus topic_workflow@<TNS_name> @populate_sample_topics_tables.sql
You are prompted to type a password.
Type the TOPIC_WORKFLOW database account password that you specified in step 2.
In a command shell, use the following command to navigate to the /u01/stage/Database directory:
$ cd /u01/stage/Database
If you have an existing TEST_IQOQ account, drop the account:
Open a command shell, and type the drop command for the account. When prompted, type the System password. For example:
$ sqlplus system@<TNS_name>
SQL> dropuser TEST_IQOQ cascade;
Exit the command shell.
Create the Oracle tables in a TEST_IQOQ Oracle account:
As the Oracle system user, execute the following SQL script. Enter this command on one line.
$ sqlplus system@<TNS_name> @4_create_test_iqoq_oracle_user.sql
At the prompt, type the system password.
At the second prompt, create a password for the TEST_IQOQ account and retype it to verify it.
|
Note: Remember the password. |
Populate the test database in the TEST_IQOQ Oracle account:
Execute the following SQL script. Enter the command on one line.
$ sqlplus TEST_IQOQ@<TNS_name> @5_populate_test_iqoq.sql
At the prompt, type the TEST_IQOQ password.
In a command shell, use the following command to navigate to the /u01/stage/Database directory:
$ cd /u01/stage/Database
Enter the following commands to upgrade the Empirica Signal schema for version 8.0:
$ sqlplus webvdme@<TNS_NAME> @update_7_3_3_3_to_8_0.sql
When prompted, type the webvdme user password.
Examine the file named disabled_userlist.txt in your current directory. This file contains usernames for accounts that had been disabled due to excessive failed login attempts. The users are locked out rather than disabled. To disable the users, perform the following steps after the upgrade is complete and you are able to log in to the Empirica Signal application:
Log in to the Emprica Signal application as a user with the Administer Users permission.
Click Settings.
Click Edit Users.
For each user to disable, click the row menu, and then click Edit.
The Edit User page appears.
Deselect Account locked, and select Account disabled.
Click Save.
Perform the following command to create the DB admin user:
$ sqlplus sys@<TNS_NAME> as sysdba @create_dbadmin_user.sql webvdme
When prompted, type the Oracle sys account password.
When prompted, create a password for the empirica_admin account. Retype the password to verify it.
|
Note: Remember this password. |
After the script completes, type exit.
Perform the following command to complete the schema upgrade to version 8.0:
$ sqlplus system@<TNS_NAME> @update_proxy_authentication.sql webvdme
When prompted, type the Oracle system account user password.
After the script completes, type exit.
If you use the Topics feature, execute the following command to upgrade each Topics schema account for release 8.0. Typical installations have a single Topics schema named topic_workflow.
$ sqlplus topic_workflow@<TNS_NAME> @update_twc_7_3_3_3_to_8_0.sql
When prompted, type the topic_workflow account password.
This section includes the following topics:
Perform these steps using the privileged user account on the application server.
Copy the following files from the installation directory to the JDK installation directory:
local_policy.jar
US_export_policy.jar
For example, using the privileged user account, execute the following commands in a command shell, updating the path to match the location of your JDK:
$ sudo su - root
# cp -f <INSTALL_DIR>/java/*.jar /usr/java/jdk1.7.x_xx/jre/lib/security/
# exit
If you are prompted to overwrite files, type y and press Enter.
Ensure that the two files have the same ownership and permissions as the rest of the files in the destination directory.
The following instructions are for installing Xvfb, the X Windows Virtual Frame Buffer.
These procedures are required on the application server for the creation of graphs.
Perform these steps using the privileged user account.
Execute the following command in a command shell:
$ which Xvfb
If the following response or some other path to Xvfb appears, Xvfb is already installed. Continue to Configuring Xvfb.
/usr/bin/Xvfb
Prerequisites: Yum must be installed and configured with an appropriate configuration file. Additionally, your system must be able to connect to the Yum repositories. For more information on configuring Yum for an Oracle Linux 6 system, see http://public-yum.oracle.com/.
If Xvfb is not installed, perform the following steps using the privileged user account.
If Xvfb is not installed, type the following command:
$ sudo yum install Xvfb
If you are prompted for your password after typing this command, type your password, not the password of root.
Perform these steps using the privileged user account.
Execute the following commands in a command shell:
$ sudo su - root
# cp <INSTALL_DIR>/service/xvfb /etc/rc.d/init.d
# /sbin/chkconfig --add xvfb
Execute the following command. This command verifies that the installation was successful.
# /sbin/chkconfig --list xvfb
The following response appears:
xvfb 0:off 1:off 2:off 3:on 4:off 5:on 6:off
Manually start Xvfb by executing the following command:
# /etc/rc.d/init.d/xvfb start
The following response appears:
Starting X Virtual Frame Buffer
Type exit to stop running as root.
Make the following modifications in the WebLogic domain bin directory, such as /u01/app/oracle/Middleware/user_projects/domains/empirica/bin.
Using the non-privileged user account, open the file setDomainEnv.sh in a text editor, such as vi.
Type the following text at the bottom of the file. If you are not using UTC for the time zone, adjust the time zone in the text accordingly:
# Local Customization export TZ=UTC export LANG=en_US.UTF-8 export DISPLAY=localhost:99.0
In the setDomainEnv.sh file, search for instances of ojdbc6dms.jar:
If no instances exist, continue to step 4.
If at least one instance exists, replace all instances with ojdbc6.jar from the $ORACLE_HOME folder.
For example, edit the following text:
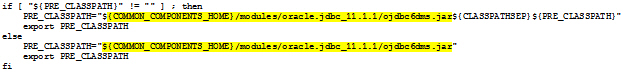
to look like the following text:
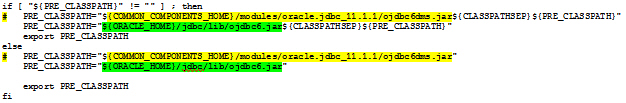
|
Note: In the previous examples, the text highlighted in green replaces the yellow text. |
Search for any instance of setting the JVM option java.awt.headless to true:
If no instances exist, continue to the next step.
If an instance exists, either remove or disable the instance.
For example, replace the following text:
EXTRA_JAVA_PROPERTIES="${EXTRA_JAVA_PROPERTIES} -Dem.oracle.home=/u01/app/oracle/Middleware/oracle_common -Djava.awt.headless=true"
with the following text:
#EXTRA_JAVA_PROPERTIES="${EXTRA_JAVA_PROPERTIES} -Dem.oracle.home=/u01/app/oracle/Middleware/oracle_common -Djava.awt.headless=true"
EXTRA_JAVA_PROPERTIES="${EXTRA_JAVA_PROPERTIES} -Dem.oracle.home=/u01/app/oracle/Middleware/oracle_common"
Save the file, and exit the editor.
Perform these steps on the application server using the non-privileged user account.
In a command shell, navigate to the WebLogic default domain bin directory, using a command such as the following:
$ cd /u01/app/oracle/Middleware/user_projects/domains/empirica/bin
If WebLogic is running, execute the command:
$ ./stopWebLogic.sh
To start WebLogic, execute the following command:
$ nohup ./startWebLogic.sh > /dev/null &
|
Note: Information messages might appear. You might need to press Enter to see the prompt. |
Verify that the Node Manager can be reached:
In an internet browser, enter the URL for the WebLogic Administration Console, such as the following::
https://<servername>:7002/console
In the left pane, expand Environment, and select Machines.
The Summary of Machines page appears.
In the list of machines, select SignalMachine.
The Settings for SignalMachine page appears.
Select the Monitoring tab.
Confirm that the status is Reachable. If status is Inactive, the Node Manager is not running.
If the Node Manager is not running, perform the following steps to start it:
Navigate to $WL_HOME/server/bin directory, such as:
/u01/app/oracle/Middleware/wlserver_10.3/server/bin
Execute the following command:
$ nohup ./startNodeManager.sh > /dev/null &
Exit the command shell.
Log into the WebLogic Administration Console using the WebLogic administrator credentials provided to you by the system administrator. Typically, the address for the WebLogic Administration Console is the following:
https://<servername>:7002/console
In the Domain Structure section on the left, expand Environment, and select Servers.
In the table of servers, select SignalServer.
The Settings for SignalServer page appears.
Select the Configuration tab, and select the Server Start sub-tab.
In the Change Center section on the left, click Lock & Edit.
In the Arguments field, type the following text:
-Xms256m -Xmx2048m -XX:MaxPermSize=1024m
|
Note: -XmxNNNNm and -XX:MaxPermSize are memory parameters that control the amount of memory used by the Empirica Signal application. You might need to adjust the parameters upwards to achieve appropriate performance. The numbers to use depend on the size of the data set installed and the number of users expected to access the system simultaneously. |
Click Save.
In the Change Center section on the left, click Activate Changes.
Your changes are activated. This might take a few moments.
On the left, select Servers.
Select the Control tab.
Start or restart the SignalServer:
In the table of servers, if the State of the SignalServer is SHUTDOWN, proceed to step d.
In the table of servers, if the State of the SignalServer is RUNNING, select the check box for the server, expand the Shutdown drop-down menu, located above and below the table, and select Force Shutdown Now.
Wait until the State of the server changes to SHUTDOWN. The page does not refresh automatically. To refresh the page, click the refresh button, located above the table, or click the refresh button for your browser.
In the table of servers, select the check box for the SignalServer, and click Start, located above and below the table.
Wait until the State of the server changes to STARTING and then RUNNING. The page does not refresh automatically. To refresh the page, click the refresh button, located above the table, or click the refresh button for your browser.