7 Process Integration for Customer Synchronization
This chapter provides an overview of the process integration for customer synchronization and discusses business process flows, assumptions and constraints, Oracle E-Business Suite (Oracle EBS) and Oracle Transportation Management (OTM) interfaces, core Oracle Application Integration Architecture (Oracle AIA) components, and integration services.
This chapter includes the following sections:
7.1 Overview
The customer synchronization integration supports these operations and corresponding synchronization of customer records from Oracle EBS to OTM:
-
Synchronize Customer: Defines the ability to synchronize the new or updated records from Oracle EBS to OTM. Synchronization represents a single service to perform either a Create or an Update call depending on the existence of the customer in the source and target applications.
-
Merge Customer: When customers are merged in Oracle EBS and are of the designated type, the data is synchronized to OTM. The types of mergers that can take place in Oracle EBS are:
-
Duplicate records are created for the same account or location and merged, making one of them inactive.
-
Two or more companies merge. As the result, there is a losing account and a winning account. All locations for the losing account (corporation in OTM) are modified to refer to the winning account.
-
Inactivate Customer: When an account is inactivated in Oracle EBS it is recorded in OTM. When customer locations are made inactive, the date of inactivation is recorded on the location within OTM. You must decide exactly how to use this information in OTM (like setting a status, placing orders on hold, and so on).
-
7.2 Business Process Flows
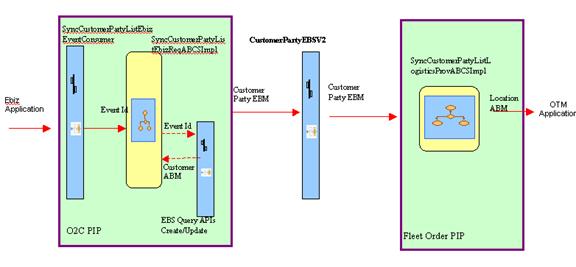
Figure 7-1 is a flow diagram that shows the customer flow synchronization.
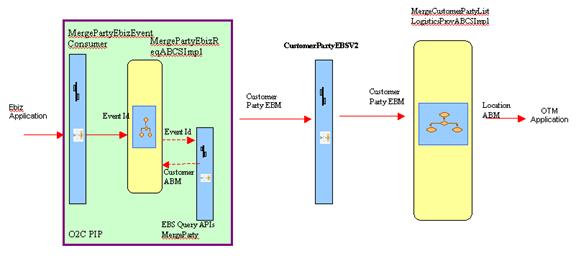
Figure 7-2 is a flow diagram that shows the customer flow for merge party:
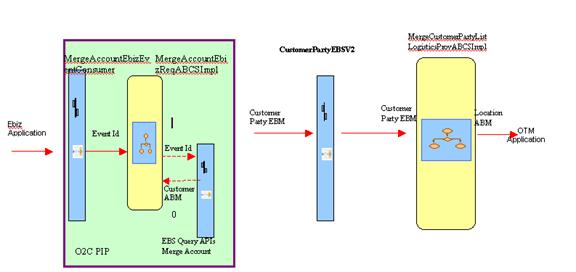
Figure 7-3 is a flow diagram that shows the customer flow for merge account:
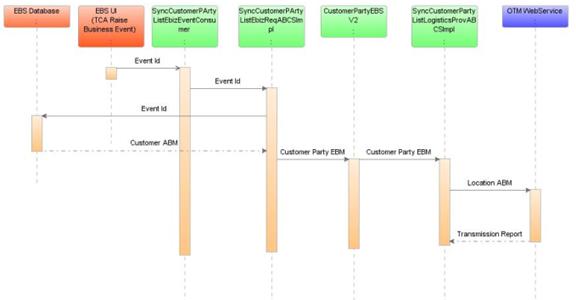
Figure 7-4 is a sequence diagram that shows the incremental changes in the customer party synchronization:
Figure 7-5 is a sequence diagram that shows the incremental changes in the customer party synchronization:
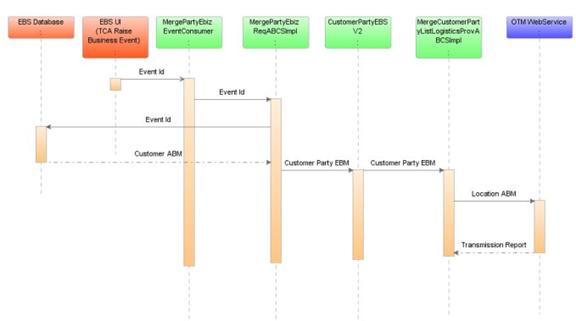
Figure 7-6 is a sequence diagram that shows the incremental changes in customer party merge:
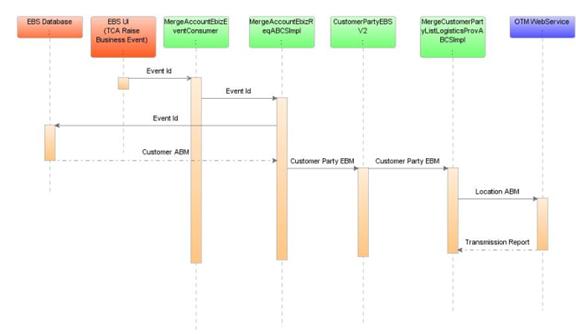
Figure 7-7 is a sequence diagram that shows the incremental changes in the customer account merge:
7.2.1 Order to Cash Integration Services
These services from Order to Cash (O2C) are available:
-
SyncCustomerPartyListEbizEventConsumer
-
MergeAccountEbizEventConsumer
-
SyncCustomerPartyListEbizReqABCSImpl
-
CustomerPartyEBSV2
-
SyncCustomerPartyListLogisticsProvABCSImpl
-
MergeAccountEbizReqABCSImpl
-
MergePartyEbizReqABCSImpl
-
MergeCustomerPartyListLogisticsProvABCSImpl
-
CreatePayableInvoiceLogisticsReqABCSImpl
-
QueryCustomerPartyListEbizCreateAdapter
-
QueryCustomerPartyListEbizUpdateAdapter
-
QueryCustomerPartyEbizAdapter
-
MergeAccountEbizEventConsumer
-
MergePartyEbizEventConsumer
-
MergeAccountEbizReqABCSImpl
-
MergePartyEbizReqABCSImpl
-
TransformAppContextEbizService
-
QueryMergeAccountEbizAdapter
-
QueryPartyMergeEbizAdapter
-
QueryMergeOrgCustEbizAdapter
-
QueryRelatedOrgCustEbizAdapter
7.3 Assumptions and Constraints
These are the assumptions and constraints:
-
Only parties of type organization are synchronized into OTM.
-
Delete for the accounts (customers) is not covered in the synchronization.
-
In case if any error occurs in the service layer and the customer message does not reach target application, then AIA error handling framework is invoked that notifies the administrator. The administrator should manually re-submit that transmission at various places that failed for re-processing.
-
This integration does not validate and raise errors due to any business validation failure in OTM or Oracle EBS.
-
O2C PIP code takes care of the requester transformation (from Oracle EBS to EBO) and Fleet Order PIP code takes care of OTM provider (EBO to OTM) transformation.
-
The cross-references are populated based on the identifiers passed from main transformation to OTM. To pass a different value to the OTM identifier, you can use transformations extensibility to update the cross-reference.
7.4 Oracle EBS Interfaces
For more information about Oracle EBS web services definition language (WSDL) and schema definition, see Oracle Customer Master Data Management Integration documentation.
For more information about Oracle EBS web services and documentation prior to Release 12.1.3, see the library on Oracle Technology Network: http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/documentation/applications-167706.html?. For Oracle EBS documentation for R12.1.3 and beyond, see this library: https://download.oracle.com/docs/cd/E18727_01/index.htm.
7.5 OTM Interfaces
The OTM provides an interface through a web service to connect to its application. This connectivity is established as a partner link in the provider service. When the logistics web service is called it returns an acknowledgment with a transmission number. Once the processing is complete, it then sends a transmission report back indicating the success or the failure.
For more information about the logistics service, see Oracle Transportation Management Integration Guide.
7.6 Core Oracle AIA Components
The integration flow uses these components:
-
CustomerPartyEBO
-
CustomerPartyEBM
The core enterprise business object (EBO) and enterprise business message (EBM) XSD files can be located by EBO within the $AIA_HOME/AIAMetaData/AIAComponents/EnterpriseObjectLibrary/Core/EBO/ parent folder.
The core enterprise business services (EBS) web services definition language (WSDL) files can be located by EBO within the $AIA_HOME/AIAMetaData/AIAComponents/EnterpriseBusinessServiceLibrary/Core/EBO/ parent folder.
For detailed documentation of individual EBOs and EBMs, click AIA Reference Doc link on EBO and EBM detail pages in the Oracle Enterprise Repository.
For more information about using the Oracle Enterprise Repository and configuring it to provide the AIA Reference Doc link, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Integration Architecture Foundation Pack, "Configuring and Using Oracle Enterprise Repository as the Oracle AIA SOA Repository."
EBOs can be extended, for instance, to add new data elements. These extensions are protected, and remain intact after a patch or an upgrade.
For more information, see Oracle Fusion Middleware Developer's Guide for Oracle Application Integration Architecture Foundation Pack, "Extensibility for AIA Artifacts".
7.7 Integration Services
These are the services delivered with this integration:
-
CustomerPartyEBSV2
-
CustomerPartyResponseEBSV2
-
MergeCustomerPartyListLogisticsProvABCSImpl
7.7.1 CustomerPartyEBSV2
CustomerPartyEBSV2 is the Enterprise Business Service to route all location related actions such as create customer, update customer, delete customer, and synchronize customer. The mediator service routes to SyncCustomerPartyListLogisticsProvABCSImpl in case of create and update operations of customer. The mediator service routes to MergeCustomerPartyListLogisticsProvABCSImpl in case of merge operations of customer. The mediator service routes to Composite Application Validation System (CAVS) based on the filter condition and operation.
7.7.2 CustomerPartyResponseEBSV2
CustomerPartyResponseEBSV2 is the Enterprise Business Service to route all customer related actions such as create customer, update customer, delete customer, and synchronize customer.
The mediator service routes the response message to MergeAccountEbizReqABCSImpl in case of merge of customer accounts. The mediator service routes to CAVS based on the filter condition and operation.
7.7.3 MergeCustomerPartyListLogisticsProvABCSImpl
MergeCustomerPartyListLogisticsProvABCSImpl is a Business Process Execution Language (BPEL) Process which receives SyncCustomerPartyListEBM as input from CustomerPartyEBSV2. This message is transformed to LogisticsABM. Cross-reference values are populated here. SyncCustomerPartyListEBM is transformed into CustomerPartyLogisticsABM and then the LogisticsWebService is invoked with this transformed application business message (ABM). This instance asynchronously waits for TransmissionReport from OTM. If the transaction is successful, the cross-reference values are populated; else, AIAAsyncErrorHandlingBPELProcess is invoked with an error message.