Oracle MaxRep for SAN uses continuous data protection (CDP) technology. Oracle MaxRep can be configured to support long-distance disaster recovery requirements and operational recovery and backup requirements.
Oracle MaxRep for SAN replicates your mission-critical LUNs to one or more secondary LUNs that can be either local or remote.
In the following illustration, which represents a local site, continuous data protection starts with new data written by the application server or host to the source Oracle FS System. The Controller copies (splits) the data by transmitting one copy to the LUN on the primary Oracle FS System, and the other copy to the Replication Engine. When the system writes the data to the primary LUN, the system sends an acknowledgment to the application server that the data is successfully written to the LUN.
The Replication Engine reads the corresponding location of the target LUN and compares the new source and the existing target data. If the target LUN requires updating, the Replication Engine updates the target LUN and the retention LUN, or journal, of the protection plan LUNs.
Retention LUNs are LUNs on the Oracle FS System that hold the retention journal for the Replication Engine. The retention journal contains a list of time indexed replication events that allow rollback to any point in time.
Figure 1: Continuous data protection process flow
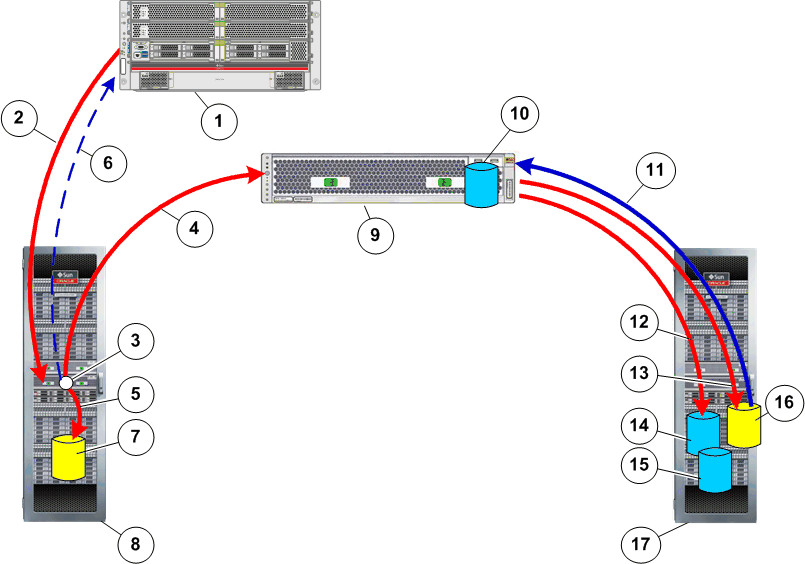
- Legend
-
1 Application Server 10 Home LUN 2 New data write to primary Oracle FS System 11 Read of target LUN data 3 Write split at Controller 12 Metadata write to replication journal 4 Data write split to Replication Engine 13 New data write to target LUN 5 Data write split to source LUN 14 Retention LUN 6 Target LUN write acknowledgment to host 15 Backup LUN 7 Source LUN 16 Target LUN 8 Primary Oracle FS System 17 Secondary Oracle FS System 9 Replication Engine
The Replication Engine is never in the data path of the source application. This configuration prevents any impact on the operation of the production server that is hosting an application if a failure or replacement of the Replication Engine occurs. The benefit of such a configuration is that Oracle MaxRep for SAN can be deployed into your existing environments without disrupting your business operations.
- Resync Step 1
The initial step of the replication process in which a baseline copy of the source LUN is replicated to the target LUN. For protection plans configured with the fast-copy option, this initial step transfers only unmatched blocks of data between the source and target LUNs between two Oracle FS Systems.
This comparison can significantly reduce the time and network resources that are required for the initial synchronization, compared to performing a complete copy.
- Resync Step 2
Any additional data that is written to the source LUN during the Resync Step 1 process is journaled for processing in Resync Step 2. The Replication Engine replicates the captured changes to the target LUN.
- Differential Sync
In the Differential Sync step Oracle MaxRep for SAN captures changes to the source LUN and sends them to the target LUN.
If resynchronization is required after the initial synchronization, the system captures ongoing changes, similar to the synchronization process. Oracle MaxRep for SAN supports Fast Resync, which replicates only unmatched blocks to the target LUN during the initial synchronization step. Asynchronous replication uses the Fast Resync feature. Synchronous replication uses Direct Resync, which reads data from the source LUN and writes the data directly to the target LUN.
During maintenance activities or an actual failure on a source LUN, Oracle MaxRep for SAN can switch direction to restore the source LUN from the target LUN. Because Oracle MaxRep for SAN uses CDP technology to replicate the data, the source can be restored to any point in time during the retention window. If optional Oracle MaxRep agents are in use, the target LUN can also be rolled back to an application consistency bookmark to ensure consistency of data.
Oracle MaxRep also supports the storing of snapshots (exact replica of the data of a source LUN as it existed in a single point-in-time copy) on physical or virtual drives.