4 Locate Address Book Records
This chapter contains these topics:
4.1 Understanding Name Search (P01200)
You use the Name Search program (P01200) to locate an address book record when you want to make revisions or to verify that the record has not been previously entered. Additionally, the Name Search program provides you with numerous options for searching records with common values for updating purposes. For example, you can locate all employee records for a specific postal code or you can review all the addresses for a particular parent number, business unit, or category code value.
4.2 Searching Records
The program provides two methods for searching and displaying address book records:
-
Using an alpha search
-
Using the Query search feature
|
Note: Both the types of searches can utilize one or more of the filter fields in the header portion of the screen to provide additional search criteria. |
After you display the results of your search you can export it to a spreadsheet to print it, if desired, using the Export to IFS File function (F23).
See the JD Edwards World Technical Tools Guide for information about using the export feature.
4.2.1 Using an Alpha Search
You can use any of the fields in the header portion of the screen to locate specific address book records. No one field is mandatory to complete (including Alpha Name); each field works independently, as well as in conjunction with the values specified in other fields. For example, using the Alpha Name, Search Type and Postal Code fields, you can locate all employee address book records beginning with S from postal code 80201 or using the Category Code/Cat Code # field, you could display all records with the value WEST in category code 2.
The system automatically applies wildcard processing to the letters that you provide in the Alpha Name field. For example, if you type CAR, the system displays all alpha names that begin with CAR. You do not need to supply the * to invoke wildcard processing.
You can also set processing options to display the Tax ID field to use in your search; otherwise, you can use the Query search feature to locate address book records by tax ID.
4.2.2 Using the Query Search Feature
If you want to perform a search over fields that are not displayed in the header portion of the screen, you can use the Query search feature to locate records from fields in addition to the Alpha Name, such as phone number, mailing address, city, Who's Who contact information, category codes, and additional search text. Using the Query search feature allows you to search on an alpha or numeric string that you enter in the Alpha Name field. In other words, if you type CAR in the Alpha Name field, the system returns records that contain CAR in the Alpha Name, Address, Phone Number, City, Category Code fields, Generic Text, and so forth.
The Query search feature locates records from the Address Book Word Search Master file (F01800), which you must build and maintain by running the Build Search Word File (P01BDWRD) and Refresh Search Word File (P01820) programs, respectively.
See Section 40.1, "Understanding the Search Word File" for detailed information.
|
Important!: The Query search feature works only on the generic text that you enter using the Additional Query Search Criteria function (F18) from Address Book Revisions; it does not include the generic text that you enter using the Additional Notes function (F6). |
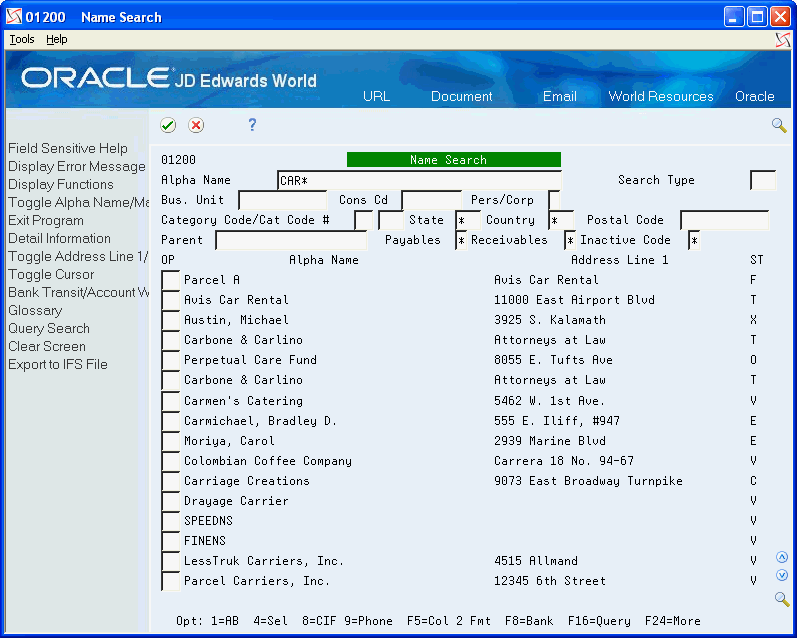
The Query search feature also allows you to use * as a wildcard. Unlike the alpha search, the system does not automatically perform a wildcard search, you must specify to do so by adding the * (wildcard) to the string you type in the Alpha Name field. For example, if you type CAR*, the system locates all records with letters that begin with CAR. The system processes the wildcard only at the end of the letters you type, regardless of where you enter it. For example, if you type *CAR, the system locates the same records as if you typed *CAR.
4.2.3 Examples of Searches
These screen prints illustrate the difference between using a simple alpha search, using a Query search, and using a Query search with a wildcard.
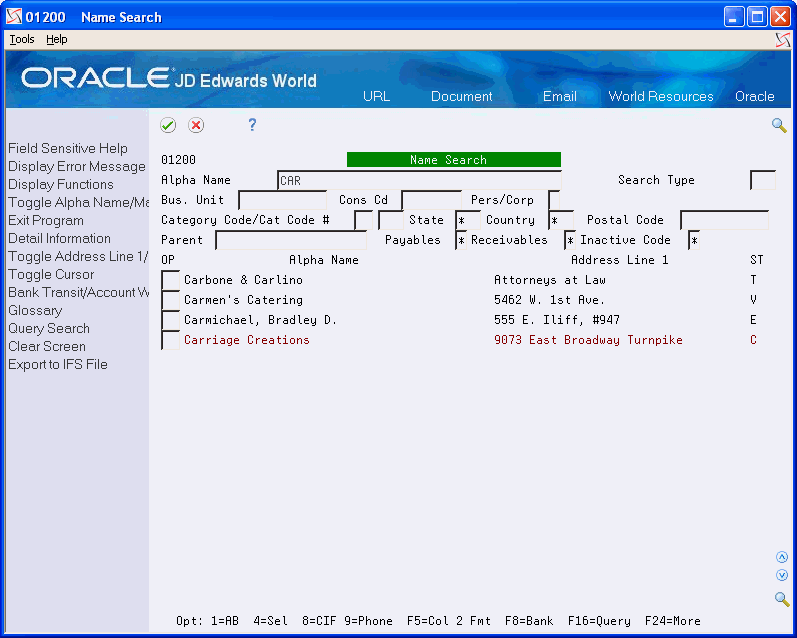
This is the results list from performing an alpha search:
The system uses only the Alpha Name field as the search criteria and returns all records that begin with CAR
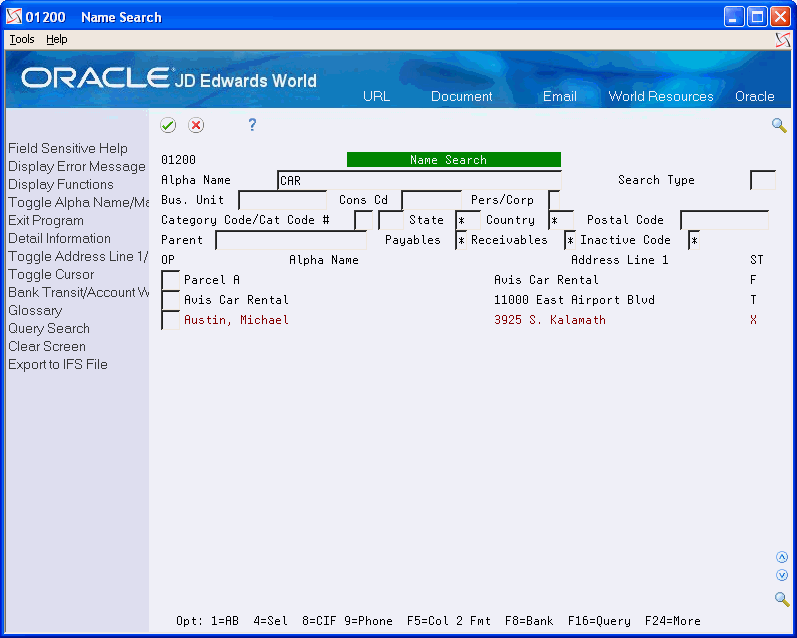
This is the results list from performing a Query search:
In this type of search, the system searches for any record that includes CAR as a separate word in any of the fields from the F01800 file. In this case, it locates CAR in the Alpha Name field, the Address 1 line field and in the Phone Number field (see below):
Figure 4-3 Phone Numbers (Results) screen
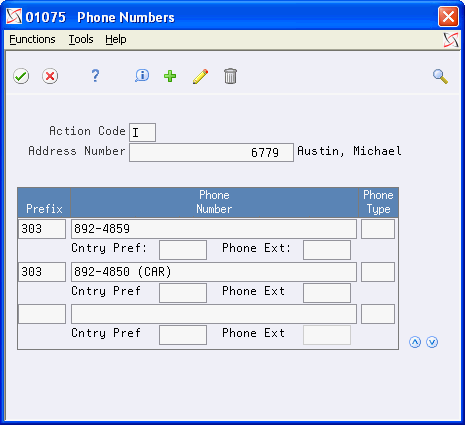
Description of "Figure 4-3 Phone Numbers (Results) screen"
This screen shows the results of performing a Query search using a wildcard:
4.3 Displaying Fields
In addition to the numerous options for searching for records, the program also provides several options for displaying different fields on the screen. By default, the system displays Alpha Name and Address Line 1 in the first two fields in the detail area of the Name Search screen, but you can change both fields, if desired:
-
Using the Toggle Alpha Name/Mailing Name function (F2), you can display either Alpha Name or Mailing Name in the first field in the detail area of the screen.
-
Using the Format Control processing option you can choose which field to display in the second field by default (Address Line One, City, Phone Number, Address Book Number, or Credit Message), and then choose the order of additional fields to display using the Toggle/Address Line 1/City/Phone Format function (F5). You sequence the fields you want to display. For example, if you never want to display the credit message, do not assign a sequence to that field.
You can set additional processing options to:
-
Provide a default value for the Search Type field
-
Display the Tax ID field to use for search criteria
-
Retain the fields that you populate for subsequent searches
-
Provide the Phone Type to use to retrieve the corresponding phone number that displays when you use that processing option format. Otherwise, you can use Option 9 to display all phone numbers for an address book record.
If you do not specify a value in this processing option, the system displays the first phone number from the Address Book Contact - Phone Numbers file (F0115) for the address book record.
4.4 Reviewing Customer and Supplier Information
The Customer Master (F0301) and Supplier Master (F0401) files store YTD and prior-year amounts, as well as other information pertaining to a customer or supplier. The information is available to display from the Name Search program using options 16 (Customer Information) and 17 (Supplier Information), as shown below:
Figure 4-5 Customer Information Window screen
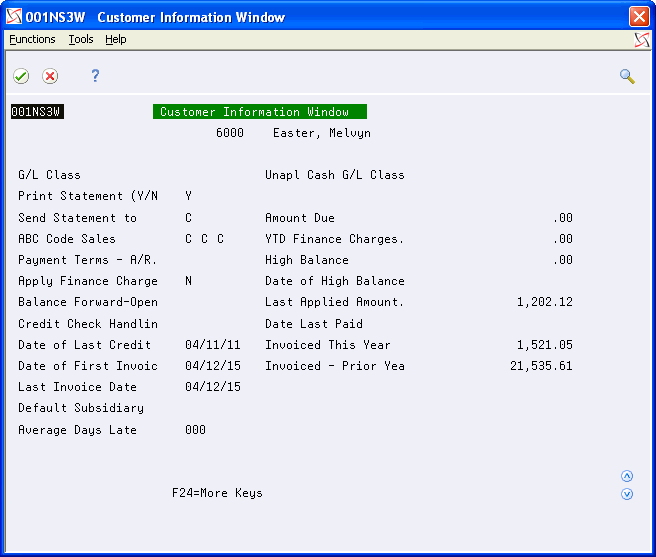
Description of "Figure 4-5 Customer Information Window screen"
Figure 4-6 Supplier Information Window screen
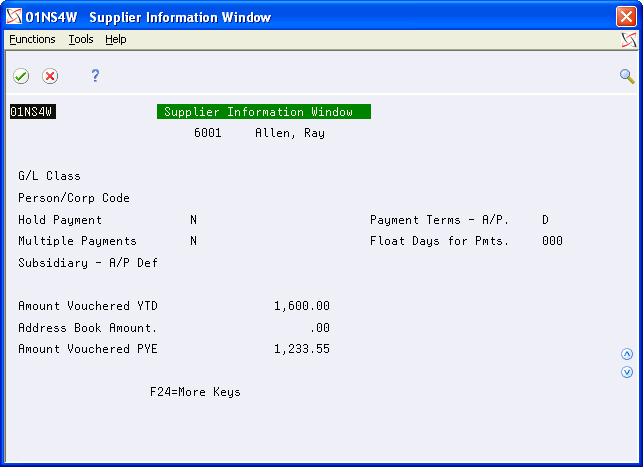
Description of "Figure 4-6 Supplier Information Window screen"
4.5 Locating Address Book Records
From Address Book (G01), choose Name Search
Figure 4-7 Name Search (Address Book Records) screen
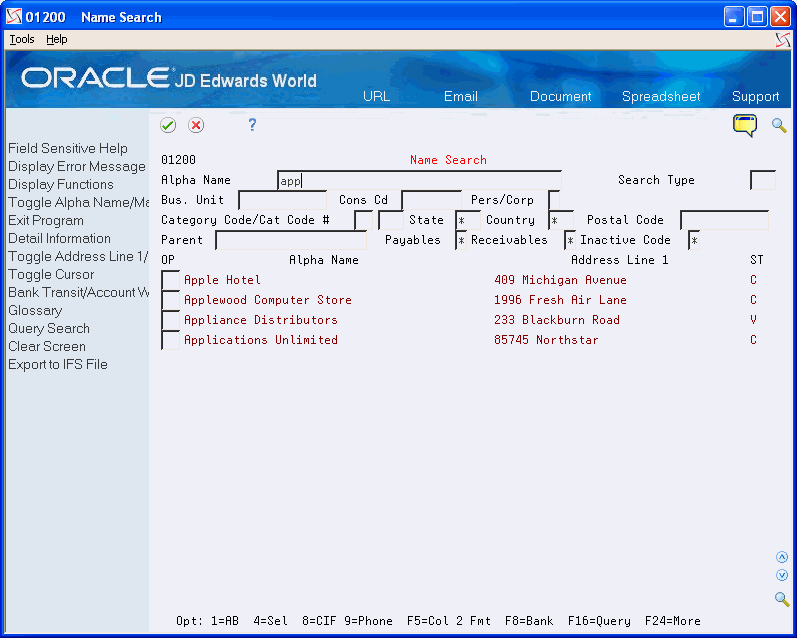
Description of "Figure 4-7 Name Search (Address Book Records) screen"
Complete one or more of the following fields to define your search criteria and press Enter or choose Additional Query Search (F16).
-
Alpha Name
-
Search Type
-
Business Unit
-
Consolidation Code
-
Person/Corporation
-
Category Code/Cat Code #
-
State
-
Country
-
Postal Code
-
Parent
-
Payables
-
Receivables
-
Inactive Code
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Alpha Name | Enter all or a portion of the alpha name to perform an alpha search or enter the alpha or numeric string to perform a Query search (F16). |
| Search Type | A user defined code (01/ST) that identifies the kind of address book record you want the system to select when you search for a name or message. For example:
E – Employees X – Ex-employees V – Suppliers C – Customers P – Prospects M – Mail distribution lists Form-specific information Placing security on search types might restrict you from viewing certain records. When security is active, a code is required in this field. |
| Business Unit | The business unit assigned to the address book record. |
| Cons Code | An eight-character code that you can assign and utilize during the Address Book Consolidation process. |
| Person/Corp | You can limit your selection to Address Book records for persons or non-person entities.
1 – Include only those address book records for persons. 2 – Include only those address book records for non-person entities. Blank – Include both. |
| Category Code/Cat Code# | Enter the address book category code (01 30), and then specify the value you want to use for the search criteria. For example 12 WES. |
| Parent | Enter the address book number of the parent to display all associated records. |
| Payables | An informational code that you can use to identify the address book record as a supplier, as well as specify the type of supplier. Valid values are:
|
| Receivables | An informational code that you can use to identify the address book record as a customer. Valid values are:
|
| Inactive Code | A code used to designate the address book record as inactive. Valid values are:
|