43 Set Up Automatic Accounting Instructions
This chapter contains the topic:
From ECS Sales Order Management (G4910), enter 29
From ECS Sales Order Management Setup (G491041), choose Automatic Accounting Instructions
43.1 Setting Up Automatic Accounting Instructions (ECS)
Automatic accounting instructions (AAIs) are the user defined bridge between your day-to-day functions, chart of accounts, and financial reports. The system uses AAIs to determine how to distribute G/L entries that the system generates. For example, in the ECS Sales Order Management system, AAIs indicate how to record the transaction when you sell a stock item to a customer.
For distribution systems, you must create AAIs for each unique combination of company, transaction, document type, and G/L class that you anticipate using. Each AAI is associated to a specific G/L account that consists of a business unit, an object, and, optionally, a subsidiary.
The system stores AAIs in the Automatic Accounting Instructions Master table (F4095).
43.1.1 AAIs Used in the ECS Sales Order Management System
| AAI | Description |
|---|---|
| 4220 (Revenue) | Provides the expense/cost amount to the cost of goods sold account.
GL class code comes from Item/Branch/Location (P41024). |
| 4221 (Deferred COGS) | Provides the journal entries for deferred COGS that were created during the Invoice Cycle Billing program.
GL class code comes from Item/Branch/Location (P41024). |
| 4230 (Revenue) | Provides the actual sales price of inventory in the sales revenue account.
GL class code comes from Item/Branch/Location (P41024). |
| 4231 (Deferred Revenue) | Provides the journal entries for deferred revenue that were created during the Invoice Cycle Billing program.
GL class code comes from Item/Branch/Location. |
| 4232 (Unbilled A/R) | Provides the journal entries for unbilled accounts receivable that were created during the Invoice Cycle Billing program.
GL class code comes from Customer Master. |
| 4240 (Inventory) | Credits the cost amount to an inventory account.
GL class code comes from Item/Branch/Location. |
| 4241 | Specifies the inventory in transit account for entries created by the Load Confirm, Cycle Billing, and Update Customer Sales programs. |
| 4245 (A/R Trade) | Debits the sales amount to an accounts receivable account. The system writes the accounts receivable offset entries to the general ledger only if the accounts receivable update option is turned off at sales update.
GL class code comes from Customer Master. |
| 4250 (Tax Liability) | Provides journal entries to tax liability accounts that were created during a sales update.
GL class code comes from Tax Rate/Area. |
| 4260 (Interbranch Revenue) | Records interbranch revenue when processing options are set behind P4211 and P42800.
GL class code comes from Item/Branch/Location. |
| 4270 (Price Adjustments) | Provides the journal entries for individual price adjustments that were created during a sales update.
GL class code comes from Price Adjustment Types definition. |
| 4280 (Rebates Payable) | Provides the offset entries of accrued accounts.
GL class code comes from price adjustment Types definition. |
| 4281 | Specifies the temperature gain/loss offset account. |
| 4282 | Specifies the temperature gain/loss account. |
After you review and revise the existing AAIs for your business needs, you might need to set up additional AAI items.
The Distribution Automatic Account form shows each predefined AAI item and information about the document type, G/L class, and accounts that are affected by transactions.
Figure 43-1 Distribution Automatic Account screen
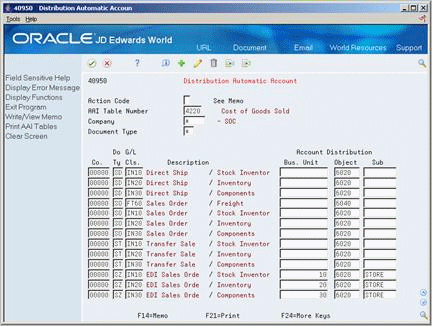
Description of "Figure 43-1 Distribution Automatic Account screen"
43.1.2 Before You Begin
-
Set up address book numbers
-
Set up companies
-
Determine transaction types
-
Set up document types
-
Set up G/L class codes
-
Determine the account numbers for recording transactions
-
Set up Business Units
-
Set up account master information
On Automatic Accounting Instructions.
Complete the following fields:
-
Company
-
Document Type
-
General Ledger Class
-
Business Unit
-
Object
-
Subsidiary
-
Access the Distribution Automatic Account form for the AAI you want to set up. You may access via any set up Menu, Hidden Selection 29 to take you to a Set Up Menu, or Fast Path using DMAAI. Skip to or inquire on an AAI number and take option 1 or click to access AAI Revisions.
-
On Distribution Automatic Account (P40950), complete the following fields:
| Field | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Company | A code that identifies a specific organization, fund, entity, and so on. This code must already exist in the Company Constants table (F0010). It must identify a reporting entity that has a complete balance sheet. At this level, you can have intercompany transactions.
Note: You can use company 00000 for default values, such as dates and automatic accounting instructions (AAIs). You cannot use it for transaction entries. Form-specific information In the inquiry field at the top of the form, the asterisk (*) is the default value. It causes the system to display AAIs for all companies. |
| Document Type | A user defined code (system 00/type DT) that identifies the origin and purpose of the transaction.
JD Edwards World reserves several prefixes for document types, such as vouchers, invoices, receipts, and timesheets. The reserved document type prefixes for codes are: P – Accounts payable documents R – Accounts receivable documents T – Payroll documents I – Inventory documents O – Order processing documents J – General ledger/joint interest billing documents The system creates offsetting entries as appropriate for these document types when you post batches. Form-specific information In the inquiry field at the top of the form, the asterisk (*) is the default and causes the system to display all document types. |
| G/L Class | A user defined code that identifies the G/L offset that you want the system to use when it searches for the account to which it will post the transaction. If you do not want to specify a class code, you can enter **** (four asterisks) in this field.
The table of Automatic Accounting Instructions (AAIs) allows you to predefine classes of automatic offset accounts for the Inventory, Purchasing, and Sales Order Management systems. The system can generate accounting entries based upon a single transaction. As an example, a single sale of a stock item can trigger the generation of accounting entries similar to these: Sales-Stock (Debit) xxxxx.xx A/R Stock Sales (Credit) xxxxx.xx Stock Inventory (Debit) xxxxx.xx Stock COGS (Credit) xxxxx.xx |
| Bus. Unit | An alphanumeric field that identifies a separate entity within a business for which you want to track costs. For example, a business unit might be a warehouse location, job, project, work center, or branch/plant.
You can assign a business unit to a voucher, invoice, fixed asset, and so on, for purposes of responsibility reporting. For example, the system provides reports of open accounts payable and accounts receivable by business units to track equipment by responsible department. Security for this field can prevent you from locating business units for which you have no authority. Note: The system uses this value for Journal Entries if you do not enter a value in the AAI table. |
| Object Account | The object account portion of a general ledger account. The term "object account" refers to the breakdown of the Cost Code (for example, labor, materials, and equipment) into subcategories (for example, dividing labor into regular time, premium time, and burden). The object account is a character field and is left justified when displayed in programs and on the database. Be aware that adding leading digits to a number creates a different entry. For example, entering 000456 is not the same as entering 456. |
| Sub | A subdivision of an object account. Subsidiary accounts include more detailed records of the accounting activity for an object account.
Form-specific information If you leave this field blank, the system uses the value you entered on the work order in the Cost Code field. |